5 Ways Calculate Wage

Understanding Wage Calculation Methods

Calculating wages is a crucial aspect of managing a business, as it directly affects the financial well-being of employees and the overall profitability of the company. There are several methods to calculate wages, each with its own set of considerations and implications. In this article, we will explore five common ways to calculate wages, highlighting their characteristics, advantages, and potential drawbacks.
1. Hourly Wage Calculation
The hourly wage calculation is one of the most straightforward methods. It involves multiplying the number of hours worked by the employee’s hourly rate. This method is commonly used in industries where employees work variable hours, such as retail, hospitality, or freelancing. The hourly wage is typically determined by the employer, based on factors like the employee’s experience, qualifications, and the prevailing market rate.
For example, if an employee works 40 hours a week at an hourly rate of 15, their weekly wage would be: 40 hours/week * 15/hour = $600/week
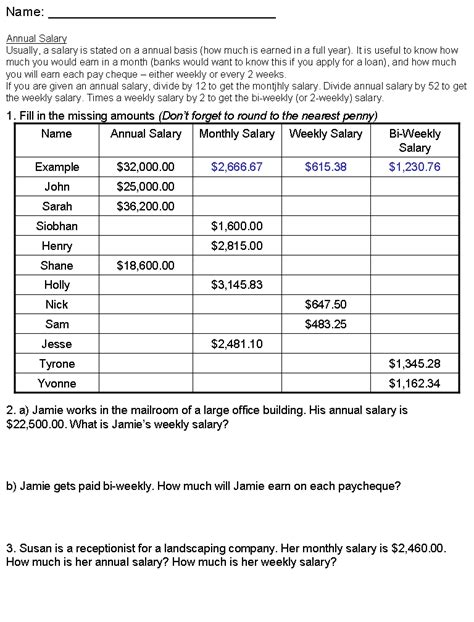
2. Salary Calculation

The salary calculation method involves paying employees a fixed amount of money per year, usually divided into monthly, bi-weekly, or weekly payments. This method is commonly used for full-time employees who work a standard number of hours per week. The annual salary is typically determined by the employer, based on factors like the employee’s experience, qualifications, and job responsibilities.
For example, if an employee has an annual salary of 60,000, their monthly salary would be: 60,000/year ÷ 12 months/year = $5,000/month
3. Piece Rate Calculation

The piece rate calculation method involves paying employees a fixed amount of money for each unit of work completed. This method is commonly used in industries where production is measurable, such as manufacturing or agriculture. The piece rate is typically determined by the employer, based on factors like the complexity of the task, the time required to complete it, and the prevailing market rate.
For example, if an employee is paid 10 per unit of work and completes 50 units in a week, their weekly wage would be: 50 units/week * 10/unit = $500/week
4. Commission-Based Calculation

The commission-based calculation method involves paying employees a percentage of the sales or revenue they generate. This method is commonly used in industries like sales, real estate, or insurance. The commission rate is typically determined by the employer, based on factors like the employee’s experience, qualifications, and the prevailing market rate.
For example, if an employee earns a 10% commission on sales and generates 10,000 in sales in a week, their weekly wage would be: 10,000/week * 10% = $1,000/week
5. Bonus-Based Calculation

The bonus-based calculation method involves paying employees a bonus or incentive payment based on their performance or achievements. This method is commonly used in industries like finance, technology, or consulting. The bonus structure is typically determined by the employer, based on factors like the employee’s performance, the company’s profitability, and the prevailing market rate.
For example, if an employee is eligible for a 20% bonus on their annual salary and earns 60,000 per year, their bonus payment would be: 60,000/year * 20% = $12,000/year
💡 Note: When calculating wages, it's essential to consider factors like taxes, benefits, and other deductions that may affect the employee's take-home pay.
To illustrate the differences between these methods, consider the following table:
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Hourly Wage | Paying employees an hourly rate | 40 hours/week * $15/hour = $600/week |
| Salary | Paying employees a fixed annual salary | $60,000/year ÷ 12 months/year = $5,000/month |
| Piece Rate | Paying employees a fixed amount per unit of work | 50 units/week * $10/unit = $500/week |
| Commission-Based | Paying employees a percentage of sales or revenue | $10,000/week * 10% = $1,000/week |
| Bonus-Based | Paying employees a bonus or incentive payment | $60,000/year * 20% = $12,000/year |

In summary, calculating wages involves considering various factors, including the employee’s experience, qualifications, and job responsibilities, as well as the prevailing market rate and the company’s profitability. By understanding the different methods of calculating wages, employers can ensure that their employees are fairly compensated and that their business remains competitive in the market.
To wrap things up, calculating wages is a critical aspect of managing a business, and there are several methods to choose from. By considering the characteristics, advantages, and potential drawbacks of each method, employers can make informed decisions about how to compensate their employees. Whether it’s hourly wage, salary, piece rate, commission-based, or bonus-based calculation, the key is to find a method that works for both the employee and the employer.
What is the most common method of calculating wages?

+
The most common method of calculating wages is the hourly wage calculation, which involves multiplying the number of hours worked by the employee’s hourly rate.
How do employers determine the hourly rate for employees?

+
Employers typically determine the hourly rate for employees based on factors like the employee’s experience, qualifications, and the prevailing market rate.
What is the difference between a salary and an hourly wage?
+
A salary is a fixed amount of money paid to an employee per year, usually divided into monthly, bi-weekly, or weekly payments, while an hourly wage is a payment made to an employee for each hour worked.