Cold War Timeline Worksheet: Comprehensive Answer Key

Understanding the Cold War: A Comprehensive Timeline

The Cold War was a defining period of the 20th century, marked by political tension between the United States and its allies on one side, and the Soviet Union and its allies on the other. This timeline worksheet provides a detailed look into the key events that shaped this era:
1945: The Beginning of the Cold War

After the defeat of Nazi Germany, tensions between the Allies began to rise:
- Yalta and Potsdam Conferences: Agreements between Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin that would later be points of contention.
- The Division of Germany: With the Allies and Soviets dividing Germany into zones, East Germany became a Soviet satellite state.
💡 Note: The Yalta and Potsdam Conferences established the framework for the post-war world, setting the stage for Cold War tensions.
1947: The Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan

- The Truman Doctrine provided political and economic aid to countries threatened by communism.
- The Marshall Plan aimed to rebuild war-devastated regions, particularly Western Europe.
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
| Truman Doctrine | Aimed to contain Soviet geopolitical expansion with military and economic aid to Greece and Turkey. |
| Marshall Plan | Provided aid to Europe to prevent communism's spread and to stimulate economic recovery. |
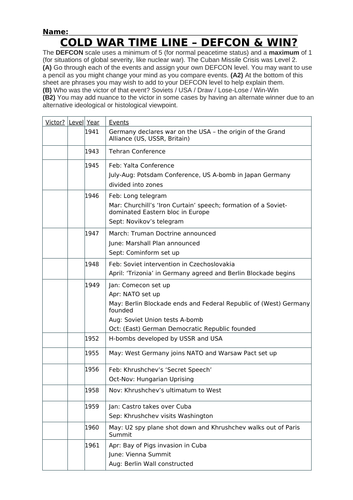
1949-1950: Key Events and Escalations

- NATO was formed as a collective defense against Soviet threats.
- The Soviet Union tested its first atomic bomb, leading to the Arms Race.
- China's fall to communism under Mao Zedong, with Soviet assistance.
- The Korean War started as communist North Korea invaded South Korea.
🚀 Note: The Arms Race was not just about nuclear weapons but also espionage, space race, and advanced military technology development.
1950s-1960s: Height of the Cold War

Key conflicts and events during this period included:
- Korean War (1950-1953): Conflict to contain communism in the Korean Peninsula.
- Cuban Missile Crisis (1962): A near-catastrophic standoff where the world came closest to nuclear war.
- Berlin Wall (1961-1989): A physical symbol of the Iron Curtain dividing the city of Berlin.
1970s-1980s: Detente, Tensions, and the End of the Cold War

During these decades, several developments shifted the dynamics:
- SALT Agreements: Strategic Arms Limitation Talks to curb the arms race.
- Afghan War: Soviet intervention in Afghanistan led to economic strain and international criticism.
- Reagan's Military Buildup and his strategic defense initiative.
- Perestroika and Glasnost: Economic and political reforms in the USSR under Gorbachev.
- The fall of the Berlin Wall and the subsequent disintegration of the Soviet Union.
The Cold War ended not with a bang but through a series of events that reflected the changing internal and external political landscape of the Soviet Union. From detente to the economic reform and transparency, these changes led to the eventual dissolution of the USSR, marking the end of the Cold War.
Throughout this timeline, the Cold War was not just about military or ideological opposition; it influenced culture, sports, technological advancements, and global politics. The legacy of this period continues to shape international relations today.
What were the main causes of the Cold War?

+
The Cold War’s root causes were ideological differences between capitalism and communism, territorial ambitions post-WWII, and mutual distrust and arms race between the USA and the USSR.
How did the Cold War influence global politics?

+
It created a bipolar world, leading to proxy wars, alliances like NATO and the Warsaw Pact, and significant arms races. It also influenced the decolonization process and the rise of non-aligned movements.
Why was the Cuban Missile Crisis significant?

+
It was the closest the world came to nuclear war, highlighting the fragility of the balance of terror between superpowers and leading to improved communication channels like the Moscow-Washington hotline.