5 Key Steps to Mastering Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
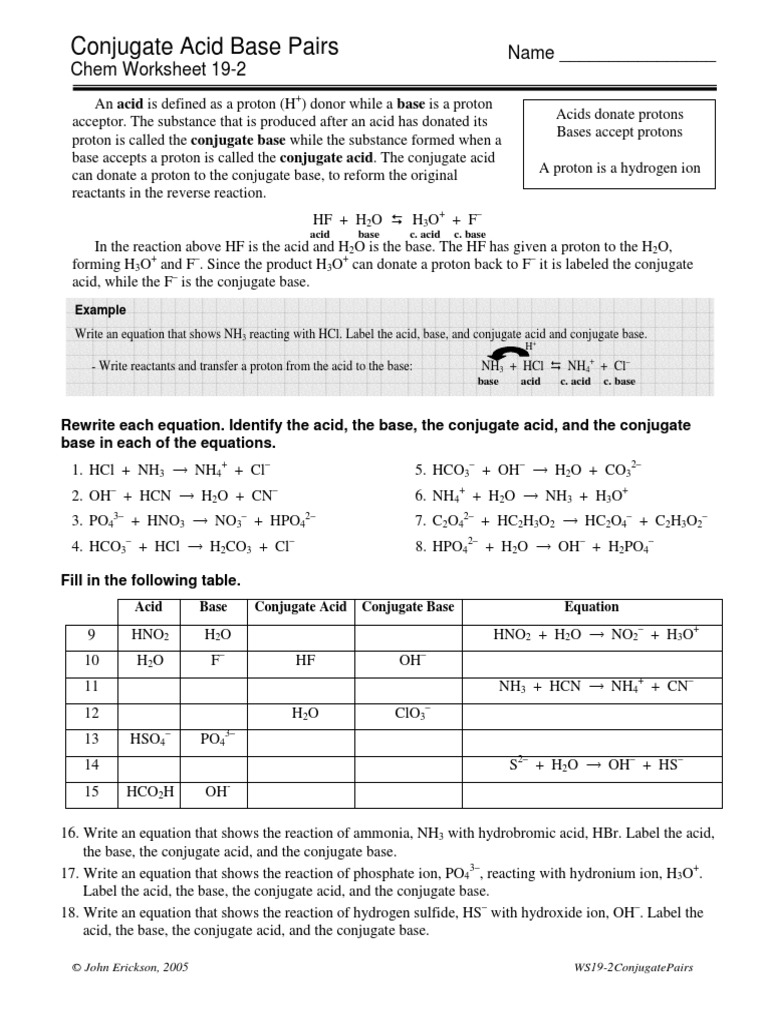
Understanding conjugate acid-base pairs is fundamental for anyone delving into the realms of chemistry, especially those focusing on acids, bases, and chemical equilibria. These concepts are not only pivotal for academic success but also in practical applications in various scientific fields. Today, we'll break down the process into five key steps, ensuring you grasp this essential chemical principle with ease.
Step 1: Understanding Definitions

Before diving into the complexities, it's crucial to solidify your understanding of the definitions:
- Acid: A substance that donates a proton (H⁺) in a reaction.
- Base: A substance that accepts a proton (H⁺) in a reaction.
- Conjugate Acid: What's left after a base accepts a proton.
- Conjugate Base: What's left after an acid donates a proton.
For example, take the reaction of ammonia (NH₃) with water (H₂O):
| Acid | ⇄ | Base | + | Conjugate Acid | + | Conjugate Base |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H₂O (acid) | ⇄ | NH₃ (base) | + | NH₄⁺ (conjugate acid) | + | OH⁻ (conjugate base) |

🔍 Note: Understanding conjugate pairs requires knowing that every acid has a conjugate base, and every base has a conjugate acid.
Step 2: Recognizing Conjugate Pairs

To identify conjugate acid-base pairs:
- Identify the proton donor (acid) and the proton acceptor (base) in any given reaction.
- Determine what species remain after the transfer of the proton.
Here’s a practical example:
- HCO₃⁻ + H₂O ⇌ H₂CO₃ + OH⁻
- HCO₃⁻ acts as a base accepting a proton to become H₂CO₃, its conjugate acid.
- Water acts as an acid donating a proton to become OH⁻, its conjugate base.
🔍 Note: For visual learners, chemical reactions can be diagrammed to show the movement of the proton, which can aid in recognizing conjugate pairs.
Step 3: Understanding the Role of Water

Water (H₂O) plays a dual role in acid-base reactions:
- It can act as a weak acid (H₂O ⇌ H⁺ + OH⁻).
- It can also act as a weak base (H₂O + H⁺ ⇌ H₃O⁺).
This ambidextrous nature of water makes it a crucial component in many reactions involving acids and bases:
- In the presence of a base, water donates a proton (acts as an acid).
- In the presence of an acid, water accepts a proton (acts as a base).
💧 Note: Remember, water is amphoteric, meaning it can behave as both an acid and a base depending on the conditions.
Step 4: Acid Strength and Conjugate Bases

The strength of an acid is directly related to the stability of its conjugate base:
- The more stable the conjugate base, the stronger the acid.
- This is due to the acid having a greater tendency to donate a proton, resulting in a more stable base.
For example:
- HCl is a strong acid because Cl⁻ is a very stable ion due to its electron shell configuration.
- HCOOH (formic acid) has a less stable conjugate base (HCOO⁻), making it a weaker acid.
⚖️ Note: There's often an inverse relationship between the strength of an acid and its conjugate base; strong acids have weaker conjugate bases, and vice versa.
Step 5: Applying Conjugate Acid-Base Pair Concepts

With the foundational knowledge in place, we can now apply these principles:
- Predicting reaction outcomes: Knowing the relative strengths of acids and bases helps predict whether a reaction will favor the forward or reverse direction.
- Understanding pH: The acid or base component of a pair affects the pH of a solution. For instance, in a buffer solution, you'll use weak acids and their conjugate bases to maintain pH stability.
- Identifying species in chemical equilibria: You can deduce which species are present in equilibrium by recognizing the proton donation and acceptance.
🔄 Note: Applying these concepts in real-life scenarios enhances your problem-solving skills in chemistry.
In summary, mastering conjugate acid-base pairs involves understanding definitions, recognizing pairs, appreciating water's dual role, understanding the relationship between acid strength and conjugate base stability, and finally, applying these concepts. This knowledge not only improves your academic standing but also equips you with the skills necessary for various scientific and industrial applications.
What are conjugate acids and bases?

+
Conjugate acids and bases are pairs of compounds that transform into each other through the loss or gain of a proton (H⁺). A base accepting a proton becomes its conjugate acid, while an acid donating a proton becomes its conjugate base.
Why is water considered amphoteric?
+
Water is considered amphoteric because it can act both as an acid and as a base. This is due to its ability to either donate a proton (acting as an acid) or accept one (acting as a base) depending on the surrounding chemical environment.
How does acid strength relate to conjugate base stability?

+
The stronger the acid, the weaker and more stable its conjugate base. This stability comes from the acid’s propensity to donate its proton, resulting in a more stable base, thereby making the acid stronger.



