5 Key Answers for Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet

The scientific world has long been fascinated by the ways in which substances move within and between biological systems. Two fundamental processes that underpin this movement are diffusion and osmosis. Both phenomena occur naturally, allowing for the dispersion and even distribution of substances across various environments. Understanding these processes is not just vital for students of science but also for everyone interested in how life functions at a cellular level. Here, we will provide 5 key answers for a common Diffusion and Osmosis worksheet, enhancing your comprehension of these vital biological processes.
1. What is Diffusion and How Does It Occur?
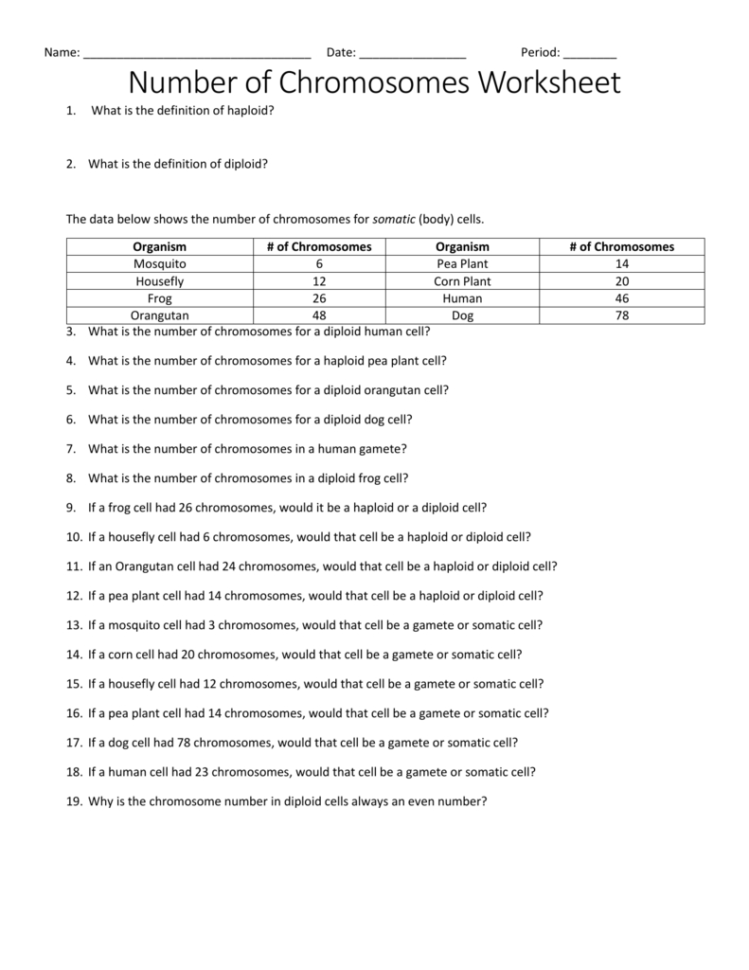
Diffusion is the process by which particles spread out from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until they are evenly distributed. This movement can occur in gases, liquids, and solids but is most commonly observed in liquid solutions and the air we breathe. Here's how it works:
- Random Movement: Particles in any medium are in constant, random motion due to thermal energy, which causes them to collide with one another.
- Concentration Gradient: Particles will move from where they are densely packed to where they are less so, following the concentration gradient.
- Equilibrium: Over time, this movement leads to a state of dynamic equilibrium where particles are evenly spread out, although still moving randomly.
🧪 Note: Diffusion is a passive process that does not require the input of energy from the system.
2. Definition of Osmosis and Its Relation to Diffusion
Osmosis is a specific type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. Unlike diffusion, osmosis specifically deals with water moving to achieve osmotic equilibrium. Here's a quick breakdown:
- Semipermeable Membranes: These allow certain molecules or ions to pass through but not others.
- Water Potential: Water moves to where there is lower water potential (or higher solute concentration), leading to osmotic pressure.
- Equilibrium: Similar to diffusion, osmosis aims to equalize concentration but uses the movement of water.
| Process | Direction of Movement | Membrane Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Diffusion | From high to low concentration | Not necessary |
| Osmosis | Water from low to high solute concentration | Semiprermable |

3. Can Osmosis Occur Without a Membrane?
This might sound counterintuitive, but osmosis can occur in the absence of a membrane, albeit with limitations. Here's how:
- Solute Dissolution: When a solute dissolves in a solvent like water, the solvent molecules move toward the solute to equalize concentration.
- Physical Barrier: Osmosis in the absence of a membrane can happen due to physical barriers like the surface tension of water, but the process is much less controlled compared to what occurs in biological systems.
💡 Note: True osmosis, as we understand it in biological contexts, requires a semipermeable membrane to facilitate the movement of water to achieve osmotic equilibrium.
4. How Does Concentration Affect the Rate of Diffusion?

The rate at which diffusion occurs is heavily influenced by concentration gradients:
- Steeper Gradient: The larger the difference in concentration between two areas, the faster diffusion will occur to equalize the concentrations.
- Temperature: Higher temperatures increase particle movement, thereby increasing diffusion rates.
- Particle Size: Smaller particles diffuse faster than larger ones.
5. Applications of Osmosis and Diffusion in Everyday Life
Diffusion and osmosis are not just abstract scientific concepts; they have practical applications that we encounter in everyday life:
- Cooking: When you salt your pasta water, the salt dissolves and diffuses through the water, while osmosis helps remove excess water from food items like salted vegetables.
- Medical Treatments: Osmotic pressure in the human body is crucial for intravenous fluid administration, ensuring patients receive the right balance of electrolytes and fluids.
- Water Purification: Reverse osmosis is used to purify water by forcing it through a membrane that filters out contaminants.
By understanding these processes, we gain insight into the fundamental interactions that occur at the cellular level, impacting how we cook, how our bodies function, and even how we approach environmental concerns like water purification.
In summary, diffusion and osmosis are essential processes that drive the movement of substances in biological systems. Their universal applicability in both nature and human endeavors underscores their importance in science education. From the simple act of scent spreading through a room to the life-sustaining process of plant cells absorbing water, these principles are at work, shaping our environment and our health.
What is the difference between osmosis and dialysis?

+
Dialysis is a process similar to osmosis but it involves the selective movement of solutes across a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis specifically deals with the movement of water to achieve osmotic equilibrium.
Can diffusion happen in solids?

+
Yes, diffusion can occur in solids, though it is much slower. This process is known as solid-state diffusion and involves the movement of atoms or molecules within the solid.
Why does osmosis not occur in a balloon filled with water?

+
Osmosis requires a semipermeable membrane. A balloon acts as a physical barrier but not a selective one, so it doesn’t facilitate osmosis.