5 Key Answers for Cycles Worksheet in Integrated Science

When delving into integrated science education, understanding fundamental concepts like cycles is essential. These cycles, encompassing everything from the water cycle to the carbon cycle, help us comprehend how various elements of our environment interact and maintain balance. Here are five key answers to questions often found in cycles worksheets, providing clarity and enhancing understanding in integrated science studies:
The Importance of Cycles in Nature


Understanding cycles is vital because they:
- Help in maintaining ecological balance.
- Illustrate how substances are recycled in ecosystems.
- Provide insight into human impacts on nature.
🌿 Note: Cycles are not just about individual elements but about the interconnectedness of all life forms.
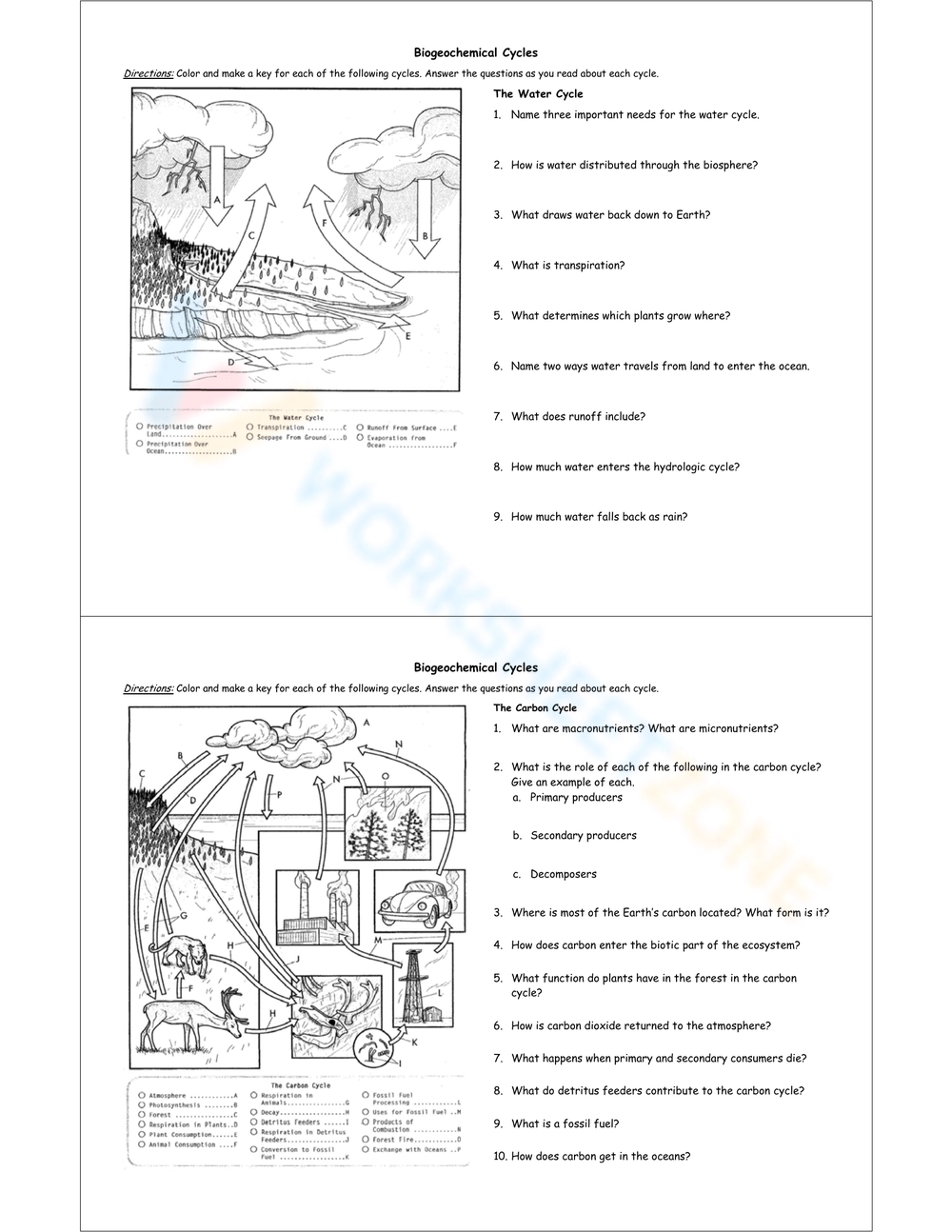
Water Cycle


The water cycle or hydrologic cycle involves several key processes:
- Evaporation: Water from the Earth’s surface turns into vapor.
- Condensation: Water vapor cools and turns into water droplets.
- Precipitation: Water droplets combine to form clouds and eventually fall back to the earth.
- Collection: Water gathers in bodies of water or permeates into the ground.
- Transpiration: Plants lose water through tiny pores called stomata, which re-enters the atmosphere.
💧 Note: The water cycle is influenced by climate change, affecting global precipitation patterns.
Carbon Cycle


The carbon cycle is crucial for:
- Regulating the Earth’s temperature.
- Providing carbon, an essential building block for life.
Key processes include:
- Photosynthesis: Plants convert CO2 into organic matter.
- Respiration: Organisms release CO2 back into the atmosphere.
- Decomposition: Dead organisms and waste decompose, releasing CO2.
- Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuel burning releases CO2, altering the natural cycle.
🌱 Note: Human activities significantly impact the carbon cycle, contributing to global warming.
Nitrogen Cycle


Nitrogen cycling is critical for:
- Protein synthesis in living organisms.
- The growth of plants which form the base of the food web.
Main steps are:
- Nitrogen Fixation: Conversion of nitrogen gas into forms usable by plants.
- Ammonification: Breakdown of organic matter into ammonia.
- Nitrification: Conversion of ammonia to nitrites and then nitrates.
- Denitrification: Conversion of nitrates back to nitrogen gas.
☀️ Note: The use of nitrogenous fertilizers has disrupted this cycle, leading to environmental problems like eutrophication.
Phosphorus Cycle


The phosphorus cycle focuses on:
- Energy transfer in organisms.
- The regulation of essential biological processes.
Crucial stages include:
- Weathering: Release of phosphorus from rocks into soil and water.
- Plant Uptake: Plants absorb phosphorus from the soil.
- Decomposition: Phosphate compounds from organic decay enrich the soil.
- Sedimentation: Phosphorus eventually accumulates in sediments of rivers and lakes.
- Geological Uplift: Processes that return phosphorus from sediments to land.
🔬 Note: Phosphorus does not have a significant atmospheric phase unlike other cycles, making it less mobile and more localized.
By now, it should be evident that natural cycles are not just sequences of events but are foundational in sustaining life and regulating environmental conditions. They are dynamic, subject to both natural processes and human influence. Understanding these cycles allows us to appreciate the interconnectivity of our planet's ecosystems, manage resources more sustainably, and mitigate human impacts on nature.
Why are cycles important in biology?

+
Cycles are essential in biology because they govern the flow of essential elements through living organisms and ecosystems, ensuring nutrient availability and maintaining ecological balance.
How do human activities impact these cycles?
+
Human activities like deforestation, fossil fuel burning, and agricultural practices can disrupt cycles by altering natural processes, leading to issues like climate change, nutrient depletion, or over-enrichment.
Can we restore or repair disrupted natural cycles?

+
Restoration efforts involve sustainable practices, reducing pollutants, reforestation, and using green technology to mimic natural cycles. However, some impacts might be irreversible or require long-term efforts to recover.



