5 Tips for Mastering Decimal Division with Ease

In the intricate world of mathematics, the art of decimal division emerges as a critical skill, impacting everything from financial calculations to engineering feats. For students and professionals alike, mastering this process is not only about proficiency but also about understanding the underlying principles that govern number manipulation. This comprehensive guide will walk you through five essential tips to help you navigate the nuances of decimal division with ease.
1. Understanding Decimal Basics

Before delving into division, a solid foundation in decimal numbers is crucial. Here’s a quick primer:
- Structure: A decimal number comprises a whole number part and a fractional part separated by a decimal point.
- Value Placement: Each digit’s value increases by a factor of 10 moving left from the decimal point, and decreases moving right.
- Representation: Decimals can represent percentages, measurements, and many other real-world quantities.

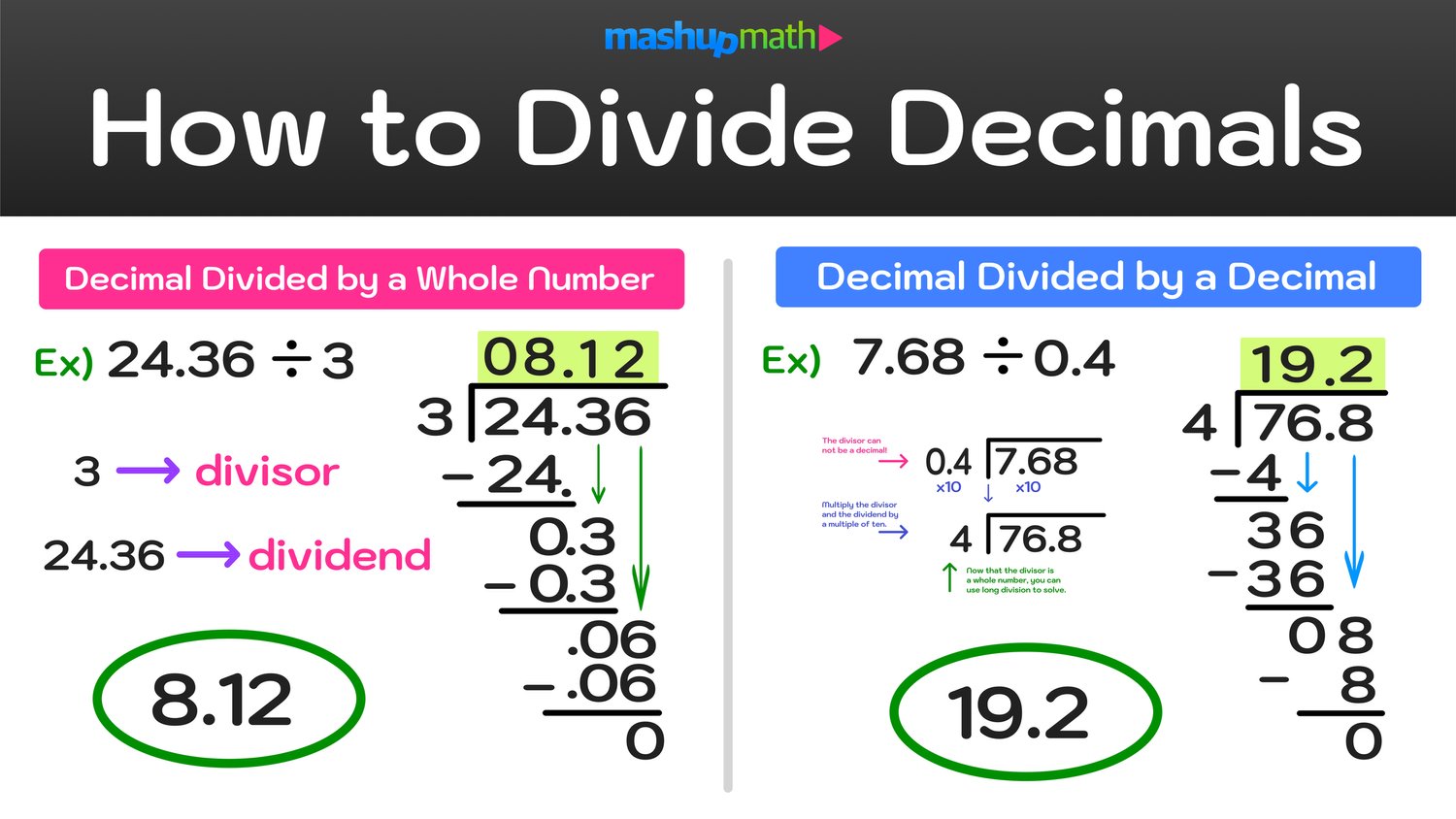
2. The Long Division Method for Decimals

The long division method is a fundamental approach to dividing whole numbers, but it seamlessly extends to decimals. Here are the steps:
- Move the Decimal Point: If the divisor (the number you’re dividing by) is a decimal, move the decimal point to the right until the divisor becomes a whole number. This movement also requires adjusting the dividend’s decimal point accordingly.
- Perform Regular Division: Divide as you would with whole numbers.
- Align Decimal Points: Place the decimal point in the quotient directly above where it appears in the dividend after step 1.
💡 Note: When the dividend becomes smaller than the divisor after several division steps, you may need to add zeroes to the dividend for continued accuracy.
3. Converting to Fractional Division

While the long division method is practical, some situations call for a different approach. Converting the problem into a fraction form can sometimes simplify complex decimal division:
- Convert decimals into fractions (e.g., 0.5 = 1⁄2)
- Perform division as you would with fractions by multiplying the numerator by the reciprocal of the denominator.
4. Use of Calculators with Accuracy
Modern calculators are equipped to handle decimal division effortlessly:
| Calculator Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Calculator | Allows for entry of large numbers with precision and provides functions like memory storage. |
| Function Keys | Keys like √, π, log can be used to simplify division involving complex calculations. |
| Decimal Settings | You can set the calculator to output results with varying precision or fixed decimal places. |

5. Practical Examples and Real-life Application

Understanding through practice:
- Finance: Calculating interest rates, tax on purchases, or budgeting with decimal figures.
- Engineering: Dividing measurements accurately for precision in design.
- Scientific Calculations: Handling molarity, concentrations, and experimental data in labs.
📝 Note: Regularly practicing with real-world scenarios sharpens your mental arithmetic skills, preparing you for spontaneous calculations.
Mastering decimal division requires an amalgamation of theory, practical application, and technology. By following these five tips, you equip yourself with the knowledge and techniques to tackle decimal division confidently. From understanding the very essence of decimals to leveraging technology and real-world application, each step provides insight into a universally applicable skill. Keep in mind that proficiency in decimal division not only enhances your mathematical abilities but also expands your problem-solving toolkit, allowing you to navigate through numerous disciplines with greater ease and accuracy.
Why is it important to move the decimal point when dividing?

+
Moving the decimal point in the divisor ensures you’re working with whole numbers, which simplifies the division process. It also ensures the result is accurate by aligning the quotient’s decimal point correctly.
Can I use a standard calculator for decimal division?

+
Yes, you can use most standard calculators for decimal division. However, for more complex calculations or when needing precise decimal place control, a scientific or financial calculator is more beneficial.
How do I know if I’m making an error in decimal division?

+
Check for the following common signs of error: misplaced decimal points, discrepancies in the magnitude of the answer, or if your calculation doesn’t align with the expected result or estimate.