Combat Jobs in the Army: Roles for the Fearless

Combat Jobs in the Army: Roles for the Fearless

The Army is a massive organization with a wide range of career paths, but for those who crave action and are not afraid of danger, combat jobs are the ultimate choice. These roles require courage, strength, and a strong sense of duty, as they involve direct engagement with enemy forces. In this article, we will explore some of the most thrilling combat jobs in the Army, what they entail, and the skills required to excel in these positions.
Infantryman (11X)

Infantrymen are the backbone of the Army’s combat force. They are trained to engage the enemy in close combat, using a variety of weapons, including rifles, machine guns, and grenades. Infantrymen must be physically fit, able to carry heavy loads, and willing to work in extreme environments.
Key Responsibilities:
- Conducting patrols and reconnaissance missions
- Engaging enemy forces in combat
- Operating and maintaining infantry equipment
- Participating in urban and terrain operations
Armor Crewman (19K)
Armor crewmen operate and maintain tanks, armored personnel carriers, and other combat vehicles. They must be skilled in both gunnery and mechanical maintenance, as well as able to work effectively in a team environment.
Key Responsibilities:
- Operating and maintaining armor vehicles
- Conducting gunnery operations
- Participating in combat maneuvers
- Performing routine maintenance and repairs
Artilleryman (13B)

Artillerymen operate and maintain howitzers, cannons, and other artillery equipment. They must be skilled in both gunnery and mathematics, as well as able to work effectively in a team environment.
Key Responsibilities:
- Operating and maintaining artillery equipment
- Conducting fire missions
- Participating in combat maneuvers
- Performing routine maintenance and repairs
Special Forces Operational Detachment-Delta (18D)

Special Forces Operational Detachment-Delta, also known as Delta Force, is an elite counter-terrorism unit. Members of Delta Force must be highly skilled in combat, language, and cultural expertise, as well as able to work effectively in small teams.
Key Responsibilities:
- Conducting counter-terrorism operations
- Participating in hostage rescue missions
- Gathering and analyzing intelligence
- Operating in a variety of environments, including urban and terrain operations
Army Ranger (75th Ranger Regiment)
Army Rangers are an elite light infantry unit. They must be highly skilled in combat, parachuting, and rappelling, as well as able to work effectively in small teams.
Key Responsibilities:
- Conducting airborne and air assault operations
- Participating in combat maneuvers
- Gathering and analyzing intelligence
- Operating in a variety of environments, including urban and terrain operations
💡 Note: These are just a few examples of combat jobs in the Army. There are many other roles available, each with its own unique set of responsibilities and requirements.
Requirements for Combat Jobs
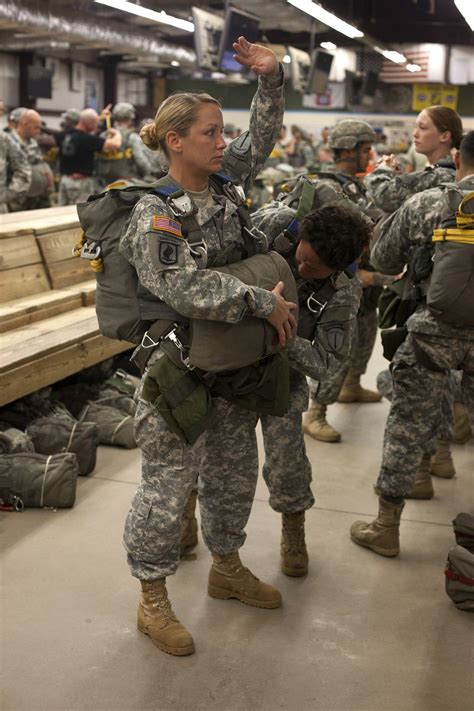

While the specific requirements for each combat job vary, there are some common qualifications that apply across the board. These include:
- Age: Must be between 17 and 35 years old (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Citizenship: Must be a U.S. citizen
- Education: Must have a high school diploma or equivalent
- Physical Fitness: Must meet Army physical fitness standards
- Background: Must undergo a background check and obtain a security clearance
- Training: Must complete Basic Combat Training (BCT) and Advanced Individual Training (AIT) for their specific Military Occupational Specialty (MOS)
Benefits of Combat Jobs

While combat jobs can be challenging and dangerous, they also offer a range of benefits, including:
- Camaraderie: Combat soldiers develop strong bonds with their fellow soldiers, which can last a lifetime.
- Personal Growth: Combat jobs require soldiers to push themselves to their limits, both physically and mentally.
- Skill-Building: Combat soldiers develop a range of skills, including marksmanship, first aid, and leadership.
- Career Advancement: Combat soldiers can advance to leadership positions and specialize in their field.
- Education Benefits: The Army offers education benefits, including tuition assistance and the GI Bill.
Conclusion

Combat jobs in the Army offer a unique combination of challenge, adventure, and personal growth. While they require courage, strength, and a strong sense of duty, they also offer a range of benefits, including camaraderie, skill-building, and career advancement. If you’re considering a career in the Army, a combat job may be the perfect fit for you.
What is the most challenging part of a combat job?

+
The most challenging part of a combat job can vary depending on the individual, but common challenges include the physical and mental demands of combat, the risk of injury or death, and the emotional toll of witnessing traumatic events.
How do I prepare for a combat job?

+
To prepare for a combat job, you should focus on building your physical fitness, learning as much as you can about the Army and your chosen MOS, and developing your mental toughness and resilience.
Can I choose my combat job?
+While you can express a preference for a particular combat job, the Army will ultimately determine your MOS based on your qualifications, the needs of the service, and the availability of positions.
Related Terms:
- Combat MOS meaning
- Army combat MOS list
- Army Roles