5 Proofs for Congruent Triangles
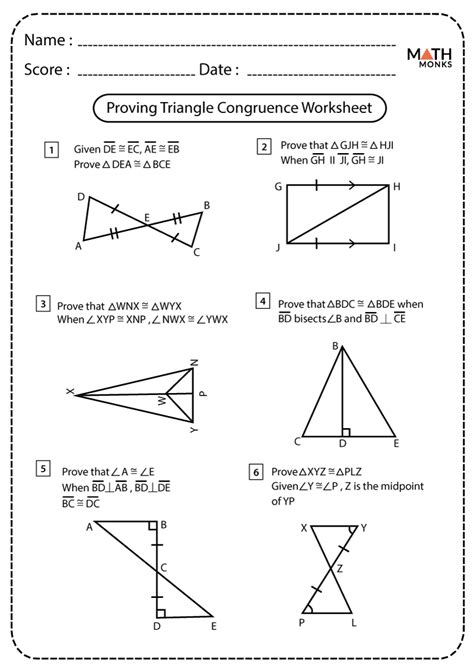
Understanding Congruent Triangles

In geometry, two triangles are said to be congruent if their corresponding sides and angles are equal. This concept is crucial in various mathematical and real-world applications, such as solving equations, finding unknown lengths, and calculating areas. In this article, we will delve into the five proofs for congruent triangles, which are essential for establishing the congruence of two triangles.
The Five Proofs for Conguent Triangles
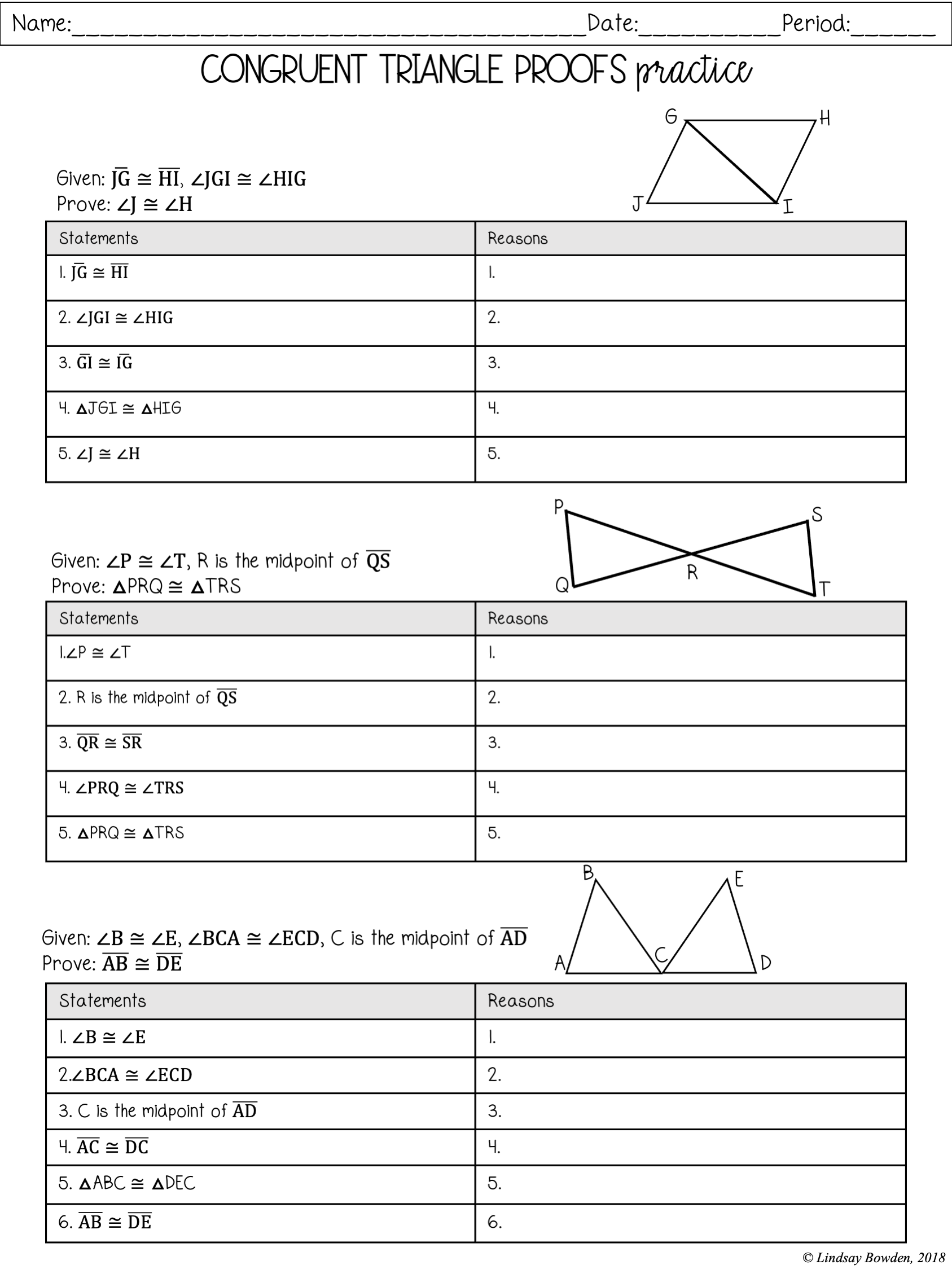
There are five fundamental proofs for congruent triangles, each providing a unique way to determine whether two triangles are congruent. These proofs are:
- Side-Side-Side (SSS)
- Side-Angle-Side (SAS)
- Angle-Side-Angle (ASA)
- Angle-Angle-Side (AAS)
- Hypotenuse-Leg (HL)
Let’s explore each of these proofs in detail:
Side-Side-Side (SSS) Proof

The SSS proof states that if three sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent. This proof is straightforward and can be applied to any triangle.
SSS Proof Example:
| Triangle A | Triangle B |
|---|---|
| AB = 5 cm | DE = 5 cm |
| BC = 7 cm | EF = 7 cm |
| AC = 9 cm | DF = 9 cm |

Since the corresponding sides of Triangle A and Triangle B are equal, we can conclude that Triangle A is congruent to Triangle B.
Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Proof

The SAS proof states that if two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides and angle of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
SAS Proof Example:
| Triangle A | Triangle B |
|---|---|
| AB = 5 cm | DE = 5 cm |
| ∠ABC = 60° | ∠DEF = 60° |
| BC = 7 cm | EF = 7 cm |
Since the two sides and included angle of Triangle A are equal to the corresponding sides and angle of Triangle B, we can conclude that Triangle A is congruent to Triangle B.
Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) Proof

The ASA proof states that if two angles and the included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding angles and side of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
ASA Proof Example:
| Triangle A | Triangle B |
|---|---|
| ∠ABC = 60° | ∠DEF = 60° |
| AB = 5 cm | DE = 5 cm |
| ∠ACB = 80° | ∠DFE = 80° |
Since the two angles and included side of Triangle A are equal to the corresponding angles and side of Triangle B, we can conclude that Triangle A is congruent to Triangle B.
Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) Proof
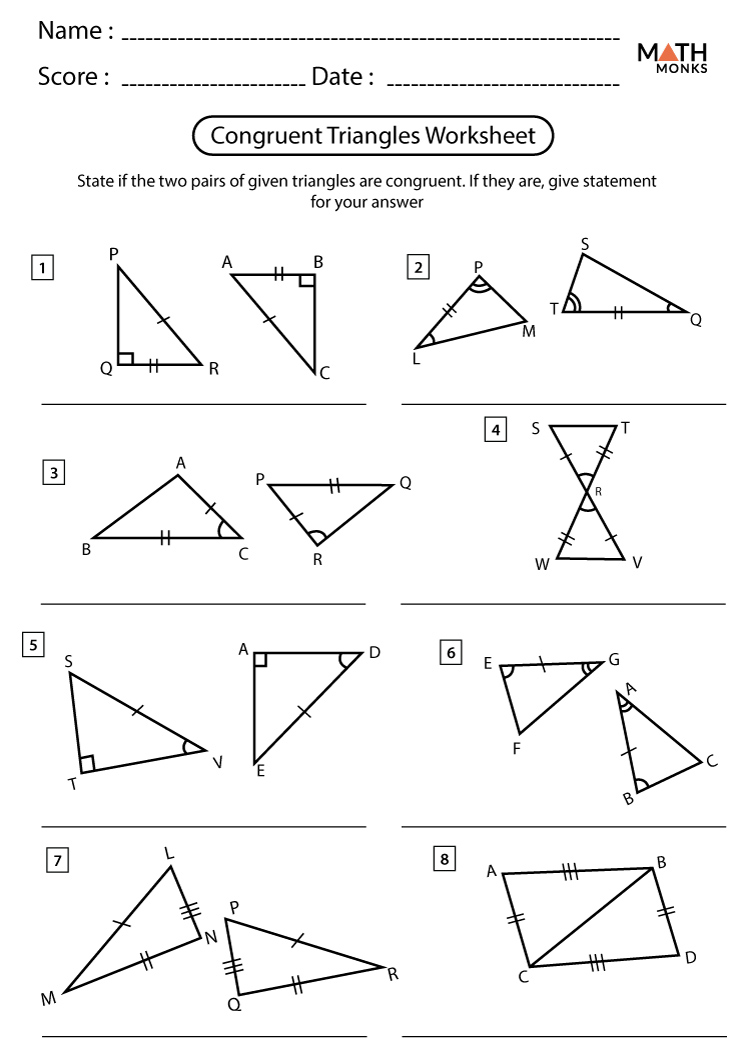
The AAS proof states that if two angles and a non-included side of one triangle are equal to the corresponding angles and side of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
AAS Proof Example:
| Triangle A | Triangle B |
|---|---|
| ∠ABC = 60° | ∠DEF = 60° |
| ∠ACB = 80° | ∠DFE = 80° |
| BC = 7 cm | EF = 7 cm |
Since the two angles and non-included side of Triangle A are equal to the corresponding angles and side of Triangle B, we can conclude that Triangle A is congruent to Triangle B.
Hypotenuse-Leg (HL) Proof

The HL proof states that if the hypotenuse and a leg of one right triangle are equal to the corresponding hypotenuse and leg of another right triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
HL Proof Example:
| Triangle A | Triangle B |
|---|---|
| AB = 5 cm (hypotenuse) | DE = 5 cm (hypotenuse) |
| BC = 7 cm (leg) | EF = 7 cm (leg) |
Since the hypotenuse and leg of Triangle A are equal to the corresponding hypotenuse and leg of Triangle B, we can conclude that Triangle A is congruent to Triangle B.
In conclusion, the five proofs for congruent triangles provide a comprehensive framework for establishing the congruence of two triangles. By applying these proofs, we can determine whether two triangles are congruent and solve various mathematical and real-world problems.
Now, let’s consider some important notes related to congruent triangles:
📝 Note: It's essential to ensure that the corresponding parts of the triangles are equal and that the triangles are not degenerate (i.e., they have a non-zero area).
What is the main difference between SSS and SAS proofs?
+
The main difference between SSS and SAS proofs is that SSS requires three equal sides, while SAS requires two equal sides and the included angle.
Can AAS proof be applied to any triangle?

+
No, AAS proof can only be applied to triangles where the two angles and non-included side are equal.
What is the significance of HL proof in right triangles?

+
HL proof is essential in right triangles as it allows us to establish congruence using the hypotenuse and a leg, which is particularly useful in trigonometric applications.
Related Terms:
- Congruent triangle proofs worksheet pdf
- Congruent triangle proofs worksheet answers
- proving triangles congruent worksheet kuta
- proving right triangles congruent worksheet
- triangle congruence practice worksheet pdf
- congruent triangles worksheet with answers