Army Jobs: Exploring Careers in the Military Service
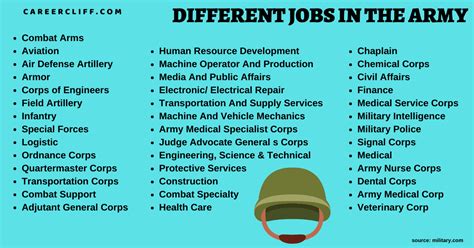
Careers in the Military Service: A Comprehensive Overview

Are you considering a career in the military service? With various branches and numerous job roles, it can be overwhelming to navigate the options. In this article, we will delve into the world of army jobs, exploring the different careers available, their requirements, and the benefits of serving in the military.
Branches of the Military

The United States Armed Forces comprise five branches, each with its unique mission and responsibilities. Understanding the roles of each branch can help you determine which one aligns with your interests and skills.
- United States Army: The Army is responsible for land-based military operations. Its primary functions include peacekeeping, humanitarian missions, and combat operations.
- United States Navy: The Navy focuses on naval operations, protecting American interests at sea, and conducting humanitarian missions.
- United States Air Force: The Air Force is responsible for air-based military operations, including combat, transport, and reconnaissance missions.
- United States Marine Corps: The Marine Corps is a rapid-response force that specializes in ground combat operations, often in conjunction with naval operations.
- United States Coast Guard: The Coast Guard is a unique branch that operates under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime, focusing on maritime law enforcement, search and rescue, and marine safety.
Military Careers: An Overview

There are numerous careers available in the military, ranging from combat and aviation to medical and administrative roles. Here are some examples of army jobs:
- Combat Roles:
- Infantryman: Engages in ground combat operations, using a variety of skills and equipment.
- Tank Crewman: Operates and maintains tanks, conducting armored combat operations.
- Artillery Specialist: Utilizes artillery systems to support ground operations.
- Aviation Roles:
- Pilot: Flies aircraft, conducting combat, transport, and reconnaissance missions.
- Aircrew Member: Assists pilots, operating and maintaining aircraft systems.
- Air Traffic Controller: Manages air traffic, ensuring safe takeoffs, landings, and flight operations.
- Medical Roles:
- Medical Doctor: Provides medical care to military personnel, conducting surgeries, and treating injuries.
- Nurse: Delivers nursing care to military personnel, conducting medical procedures and providing patient care.
- Medic: Administers first aid, treating injuries and illnesses in the field.
- Administrative Roles:
- Human Resources Specialist: Manages personnel records, coordinating training and deployments.
- Logistics Specialist: Oversees supply chain operations, ensuring equipment and resources are available.
- Intelligence Analyst: Analyzes data, providing strategic insights to support military operations.
Benefits of Military Service

Serving in the military offers numerous benefits, including:
- Education Benefits: The military provides education assistance, including tuition reimbursement and student loan forgiveness.
- Career Advancement: Military service can enhance career prospects, providing valuable skills and experience.
- Healthcare Benefits: Military personnel and their families receive comprehensive healthcare benefits.
- Home Loan Guarantees: The military offers home loan guarantees, making it easier to purchase a home.
- Travel Opportunities: Military service provides opportunities to travel and experience different cultures.
📝 Note: Military service requires a significant commitment, including deployments, training, and potential combat operations. It's essential to carefully consider your decision before enlisting.
How to Get Started

If you’re interested in pursuing a career in the military, follow these steps:
- Research: Explore the different branches and careers, understanding the requirements and benefits.
- Meet the Requirements: Ensure you meet the basic requirements, including age, education, and physical fitness standards.
- Take the ASVAB: The Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test assesses your aptitude for various military careers.
- Enlist: Visit a recruiter, and complete the enlistment process, which includes medical evaluations, background checks, and swearing-in ceremonies.
- Attend Basic Training: Complete basic training, also known as boot camp, which prepares you for military life.
| Branch | Basic Training Location | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Army | Fort Jackson, SC; Fort Leonard Wood, MO; Fort Benning, GA | 10 weeks |
| Navy | Great Lakes, IL | 8 weeks |
| Air Force | Lackland AFB, TX | 7 weeks |
| Marine Corps | Parris Island, SC; San Diego, CA | 13 weeks |
| Coast Guard | Cape May, NJ | 8 weeks |

Conclusion

A career in the military service offers numerous benefits, including education assistance, career advancement, and comprehensive healthcare benefits. With various branches and careers to choose from, it’s essential to research and understand the requirements and benefits before making a decision. If you’re interested in serving, follow the steps outlined above, and you’ll be well on your way to a rewarding and challenging career in the military.
What is the minimum age to enlist in the military?

+
The minimum age to enlist in the military varies by branch. The Army and Navy require applicants to be at least 17 years old, while the Air Force and Marine Corps require applicants to be at least 17 years old, with parental consent, or 18 years old without parental consent. The Coast Guard requires applicants to be at least 17 years old, with parental consent, or 18 years old without parental consent.
Do I need a college degree to join the military?

+
No, a college degree is not required to join the military. However, some careers may require a degree or specific certifications. Additionally, the military offers education assistance programs to help personnel pursue higher education.
How long is basic training?

+
The duration of basic training varies by branch. The Army’s basic training is 10 weeks, the Navy’s is 8 weeks, the Air Force’s is 7 weeks, the Marine Corps’ is 13 weeks, and the Coast Guard’s is 8 weeks.