Dalton's Law: Mastering Partial Pressures Simply Explained
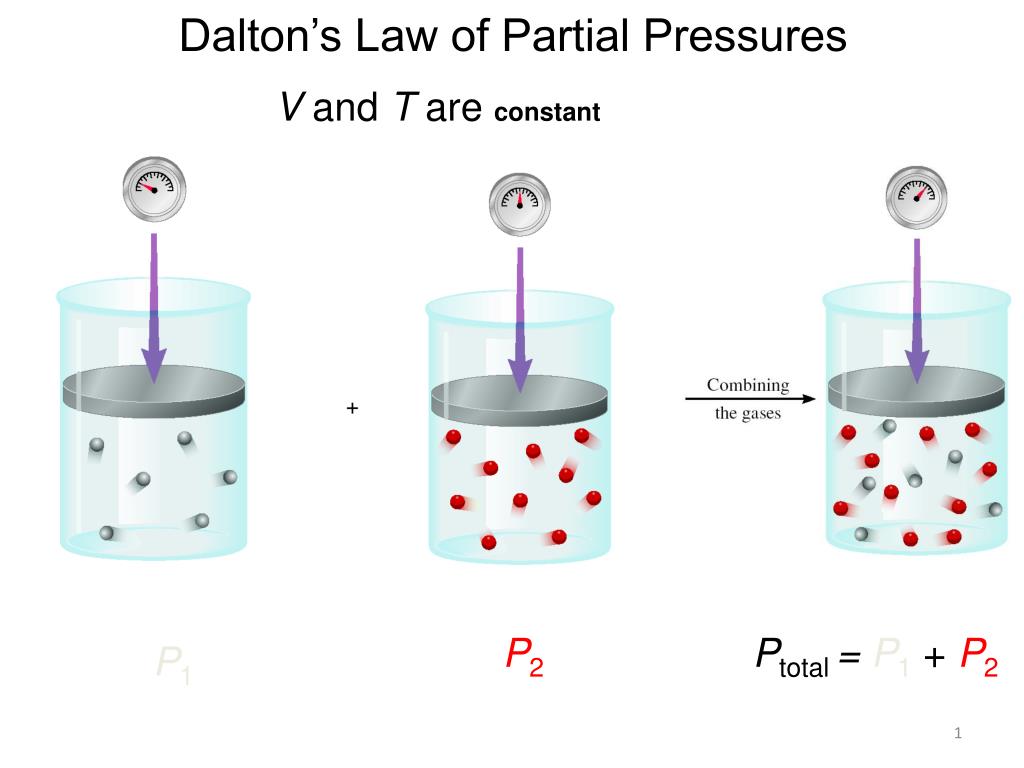
Understanding Dalton's Law

In the vast field of chemistry, especially when dealing with gases, understanding the partial pressures of individual gases within a mixture is fundamental. Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures, introduced by John Dalton in 1801, provides a straightforward method to comprehend how gas mixtures behave. Here, we will delve into Dalton's Law, explore its applications, and ensure that by the end of this discussion, you'll have a comprehensive grasp of this principle.
The Basic Concept

Dalton's Law states that the total pressure exerted by a mixture of non-reacting gases is equal to the sum of the pressures each gas would exert if it occupied the same volume alone. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
\[ P_{total} = P_1 + P_2 + P_3 + \ldots + P_n \]
- Ptotal - Total pressure of the mixture.
- P1, P2, P3, ... Pn - Partial pressures of the individual gases in the mixture.
Why is Dalton's Law Important?

Dalton's Law is not just a theoretical construct; it has real-world applications:
- Atmospheric Composition: The atmosphere is a mixture of gases, each contributing to the total atmospheric pressure. Understanding partial pressures helps in meteorological studies.
- Gas Collection: When gases are collected over water, they are saturated with water vapor, and Dalton's Law helps to calculate the pressure exerted by the dry gas.
- Industrial Processes: In industries like gas storage, transportation, and chemical synthesis, understanding partial pressures is crucial for safety and efficiency.
- Respiratory Physiology: Partial pressures are essential in understanding how oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the lungs.
Exploring Dalton's Law in Practice

Experimentation with Dalton's Law

Here's a simple experiment to understand Dalton's Law:
- Take a flask, measure its volume.
- Fill it with a known amount of one gas at a specific temperature, note the pressure (P1).
- Add another gas without changing the volume or temperature, note the new total pressure (Ptotal).
- Repeat for additional gases, each time noting the partial pressure of the new gas.
- Verify that the total pressure is indeed the sum of all individual partial pressures.
This practical approach demonstrates how Dalton's Law holds true in a real-world scenario.
Calculating Partial Pressures
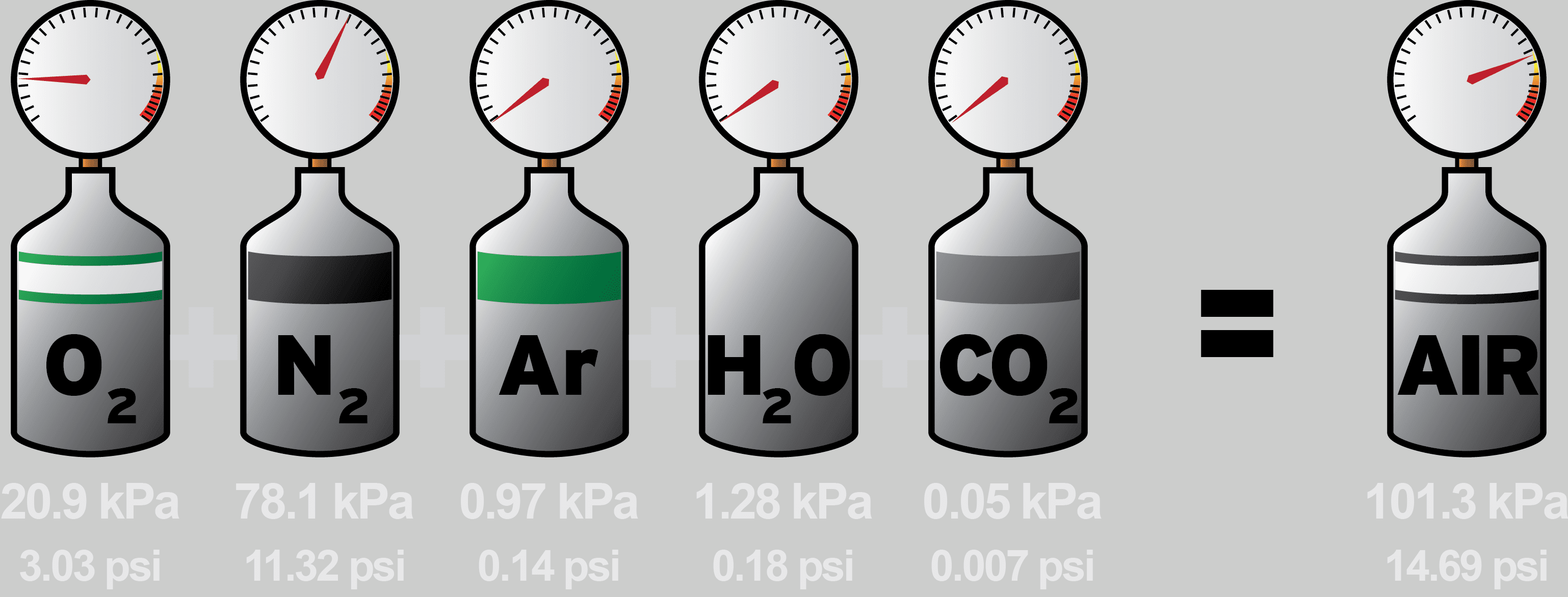
Let's consider an example where you have a mixture of oxygen, nitrogen, and helium:
- Oxygen exerts a pressure of 250 mmHg.
- Nitrogen exerts a pressure of 150 mmHg.
- Helium exerts a pressure of 100 mmHg.
Using Dalton's Law:
[ P_{total} = 250 \, \text{mmHg} + 150 \, \text{mmHg} + 100 \, \text{mmHg} = 500 \, \text{mmHg} ]
🌍 Note: Partial pressure calculations are not always straightforward due to gases that react or interact with each other. Dalton's Law holds only for non-reacting gases.
Partial Pressures in Real Gases

Real gases do not always behave ideally, especially at high pressures or low temperatures. Here, Dalton's Law can still be used as an approximation:
| Gas | Partial Pressure (mmHg) | Real Behavior Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen | 150 | Minor deviations |
| Argon | 75 | Significant deviations at high pressures |
| Water Vapor | 25 | Condensation can affect partial pressure |
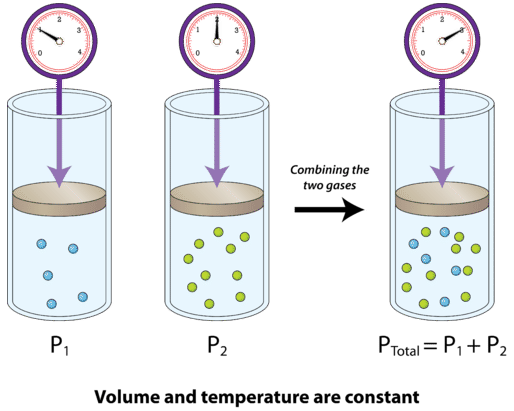
Concluding Thoughts

In closing, Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures offers a fundamental insight into how gases interact in mixtures. While ideal for many applications, understanding the limits of this law in real-world scenarios, particularly with gases that interact or at extreme conditions, is equally important. Whether in atmospheric studies, industrial applications, or biological processes, mastering Dalton's Law equips you with the tools to dissect complex gas mixtures into their constituent pressures, providing clarity on a wide range of scientific phenomena.
What is Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures?

+
Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures states that the total pressure of a mixture of non-reacting gases is the sum of the partial pressures each gas would exert alone in the same volume.
Can Dalton’s Law be applied to all gas mixtures?

+
It is applicable for mixtures where the gases do not react with each other. If gases react, the law cannot be applied directly due to changes in composition.
How does Dalton’s Law help in real life?

+
It’s crucial for understanding gas storage, chemical reactions involving gases, atmospheric studies, and even medical applications like how gases are absorbed in biological systems.