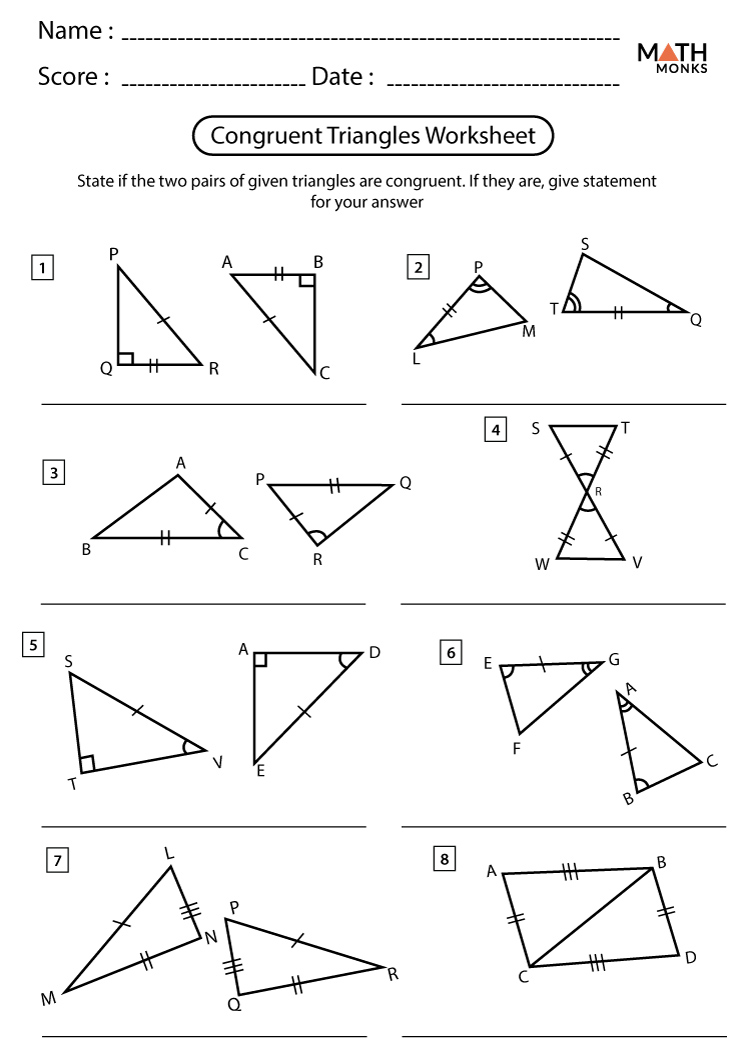
Congruent Triangles Worksheet Answers
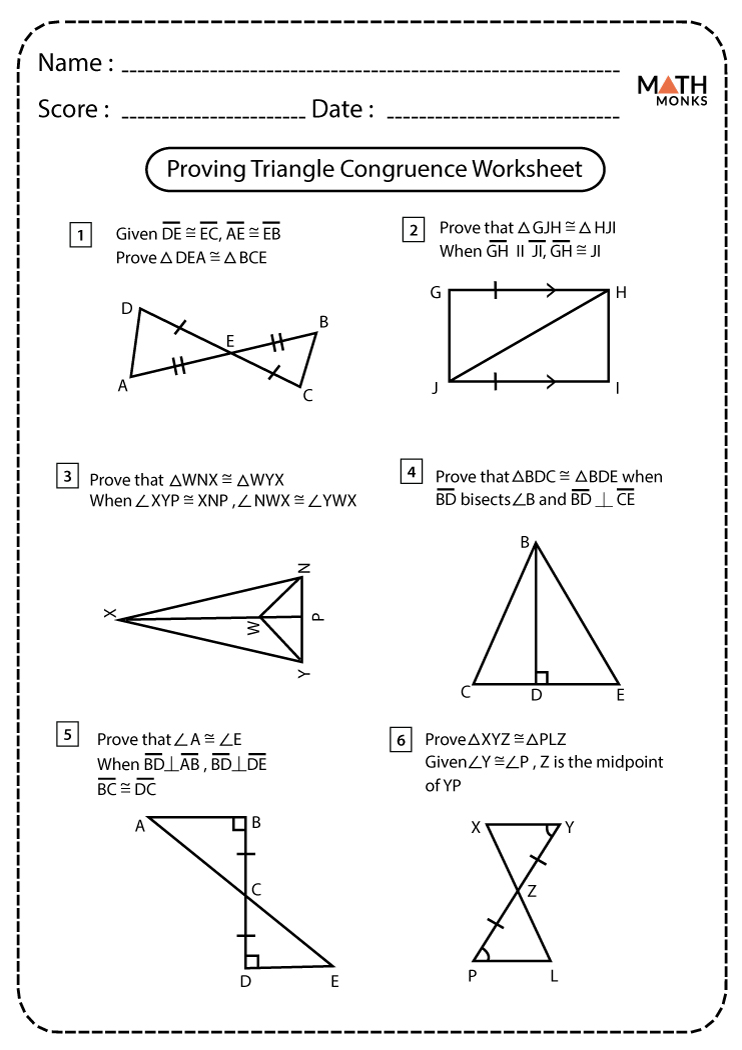
Congruent Triangles: Understanding the Concept

In geometry, congruent triangles refer to triangles that have the same size and shape. This means that corresponding angles and sides of congruent triangles are equal. The concept of congruence is crucial in various geometric proofs and theorems, including the construction of similar triangles and the calculation of area and perimeter. To determine if two triangles are congruent, we can use several theorems, such as SSS (Side-Side-Side), SAS (Side-Angle-Side), ASA (Angle-Side-Angle), and AAS (Angle-Angle-Side).
SSS Congruence Theorem
The SSS congruence theorem states that if three sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding three sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. This theorem is often used in real-world applications, such as architecture and engineering, where precise measurements are essential. For instance, when constructing a building, architects need to ensure that the triangles formed by the building’s framework are congruent to guarantee stability and symmetry.
SAS Congruence Theorem

The SAS congruence theorem asserts that if two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. This theorem is particularly useful when dealing with right triangles, as it allows us to determine congruence based on the lengths of the legs and the hypotenuse. For example, in a right triangle with legs of length 3 and 4, and a hypotenuse of length 5, we can use the SAS theorem to show that another triangle with the same measurements is congruent.
ASA and AAS Congruence Theorems

The ASA and AAS congruence theorems are similar to the SAS theorem but involve different combinations of angles and sides. The ASA theorem states that if two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two angles and the included side of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. The AAS theorem, on the other hand, asserts that if two angles and a non-included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two angles and a non-included side of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. These theorems are essential in proving the congruence of triangles in various geometric contexts.
Example Problems and Solutions

Here are some example problems and solutions to illustrate the application of congruence theorems: * Problem 1: Determine if the triangles ABC and DEF are congruent, given that AB = DE = 5, BC = EF = 6, and AC = DF = 7. * Solution: Since the three sides of triangle ABC are equal to the corresponding three sides of triangle DEF, we can apply the SSS congruence theorem to conclude that the two triangles are congruent. * Problem 2: Show that the triangles GHI and JKL are congruent, given that GH = JK = 4, HI = KL = 5, and angle GHI = angle JKL = 60°. * Solution: Since two sides and the included angle of triangle GHI are equal to the corresponding two sides and the included angle of triangle JKL, we can apply the SAS congruence theorem to conclude that the two triangles are congruent.
Worksheet Answers
Here are the answers to a sample congruent triangles worksheet:
| Problem Number | Given Information | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AB = DE = 3, BC = EF = 4, AC = DF = 5 | Triangles ABC and DEF are congruent by SSS |
| 2 | GH = JK = 6, HI = KL = 8, angle GHI = angle JKL = 45° | Triangles GHI and JKL are congruent by SAS |
| 3 | angle ABC = angle DEF = 60°, AB = DE = 5, BC = EF = 6 | Triangles ABC and DEF are congruent by ASA |

📝 Note: When solving congruent triangle problems, it is essential to carefully examine the given information and apply the appropriate congruence theorem to determine the conclusion.
In summary, understanding congruent triangles is vital in geometry, and applying the various congruence theorems, such as SSS, SAS, ASA, and AAS, allows us to determine the congruence of triangles in different contexts. By practicing with example problems and worksheets, students can develop a deeper understanding of this fundamental concept in geometry.
What is the difference between congruent and similar triangles?

+
Congruent triangles have the same size and shape, while similar triangles have the same shape but not necessarily the same size.
How do I determine if two triangles are congruent using the SSS theorem?

+
To determine if two triangles are congruent using the SSS theorem, you need to show that the three sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding three sides of the other triangle.
Can I use the SAS theorem to prove that two right triangles are congruent?

+
Yes, you can use the SAS theorem to prove that two right triangles are congruent by showing that the two legs and the hypotenuse of one triangle are equal to the corresponding two legs and hypotenuse of the other triangle.