5 Tips to Master Denotation vs Connotation Distinctions
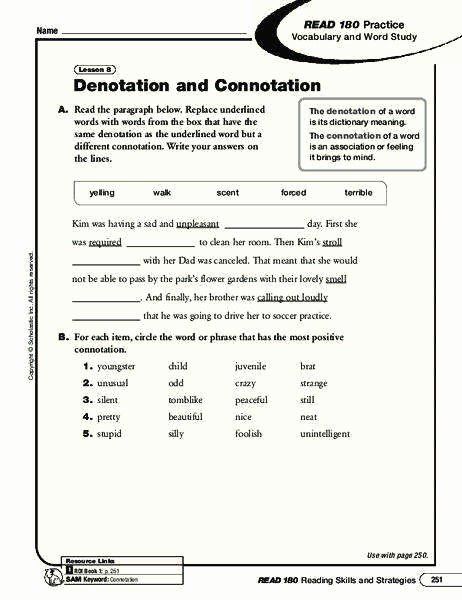
The English language is rich with nuances that often require a keen eye to distinguish subtle differences. Among these nuances, denotation and connotation play pivotal roles in how we interpret and communicate. Understanding the distinction between denotation, which is the literal meaning of a word, and connotation, the emotional or cultural association tied to it, is essential for effective and nuanced communication. Here are five tips to help you master these distinctions and enhance your command of language:
Tip 1: Understand the Literal Meaning

Before delving into connotations, you must master the denotation of words. This means:
- Consulting a dictionary for the precise meaning of words.
- Reading definitions carefully to grasp all the nuances of a word’s primary meaning.
- Recognizing that words often have multiple denotations, and context determines which one is relevant.
Knowing the denotation helps set the foundation for recognizing when and how connotation shifts the meaning.
Tip 2: Recognize Cultural and Emotional Nuances

Connotation is where language becomes an art. Here are steps to identify connotations:
- Observe how words are used in different contexts, from literature to everyday speech.
- Consider the history, culture, and the audience's background when interpreting a word.
- Understand that connotations can change over time, influenced by societal shifts or movements.
This awareness allows you to appreciate the layers of meaning that words carry beyond their literal definitions.
Tip 3: Use Context to Your Advantage

Context is king in distinguishing denotation from connotation:
- Analyze the sentence or passage for clues that suggest additional meanings.
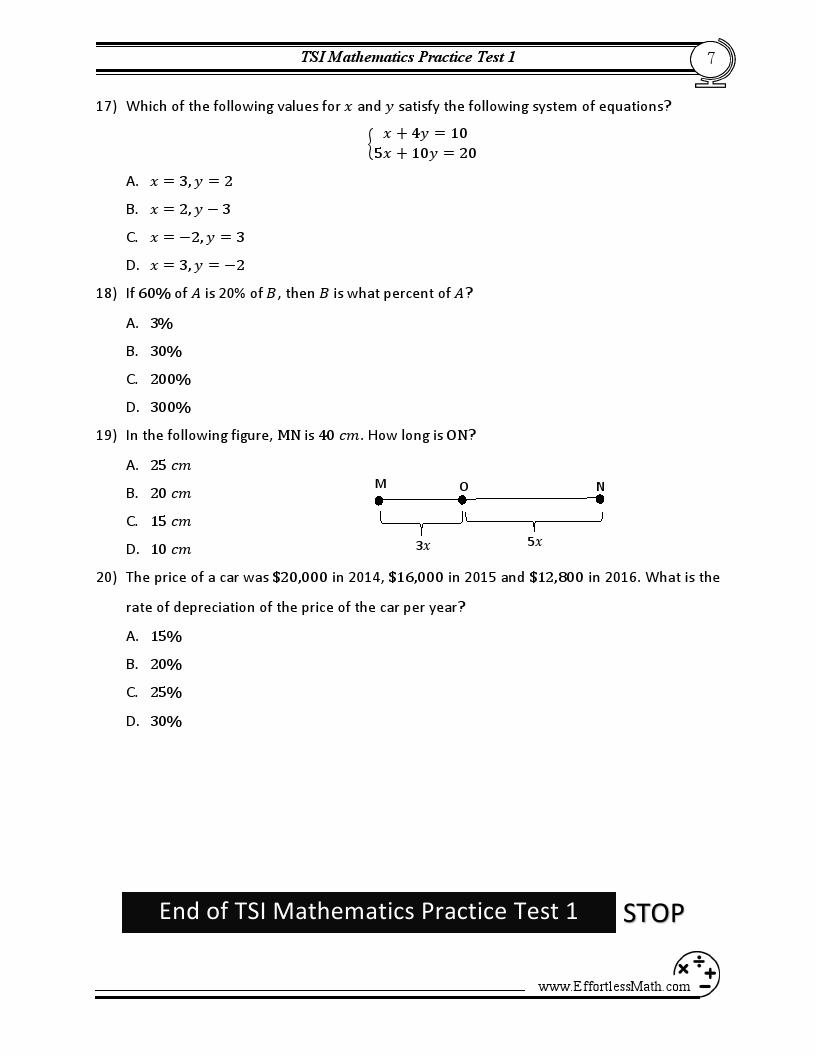
- Be aware of the speaker or writer’s intention, tone, and potential biases.
- Take note of how words are used in different settings, like poetry, advertising, or professional communication.
By understanding context, you'll discern whether a word is being used for its denotative meaning or to evoke specific connotations.
Tip 4: Engage with Examples

Practicing with examples is a practical way to understand the difference between denotation and connotation. Here's how:
- Create or find lists of words with similar denotations but different connotations, like "house" vs. "home" or "clever" vs. "smart."
- Discuss or analyze these examples with others to see how different interpretations emerge.
- Write sentences using the same word but with different connotations, and explain the intended meaning behind each.
📝 Note: When discussing examples, make sure to cite real-life contexts where these words are commonly used with varied connotations.
Tip 5: Read Widely and Actively

To truly internalize the difference:
- Read a variety of texts from different genres, time periods, and cultural backgrounds.
- Pay attention to how authors choose words to create specific effects or impressions.
- Make notes or annotations to track your understanding of word choices.
Wide reading exposes you to the full spectrum of language use, helping you see how denotative and connotative meanings shift in different environments.
In mastering the distinction between denotation and connotation, you gain a deeper understanding of language’s power to convey both fact and feeling. This skill not only enriches your comprehension but also empowers you to use language with precision and impact. Whether you’re writing, speaking, or interpreting messages, this knowledge allows you to navigate the subtleties of English with confidence.
What is the primary difference between denotation and connotation?

+
The primary difference is that denotation refers to the literal or dictionary definition of a word, whereas connotation is the emotional or cultural associations that come with a word.
How does context affect the interpretation of a word?
+
Context is crucial as it provides clues on whether a word is being used for its literal meaning (denotation) or to convey a broader or different implication (connotation). Context includes the surrounding text, the speaker or writer’s intent, and the audience’s background.
Can the connotation of a word change over time?

+
Yes, the connotation of words can evolve due to shifts in culture, social movements, historical events, or changes in language use. Words once considered neutral or positive can become derogatory or vice versa.