Combined Gas Law Worksheet 1 Answer Key Revealed

In the realm of chemistry and physics, understanding gas laws is fundamental for anyone delving into the behavior of gases under different conditions. Among the various laws, the Combined Gas Law stands as a critical formula merging Boyle's Law, Charles's Law, and Gay-Lussac's Law. It explains how the pressure, volume, and temperature of a gas interact with each other. This comprehensive guide offers insights into the Combined Gas Law with a detailed exploration of the Worksheet 1 Answer Key, aimed at students and enthusiasts looking to master this concept.
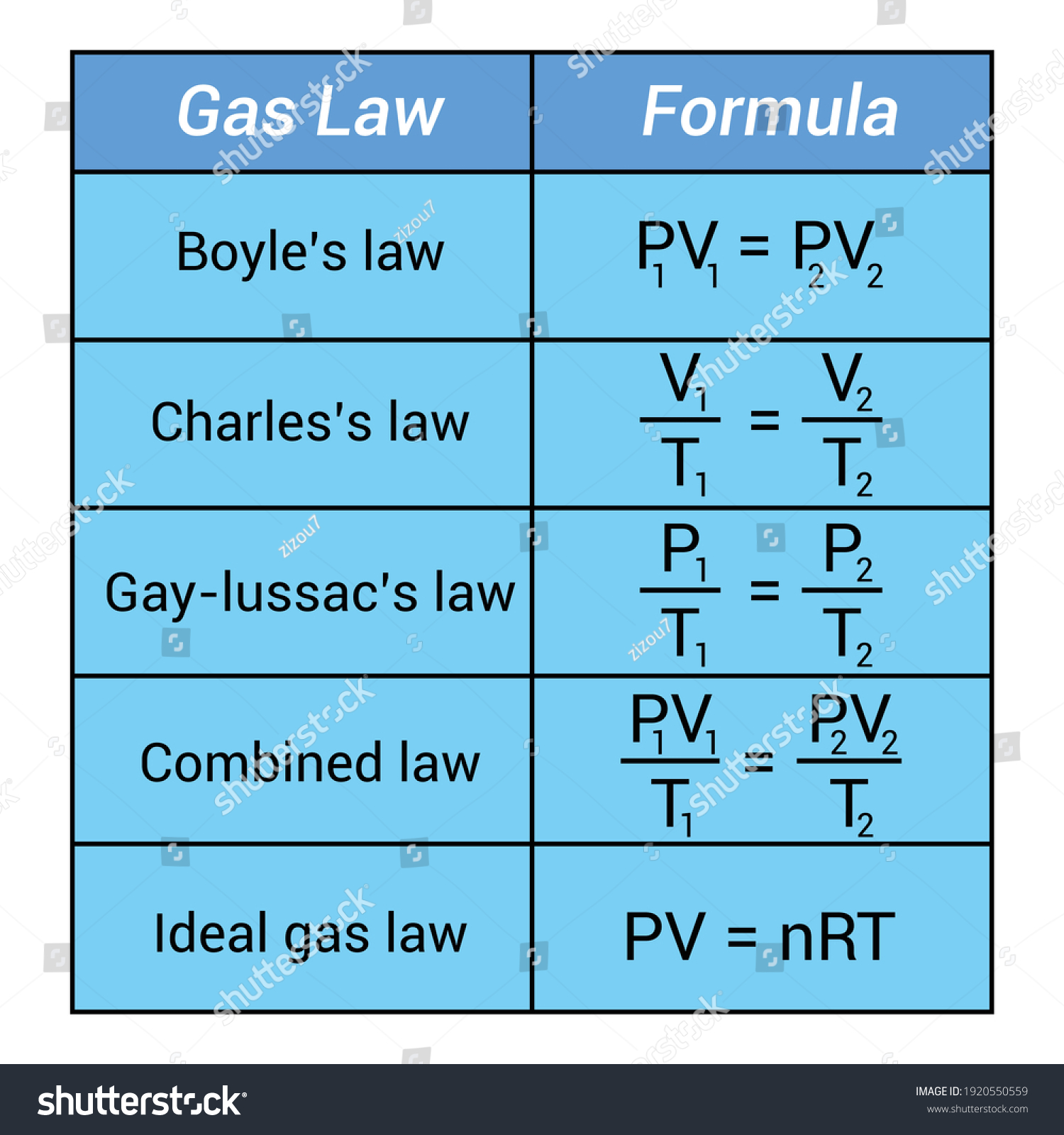
Understanding the Combined Gas Law

Before we dive into the specifics of the worksheet, let's clarify what the Combined Gas Law is. The formula is:
[ \frac{P_1 \times V_1}{T_1} = \frac{P_2 \times V_2}{T_2} ]
Where:
- P_1 and V_1 are the initial pressure and volume,
- T_1 is the initial temperature in Kelvin,
- P_2 and V_2 are the final pressure and volume, and
- T_2 is the final temperature in Kelvin.
This law essentially combines three gas laws by describing how the product of pressure and volume of a gas divided by its temperature remains constant if the amount of gas remains unchanged.
Applying the Combined Gas Law

Here's how we can apply this formula:
- Determine Initial Conditions: You'll start with given initial values for pressure, volume, and temperature.
- Find Unknown Variables: Using the formula, you can calculate any one of the final conditions if the other three are known.
- Units Conversion: Ensure that all units are consistent, especially converting temperature to Kelvin.
🔍 Note: Kelvin temperature is essential in gas law equations as it starts from absolute zero, which is the lowest possible temperature where molecular motion theoretically stops.
Dissecting Combined Gas Law Worksheet 1 Answer Key

Problem 1: Pressure and Volume Change

The first problem often deals with a scenario where the temperature remains constant but both pressure and volume change. Here's an example:
| Initial Conditions | Final Conditions |
|---|---|
| P_1 = 3.0 \, \text{atm} | P_2 = ? |
| V_1 = 2.5 \, \text{L} | V_2 = 1.0 \, \text{L} |
| T_1 = 298 \, \text{K} | T_2 = 298 \, \text{K} |

Since T_1 = T_2 , we can simplify the equation to:
[ P_1 V_1 = P_2 V_2 ]
Substituting the known values:
[ (3.0 \, \text{atm})(2.5 \, \text{L}) = P_2 (1.0 \, \text{L}) ]
Solving for P_2 :
[ P_2 = \frac{7.5 \, \text{atm-L}}{1.0 \, \text{L}} = 7.5 \, \text{atm} ]
✅ Note: In this case, the pressure must increase to compensate for the decrease in volume when temperature remains constant, adhering to Boyle's Law.
Problem 2: Temperature and Volume Change
Here, we examine a scenario where pressure remains constant while both temperature and volume change. This is typical of Charles's Law conditions:
| Initial Conditions | Final Conditions |
|---|---|
| P_1 = 2.0 \, \text{atm} | P_2 = 2.0 \, \text{atm} |
| V_1 = 1.5 \, \text{L} | V_2 = ? |
| T_1 = 273 \, \text{K} | T_2 = 313 \, \text{K} |
Since P_1 = P_2 , the equation simplifies to:
[ \frac{V_1}{T_1} = \frac{V_2}{T_2} ]
Substituting the known values:
[ \frac{1.5 \, \text{L}}{273 \, \text{K}} = \frac{V_2}{313 \, \text{K}} ]
Solving for V_2 :
[ V_2 = \frac{1.5 \, \text{L} \times 313 \, \text{K}}{273 \, \text{K}} \approx 1.72 \, \text{L} ]
🔥 Note: The volume increases proportionally with the temperature when pressure is constant, as per Charles's Law.
Problem 3: All Variables Change

This problem showcases a true combined gas law scenario where all variables change:
| Initial Conditions | Final Conditions |
|---|---|
| P_1 = 1.0 \, \text{atm} | P_2 = 1.5 \, \text{atm} |
| V_1 = 3.0 \, \text{L} | V_2 = 2.0 \, \text{L} |
| T_1 = 300 \, \text{K} | T_2 = ? |
Using the full Combined Gas Law:
[ \frac{(1.0 \, \text{atm})(3.0 \, \text{L})}{300 \, \text{K}} = \frac{(1.5 \, \text{atm})(2.0 \, \text{L})}{T_2} ]
Solving for T_2 :
[ T_2 = \frac{(1.5 \, \text{atm} \times 2.0 \, \text{L}) \times 300 \, \text{K}}{1.0 \, \text{atm} \times 3.0 \, \text{L}} \approx 300 \, \text{K} ]
💡 Note: Here, the increase in pressure and decrease in volume result in no net change in temperature, illustrating the balance that can occur under combined gas law conditions.
Real-World Applications of the Combined Gas Law

The Combined Gas Law isn't just a theoretical concept; it has practical implications:
- Scuba Diving: Divers need to understand how the pressure of the gas in their tanks changes with depth to avoid decompression sickness.
- Weather Balloons: Weather balloons expand as they rise and the atmospheric pressure decreases, making it essential to apply the combined gas law for accurate predictions.
- Engine Performance: Automotive engineers consider gas laws when designing engines, especially turbochargers and superchargers.
In essence, the Combined Gas Law provides a comprehensive understanding of gas behavior, which is crucial for fields ranging from meteorology to engineering. The calculations you've explored here are fundamental in grasping how gases behave under varying conditions.
Why is the Combined Gas Law useful in chemistry?

+
The Combined Gas Law is useful because it integrates the three primary gas laws into one formula, allowing chemists to predict how changes in pressure, volume, and temperature affect a gas’s behavior. This understanding is critical for experimental setups, industrial applications, and in designing systems that involve gases.
How do you handle changes in units when using the Combined Gas Law?

+
Ensure all units are consistent before applying the Combined Gas Law. Use standard units for pressure (like atmospheres or Pascals), volume (liters or cubic meters), and temperature (always in Kelvin). Convert any Celsius readings to Kelvin by adding 273.15.
Can the Combined Gas Law be applied to gases that are not ideal?

+
While the Combined Gas Law assumes ideal gas behavior, it can still provide a reasonable approximation for real gases at relatively low pressures and high temperatures where their behavior approaches that of an ideal gas. For more accurate predictions with real gases, corrections like the Van der Waals equation are used.
