Army vs Marines: What's the Difference
Understanding the Branches of the US Military: Army vs Marines

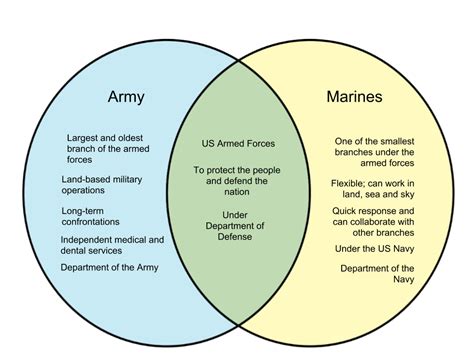
The United States Armed Forces are divided into five branches: the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. Among these branches, the Army and Marine Corps are often confused with one another due to their similar roles and responsibilities. However, there are significant differences between the two branches that set them apart. In this article, we will delve into the differences between the Army and Marine Corps, exploring their history, mission, structure, and culture.
History and Mission

The United States Army is the oldest branch of the US military, established on June 14, 1775, as the Continental Army. Its primary mission is to protect the country and its interests by fighting and winning wars on land. The Army is responsible for defending the nation against external threats, maintaining peace and stability, and providing humanitarian assistance.
On the other hand, the United States Marine Corps was established on November 10, 1775, as a branch of the Continental Army. Its primary mission is to provide power projection from the sea, using the mobility of the US Navy to deploy rapidly and decisively in response to crises. The Marine Corps is known for its expeditionary nature, with a focus on amphibious warfare, ground combat, and security cooperation.
Structure and Organization
The Army is organized into several components, including the Regular Army, Army National Guard, and Army Reserve. The Regular Army is the active duty component, comprising full-time soldiers who serve in various units and installations around the world. The Army National Guard and Army Reserve are part-time components, consisting of citizen-soldiers who can be called upon to support the Regular Army in times of crisis.
The Marine Corps, on the other hand, is a single, unified force with no distinction between active duty and reserve components. Marines are organized into several types of units, including infantry, artillery, aviation, and logistics. The Marine Corps is known for its emphasis on small unit leadership and initiative, with a focus on developing junior leaders who can operate independently in complex environments.
Culture and Values

The Army and Marine Corps have distinct cultures and values that shape their approach to warfare and service. The Army values loyalty, duty, respect, selfless service, honor, integrity, and personal courage. These values are reflected in the Army’s motto, “This We’ll Defend,” which emphasizes the branch’s commitment to defending the nation and its people.
The Marine Corps, on the other hand, values honor, courage, and commitment. The Marine Corps’ motto, “Semper Fidelis” (Always Faithful), reflects its commitment to loyalty and fidelity to the nation, the Corps, and fellow Marines. The Marine Corps is known for its esprit de corps, with a strong emphasis on camaraderie, teamwork, and shared sacrifice.
Training and Doctrine

The Army and Marine Corps have different approaches to training and doctrine. The Army’s training is focused on developing soldiers who can operate in a variety of environments, from urban warfare to counterinsurgency. Army doctrine emphasizes the importance of teamwork, coordination, and communication in achieving military objectives.
The Marine Corps, on the other hand, is known for its rigorous training and emphasis on individual initiative. Marine training is focused on developing Marines who can operate in small units, using speed, surprise, and violence of action to achieve their objectives. Marine doctrine emphasizes the importance of maneuver warfare, with a focus on rapid deployment, decisive action, and exploitation of the initiative.
Comparison of Roles and Responsibilities

| Branch | Primary Role | Secondary Role |
|---|---|---|
| Army | Ground warfare, homeland defense | Humanitarian assistance, disaster response |
| Marine Corps | Expeditionary warfare, power projection | Security cooperation, crisis response |

👉 Note: The above table provides a general comparison of the primary and secondary roles of the Army and Marine Corps. However, it's essential to recognize that both branches have a wide range of responsibilities and can be called upon to perform various tasks in support of national objectives.
Conclusion

In conclusion, while the Army and Marine Corps share some similarities, they are distinct branches with different histories, missions, structures, and cultures. Understanding the differences between these two branches can provide valuable insights into the complexities of the US military and its various components. Whether you’re considering a career in the military or simply interested in learning more about the Army and Marine Corps, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the differences between these two esteemed branches.
What is the main difference between the Army and Marine Corps?

+
The main difference between the Army and Marine Corps is their primary mission and role. The Army’s primary mission is to protect the country and its interests by fighting and winning wars on land, while the Marine Corps’ primary mission is to provide power projection from the sea, using the mobility of the US Navy to deploy rapidly and decisively in response to crises.
What is the difference between the Army’s and Marine Corps’ training programs?

+
The Army’s training program is focused on developing soldiers who can operate in a variety of environments, from urban warfare to counterinsurgency. The Marine Corps’ training program, on the other hand, is known for its rigorous training and emphasis on individual initiative, with a focus on developing Marines who can operate in small units, using speed, surprise, and violence of action to achieve their objectives.
What is the difference between the Army’s and Marine Corps’ cultures and values?

+
The Army values loyalty, duty, respect, selfless service, honor, integrity, and personal courage, while the Marine Corps values honor, courage, and commitment. The Marine Corps is known for its esprit de corps, with a strong emphasis on camaraderie, teamwork, and shared sacrifice.



