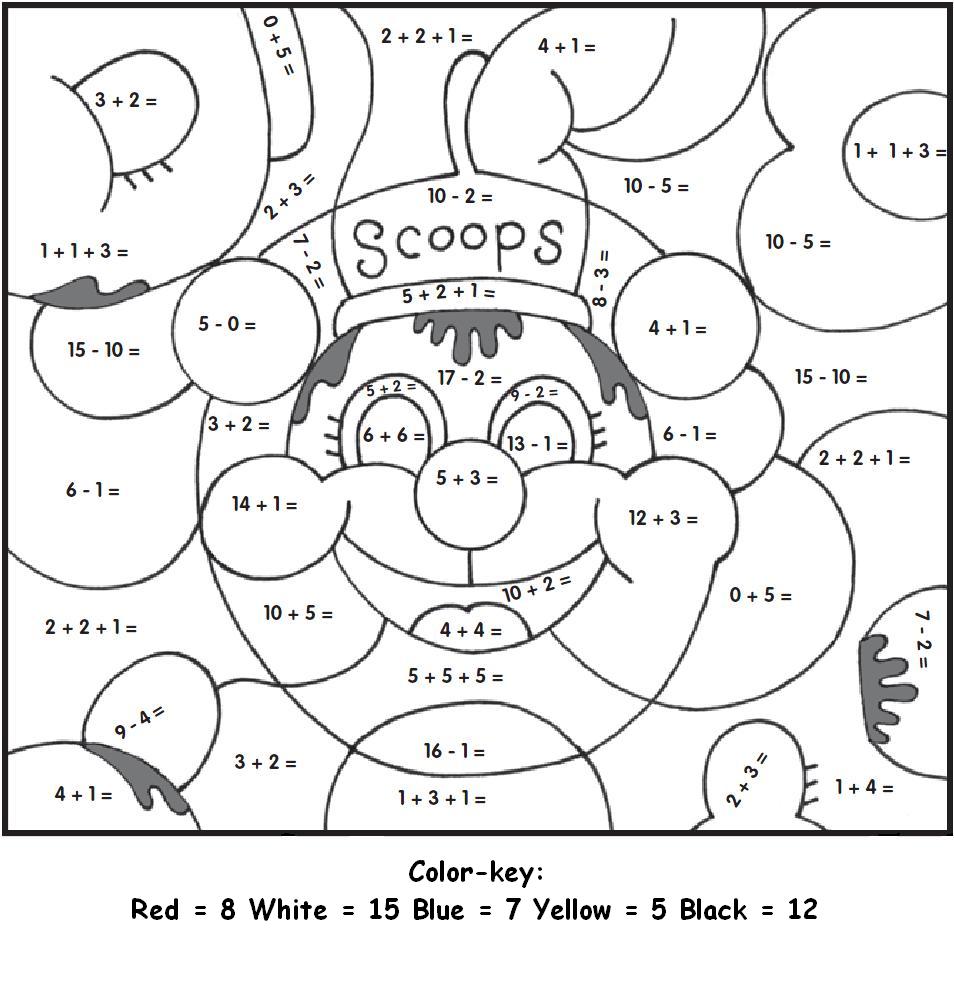
Diffusion Osmosis Active Transport Worksheet Answer Key Revealed

Understanding Osmosis, Diffusion, and Active Transport
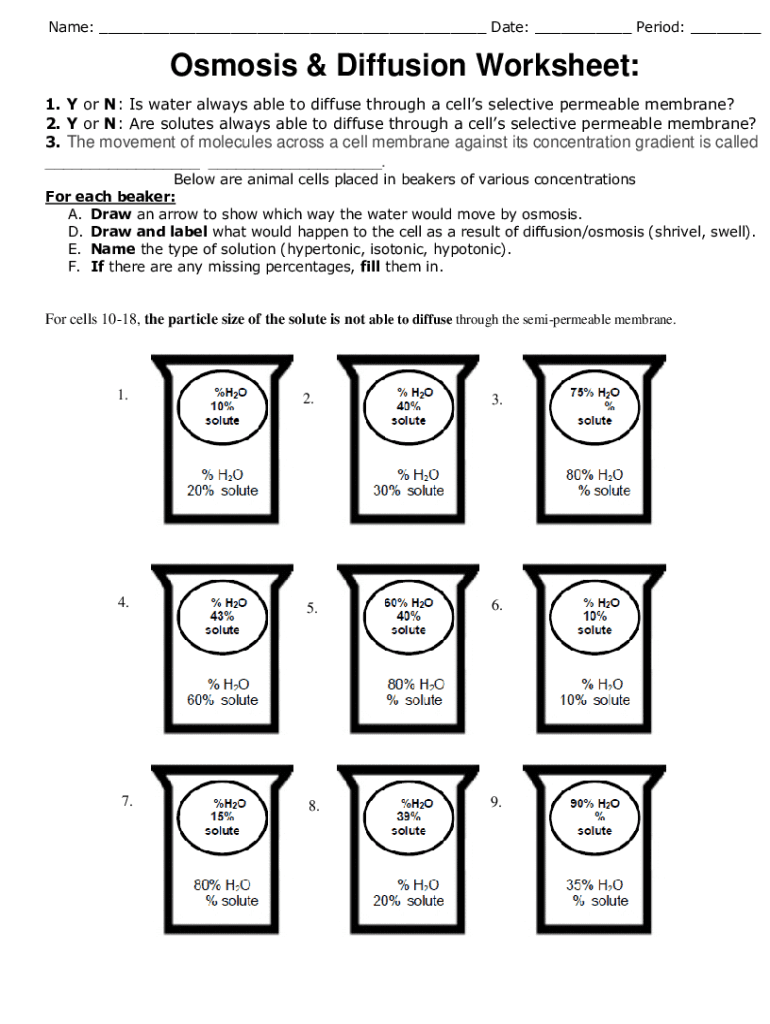
In the study of biology, understanding the ways in which cells manage to exchange materials with their environment is crucial. Three key processes that facilitate this exchange are osmosis, diffusion, and active transport. These processes are essential for maintaining the cell's homeostasis, where the internal conditions are kept stable despite external changes. This article dives into each of these processes, explaining how they work and why they are important, along with providing you with a comprehensive worksheet answer key for better understanding.
What is Osmosis?

Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher solute concentration. Here’s how osmosis can be understood:
- Direction of Movement: Water moves towards the area with more solutes.
- Passive Process: No energy expenditure is required; it follows the natural movement of water down its concentration gradient.
To illustrate, here’s a simple example:

🌿 Note: Osmosis plays a vital role in water regulation within cells and the plant's structural integrity.
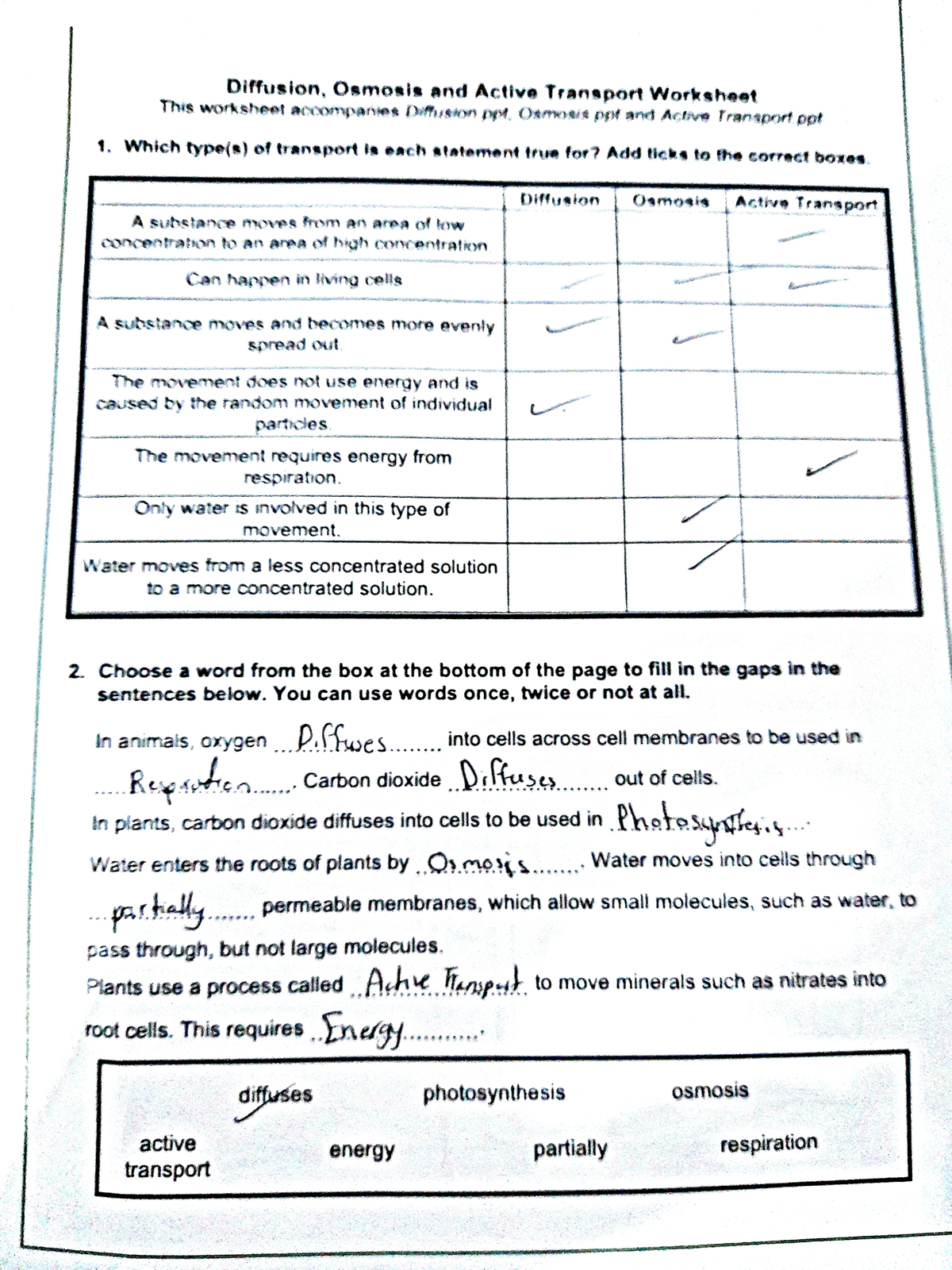
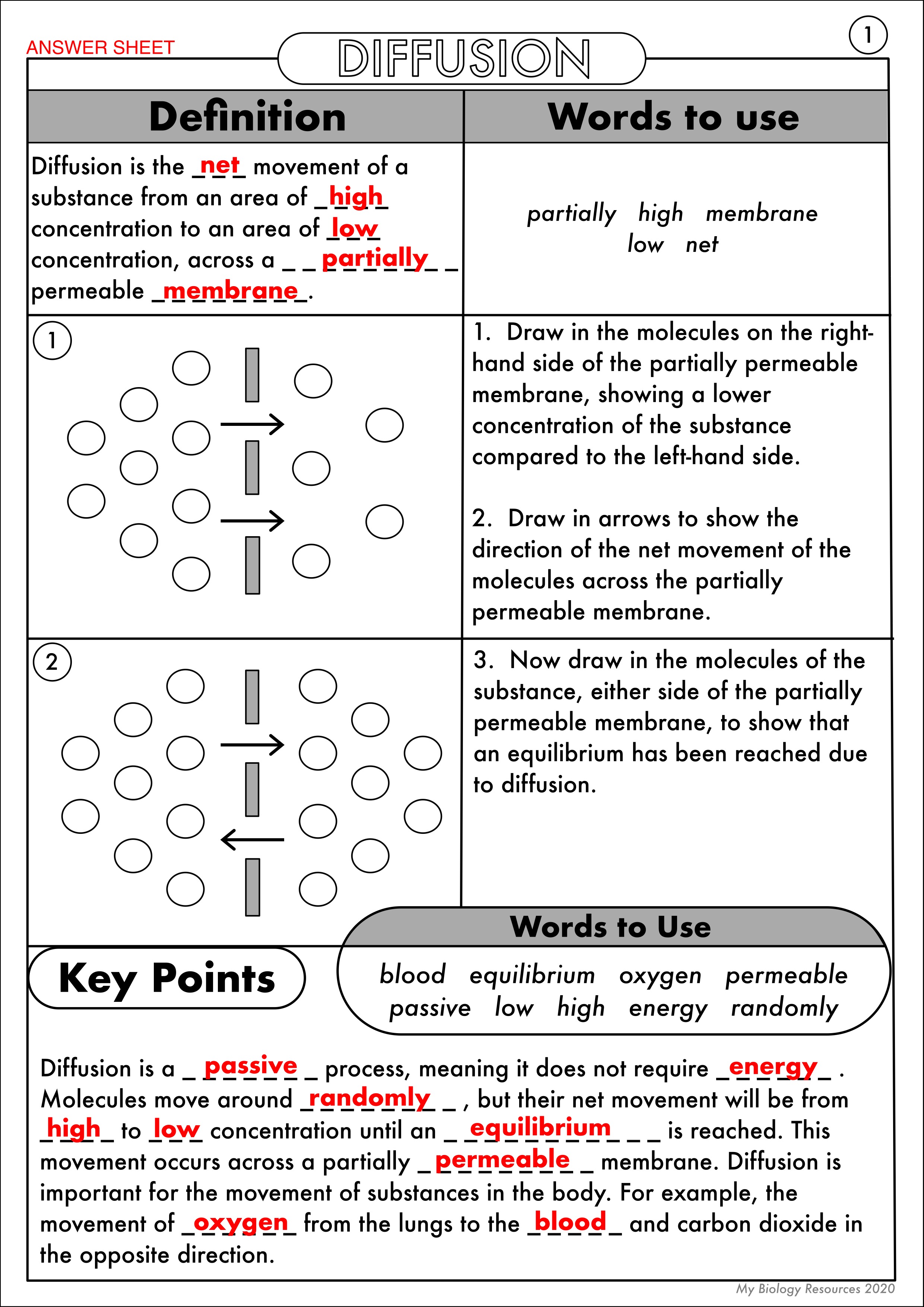
What is Diffusion?

Diffusion is the passive movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, eventually reaching equilibrium. Key points include:
- Random Motion: It occurs due to the random motion of particles.
- Concentration Gradient: Movement happens until equilibrium is reached.
- Passive Process: Like osmosis, diffusion requires no energy from the cell.
A common example is the spread of a gas or liquid in a room:

💨 Note: Diffusion is key for gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide to reach cells in animals and plants.
Active Transport

Active transport is the movement of molecules or ions against their concentration gradient, requiring energy input in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Here’s what makes it unique:
- Requires Energy: ATP is hydrolyzed to provide the necessary energy.
- Against the Gradient: Molecules move from areas of lower to higher concentration.
Here is an example of active transport:

⚡ Note: Active transport allows cells to concentrate nutrients or eject waste, which is vital for cellular function.
| Process | Requires Energy? | Direction of Movement |
|---|---|---|
| Osmosis | No | Lower to Higher Solute Concentration |
| Diffusion | No | Higher to Lower Concentration |
| Active Transport | Yes | Lower to Higher Concentration |

Worksheet Answer Key

Let’s break down the answers to common worksheet questions about osmosis, diffusion, and active transport:
- Q1. Define Osmosis.
A1. Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane, from an area of low solute concentration to high solute concentration.
- Q2. What is the difference between diffusion and facilitated diffusion?
A2. Diffusion is the simple movement of solutes down their concentration gradient, while facilitated diffusion involves transport proteins to move substances that are too large or charged to cross the membrane easily.
- Q3. Explain why active transport requires energy.
A3. Active transport moves solutes against their concentration gradient, which requires an energy input, typically ATP, to move substances into or out of the cell.
Conclusion

Understanding osmosis, diffusion, and active transport not only helps in comprehending how cells maintain homeostasis but also is fundamental for various biological processes. These mechanisms allow organisms to absorb nutrients, expel waste, and regulate their internal environment, making these processes critical in both cellular biology and physiology. Students and enthusiasts can use this worksheet answer key to deepen their understanding of these concepts, ensuring better scores and a clearer understanding of cellular transport mechanisms.
What is the significance of water potential in osmosis?
+
Water potential determines the direction water will move during osmosis. Water moves from an area of higher water potential to an area of lower water potential, where the solutes are more concentrated.
Can osmosis occur without a membrane?
+
No, osmosis specifically refers to water movement across a semipermeable membrane. Without a membrane, the process would simply be diffusion of water molecules.
How does active transport differ from passive transport?

+
Active transport uses energy to move substances against their concentration gradient, while passive transport, including diffusion and osmosis, moves substances down their concentration gradient without needing energy input.