Combine Supply and Demand Worksheet Easily

The intersection of supply and demand forms the crux of economic theory, where business decisions, market prices, and economic trends are determined. Understanding how these concepts interact is key for students, professionals, and enthusiasts in the world of economics. This blog post will guide you through how to combine supply and demand worksheet elements effectively to analyze market equilibrium and its implications.
Understanding Supply and Demand

Before diving into combining supply and demand on a worksheet, it's essential to grasp their basic definitions:
- Supply refers to how much the market can offer. It depends on several factors, including resource costs, production capacity, and market expectations.
- Demand is the consumer's desire and willingness to pay for a good or service. It's influenced by income, tastes, expectations, and the number of potential buyers.
These two forces operate on a plane of interaction which we can visualize with a supply and demand curve. When supply or demand changes, the curves shift, and so does the market equilibrium.
Steps to Combine Supply and Demand on a Worksheet
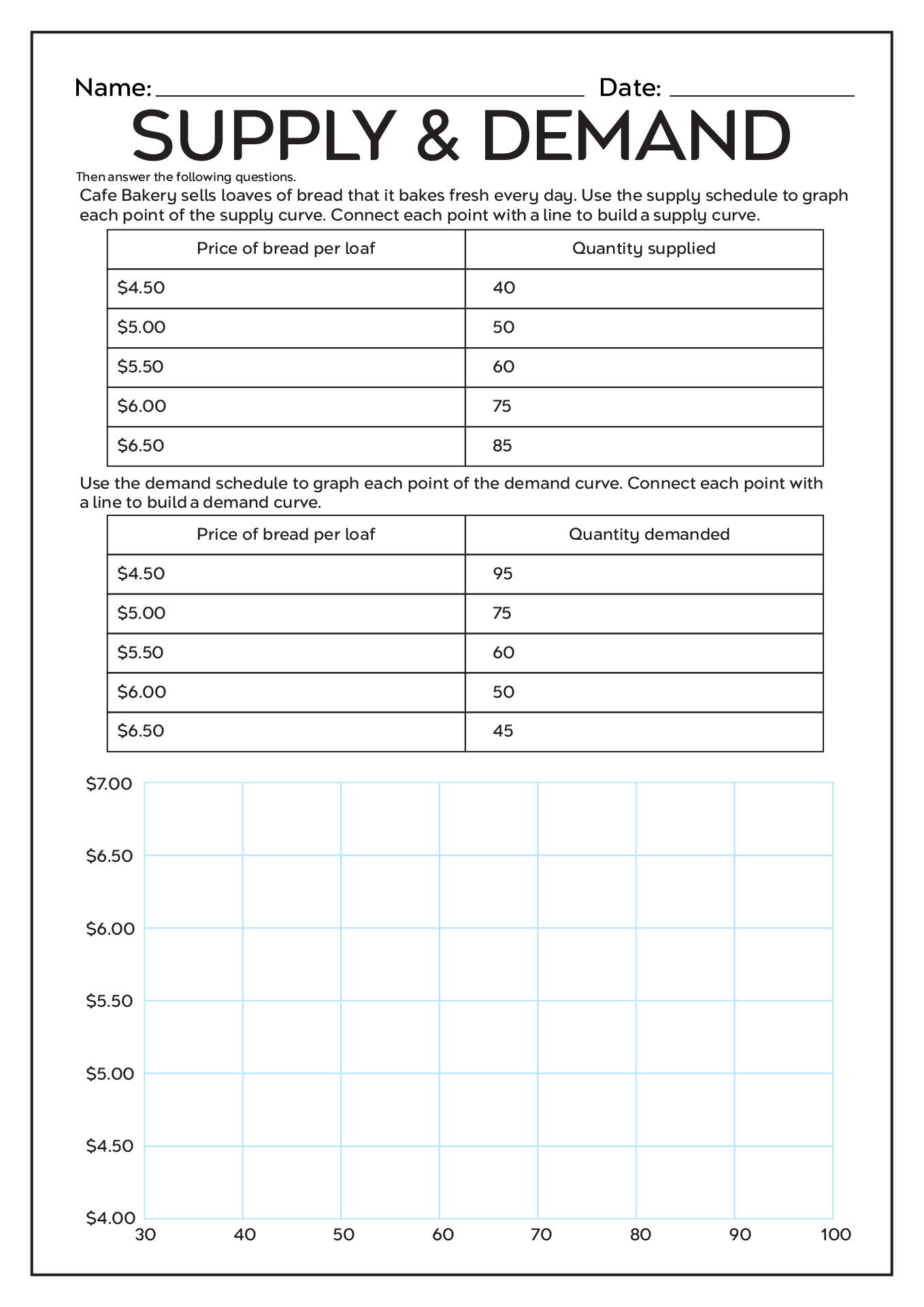
Here's how you can effectively analyze these dynamics on a worksheet:
1. Set Up Your Worksheet

Start with a blank spreadsheet or worksheet. Here’s what your setup should include:
- Columns for price, quantity supplied, and quantity demanded.
- Rows for each price point where you’ll calculate quantities.
Here is a simple example of how your worksheet might look:
| Price | Quantity Supplied | Quantity Demanded |
|---|---|---|
| 5</td><td>25</td><td>75</td></tr> <tr><td>10 | 50 | 50 |
| $15 | 75 | 25 |

2. Plot the Supply Curve
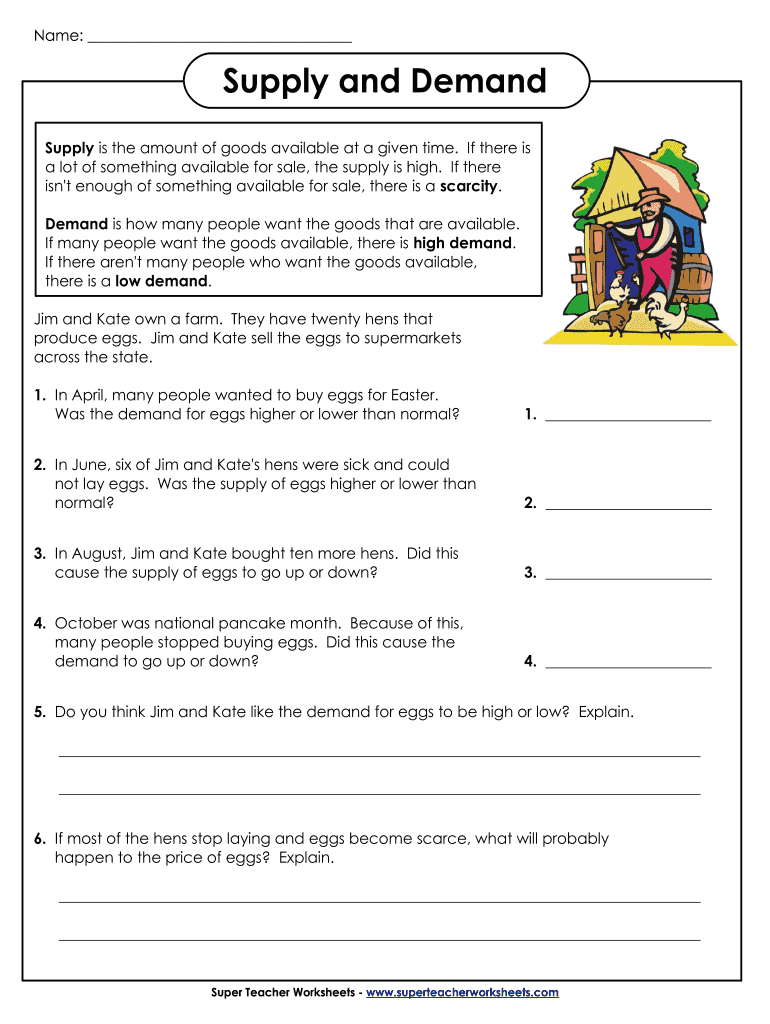
The supply curve typically slopes upward, indicating that as price increases, the quantity supplied also increases. Using your worksheet, plot points where the price on the y-axis corresponds with the quantity supplied on the x-axis.
- Connect the points with a line or a curve to form your supply line.
✏️ Note: Make sure your supply points are in ascending order of price from left to right for a positive slope.
3. Plot the Demand Curve
Conversely, the demand curve slopes downward. Higher prices deter potential buyers, reducing the quantity demanded.
- Plot the demand points on your worksheet.
- Connect these points to form the demand curve.
4. Determine the Market Equilibrium

The market equilibrium is where the supply and demand curves intersect, indicating where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.
- Identify this point on your worksheet.
- Highlight this equilibrium point as it’s crucial for your analysis.
5. Analyze Changes in Supply and Demand

When external factors cause shifts in either the supply or demand curve:
- Adjust your plotted curves accordingly. For instance, an increase in demand would shift the demand curve to the right.
- Re-calculate the equilibrium, noting changes in price and quantity.
6. Label and Annotate
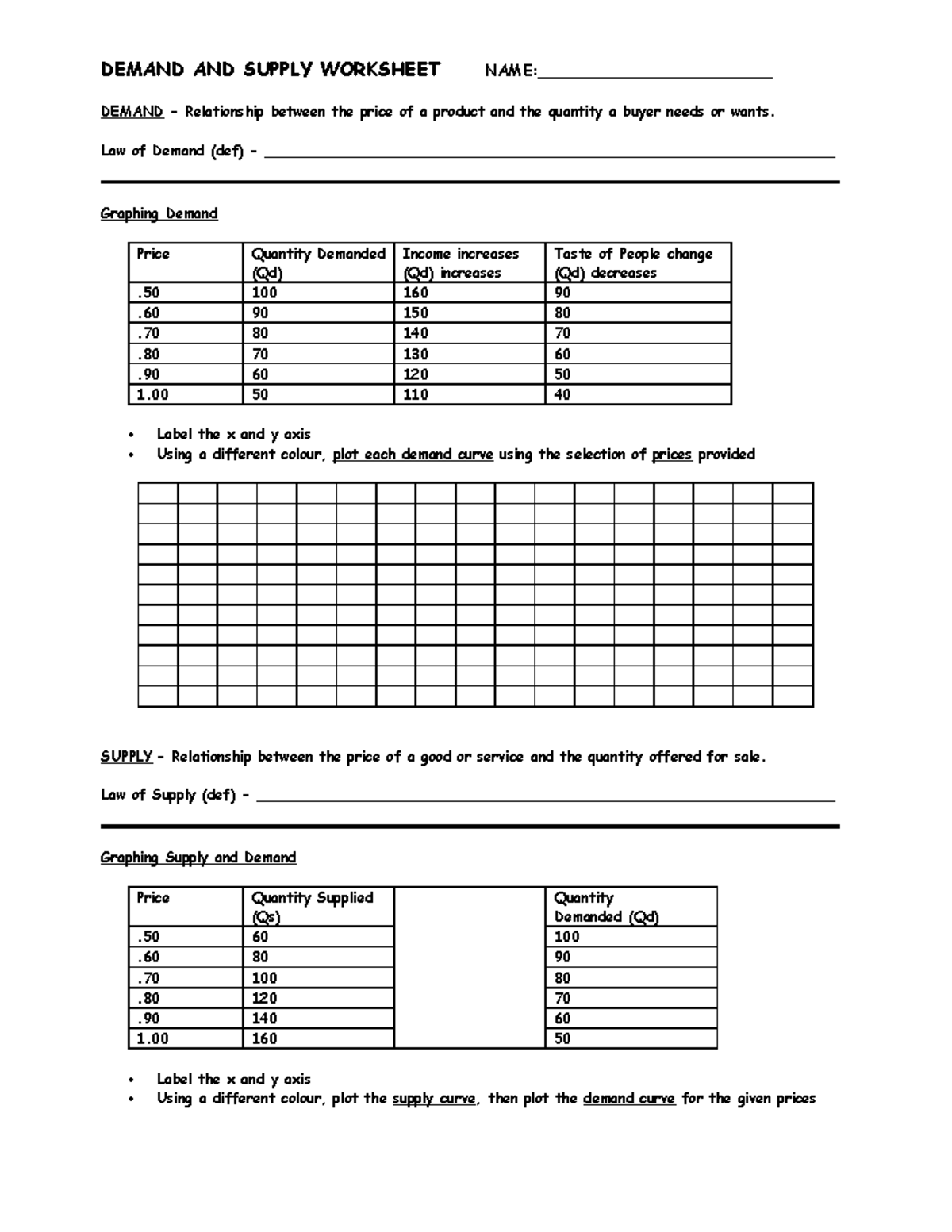
Proper labeling enhances understanding:
- Label your axes, supply and demand curves, and equilibrium point.
- Use notes or callouts to explain specific scenarios, like shifts due to government taxes or subsidies.
By following these steps, your worksheet will provide a clear, visual representation of how supply and demand interact, making it easier to analyze market conditions, assess policy impacts, or understand the effects of various market interventions.
In conclusion, combining supply and demand on a worksheet offers a practical approach to understanding market dynamics. This analysis helps in making informed decisions in both academic and real-world economic scenarios. Whether you're studying for an exam, setting up a business plan, or analyzing current market trends, mastering this technique can provide invaluable insights into how economic forces shape the world around us.
Why is the supply curve upward sloping?

+
The supply curve slopes upward because producers are willing to supply more goods or services at higher prices due to increased profitability. It also reflects the law of supply, which states that the quantity of a good supplied increases as the price rises and decreases as the price falls, all else being equal.
Can the supply and demand model apply to services?

+
Yes, the principles of supply and demand apply to services just as they do to physical goods. The supply of services can be influenced by factors like labor availability and cost, while demand is driven by consumer needs, competition, and economic conditions.
How do taxes affect the supply and demand model?

+
Taxes can shift the supply curve leftward, reducing the quantity supplied at every price because the cost of production increases. This leads to a higher market price and a lower equilibrium quantity. In some cases, taxes might also shift the demand curve, depending on who the tax is levied on.