Crash Course Globalization Worksheet Answer Key Revealed

Globalization is a multifaceted process that has significantly reshaped economies, cultures, and the way people interact across the world. As educational institutions strive to make their curriculums more relevant to the modern era, understanding globalization becomes essential. This article serves as an in-depth answer key to the "Crash Course Globalization Worksheet," providing insights into the various dimensions of globalization, from economic to cultural, and from technological to environmental impacts.
Understanding Globalization

Globalization is the interconnection of different parts of the world through the spread of communication, transportation, and economic exchanges. Here’s what you need to know:
- Economic Globalization: This involves the growth of international trade, investment, and capital flows. It has been facilitated by advancements in transportation, trade liberalization, and communication technology.
- Cultural Globalization: This pertains to the global spread of ideas, values, practices, and cultural products across borders. While it can lead to cultural homogenization, it also promotes cultural diversity.
- Technological Globalization: The spread of technology worldwide, which has dramatically changed how information is accessed, shared, and used, thereby affecting every aspect of society.
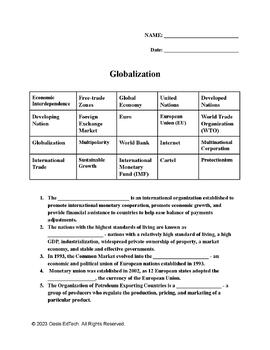
- Political Globalization: The influence of international organizations like the United Nations, World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund in shaping global policies and agreements.

Economic Aspects of Globalization

Economic globalization has both proponents and critics:
- Positive Effects:
- Increased trade leading to economic growth in many countries.
- Access to a larger variety of goods at potentially lower prices.
- Opportunities for foreign direct investment and multinational corporations to set up businesses in different countries.
- Negative Effects:
- Income inequality within and between nations.
- Job losses due to outsourcing in developed countries.
- Environmental degradation due to increased industrial activity.
🌍 Note: Globalization is not a zero-sum game; it has the potential to benefit all, but policies must be designed to mitigate negative impacts.
| Aspect | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Economy | Economic growth, trade enhancement | Job displacement, income inequality |
| Environment | Global awareness of environmental issues | Resource depletion, pollution |
| Culture | Cultural exchange, global understanding | Cultural erosion, loss of local traditions |

Cultural Impacts

Here's how globalization influences culture:
- Homogenization vs. Hybridization: There's a fear that global culture might dominate local cultures, leading to homogenization. However, hybridization can occur where local and global cultures blend, creating new cultural expressions.
- Cultural Export: Western culture, particularly from the United States, has a significant influence worldwide, through movies, music, fashion, and fast food.
- Indigenous Cultures: Globalization can both endanger and empower indigenous cultures by exposing them to global issues or enabling them to share their stories and practices more widely.

Technological Influence
Technology has been a catalyst for globalization:
- Communication: The internet, social media, and instant messaging have made global communication almost instantaneous.
- Transportation: Air travel and shipping advancements have reduced the barriers of distance, allowing goods, services, and people to move more freely.
- Global Workforce: Technology enables remote work, outsourcing, and international collaboration, creating a globalized workforce.
📝 Note: While technology drives globalization, it also demands ethical considerations regarding privacy, digital divide, and cyber security.
Environmental Impacts

The environmental consequences of globalization are complex:
- Positive Impacts:
- Global cooperation on environmental issues.
- Increased awareness of climate change and efforts towards sustainability.
- Negative Impacts:
- Increased carbon footprint from global transport.
- Resource depletion and environmental degradation due to industrialization.
Globalization Challenges

The process of globalization presents several challenges:
- Income Inequality: While some countries and individuals benefit greatly from globalization, others face economic marginalization.
- Cultural Loss: There's a risk that traditional cultures could be overwhelmed by dominant global culture.
- Environmental Damage: The drive for economic growth can sometimes overlook the need for sustainable practices.
- Global Governance: There's a lack of effective global governance to address international problems like climate change or trade disputes.
In wrapping up our exploration of globalization, we've seen that while it opens up new avenues for growth and interaction, it also poses significant challenges that require thoughtful, balanced policies. Globalization, at its core, is about connections. It's about how economies, cultures, and technologies intertwine, creating a world where borders are less significant but where care must be taken to ensure benefits are equitably distributed, cultural diversity is preserved, and our planet's health is maintained for future generations.
What are the benefits of economic globalization?

+
Some key benefits include increased trade, economic growth, job creation, and consumer choice. Countries can specialize in producing goods where they have a comparative advantage, leading to efficiency and potentially lower prices for consumers.
How does globalization affect cultural diversity?

+
Globalization can lead to both the spread and potential erosion of cultural diversity. On one hand, it allows for the exchange of cultural practices and ideas; on the other, dominant cultures can overshadow local traditions, leading to cultural homogenization. However, there are instances where cultures blend, creating unique hybrids.
What role does technology play in globalization?

+
Technology has been a major driver of globalization by enabling instantaneous communication, lowering transportation costs, and allowing for global business operations. It facilitates the exchange of ideas, goods, and services across the globe at unprecedented speed.
Are there any environmental costs associated with globalization?

+
Yes, globalization has environmental costs including increased carbon emissions due to transportation, depletion of resources due to increased production, and often a lack of adherence to environmental regulations in countries with less stringent laws.
How can globalization be made more equitable?

+
To make globalization more equitable, policies need to focus on reducing income inequality, protecting workers’ rights, ensuring access to technology, and promoting sustainable economic development. Global cooperation and fair trade agreements can also play a crucial role.



