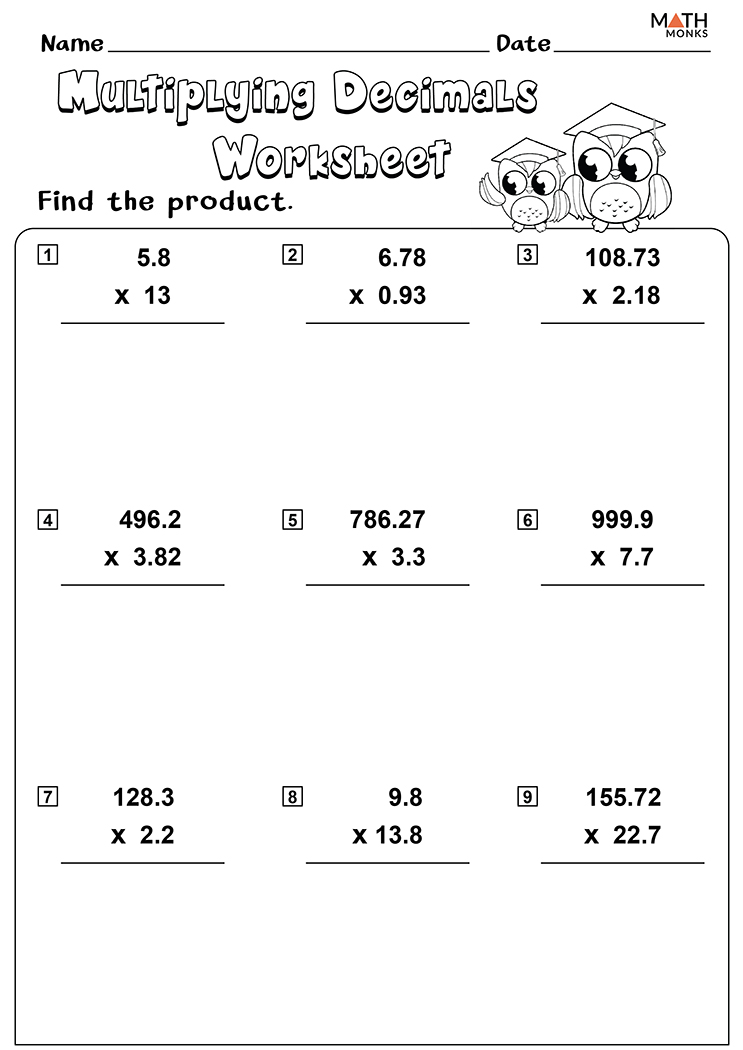
5 Tips for Mastering Decimal Multiplication and Division

The intricacies of decimal arithmetic can be a challenging yet rewarding aspect of mathematics education. Understanding how to navigate the world of decimal multiplication and division can significantly boost mathematical proficiency. Here, we dive into five strategies designed to help you master these operations, enhancing both your speed and accuracy in handling decimals.
Understand the Basics

Before tackling advanced techniques, ensure you’re solid on the basics:
- Decimal place values: Each digit in a number has a specific place value. For example, in the number 25.47, the digit ‘4’ represents four-tenths.
- Multiplication and division rules: When multiplying or dividing by 10, 100, or any power of ten, the decimal point moves accordingly.
- Estimation: This helps you check your results. For multiplication, round numbers and multiply; for division, estimate the quotient by rounding both the dividend and divisor.
⚠️ Note: Estimation is a key step before calculation to catch potential errors.
Use Place Value Alignment

Aligning numbers by their place value is critical in both multiplication and division:
- Multiplication: When multiplying, ignore the decimal points at first. Multiply the numbers as if they were whole numbers. Then, count the total number of decimal places in the original numbers to determine where to place the decimal point in your result.
- Division: For division, count the number of decimal places in the divisor and dividend. Place the decimal point in the quotient directly above its position in the dividend.
| Original Numbers | Multiplication | Division |
|---|---|---|
| 2.5 x 3.4 | Ignore decimals: 25 x 34 = 850 | 2.5 / 0.2 = Count decimals then divide |
| Add 1 decimal from 2.5 + 1 from 3.4: Result = 8.50 | Move the decimal point: 25 / 2 = 12.5 |

Master Long Multiplication and Division

Once the basics are down, these methods are indispensable:
- Long Multiplication: Line up the numbers vertically and multiply each digit of one number by each digit of the other, carrying where necessary.
- Long Division: Set up the problem, divide digit by digit, and manage remainders or decimal places accurately.
Here’s how to set up long division:
12
---------
13 | 156.0
- 13
-----
26
- 26
-----
0
🔎 Note: For long division, handle remainders carefully to ensure accuracy.
Practice with Real-Life Scenarios
Applying decimal arithmetic to practical problems enhances understanding:
- Shopping: Calculate total costs when dealing with decimal prices or discounts.
- Cooking: Adjust recipes for different serving sizes, converting quantities in decimal.
- Finance: Work out interest, taxes, and discounts.
Utilize Visual Aids and Mnemonics

To make abstract concepts more tangible:
- Use grid paper to visualize how numbers align in multiplication or division.
- Place value chart: Helps in understanding where the decimal point should go.
- Memory tricks: Create mnemonics to remember rules. For example, “Dots Align” for division.
The journey through decimal multiplication and division can transform mathematical fear into mastery. By focusing on understanding place values, utilizing precise methods, practicing in real-life contexts, and employing visual aids, you're not just learning math; you're mastering a life skill. Here’s a final thought for you to ponder:
Why is decimal alignment important in multiplication?
+
Decimal alignment helps determine the correct placement of the decimal point in the product, ensuring accuracy in the calculation.
How can I check if my decimal division is correct?

+
You can multiply the quotient by the divisor to see if it equals the dividend. Also, estimation can give you a quick check.
What are some common mistakes to avoid?

+
Common mistakes include forgetting to align decimals correctly, misplacing the decimal point, and ignoring remainders or carrying digits incorrectly.