Cold War Map Europe 1945: Worksheet Answers Revealed
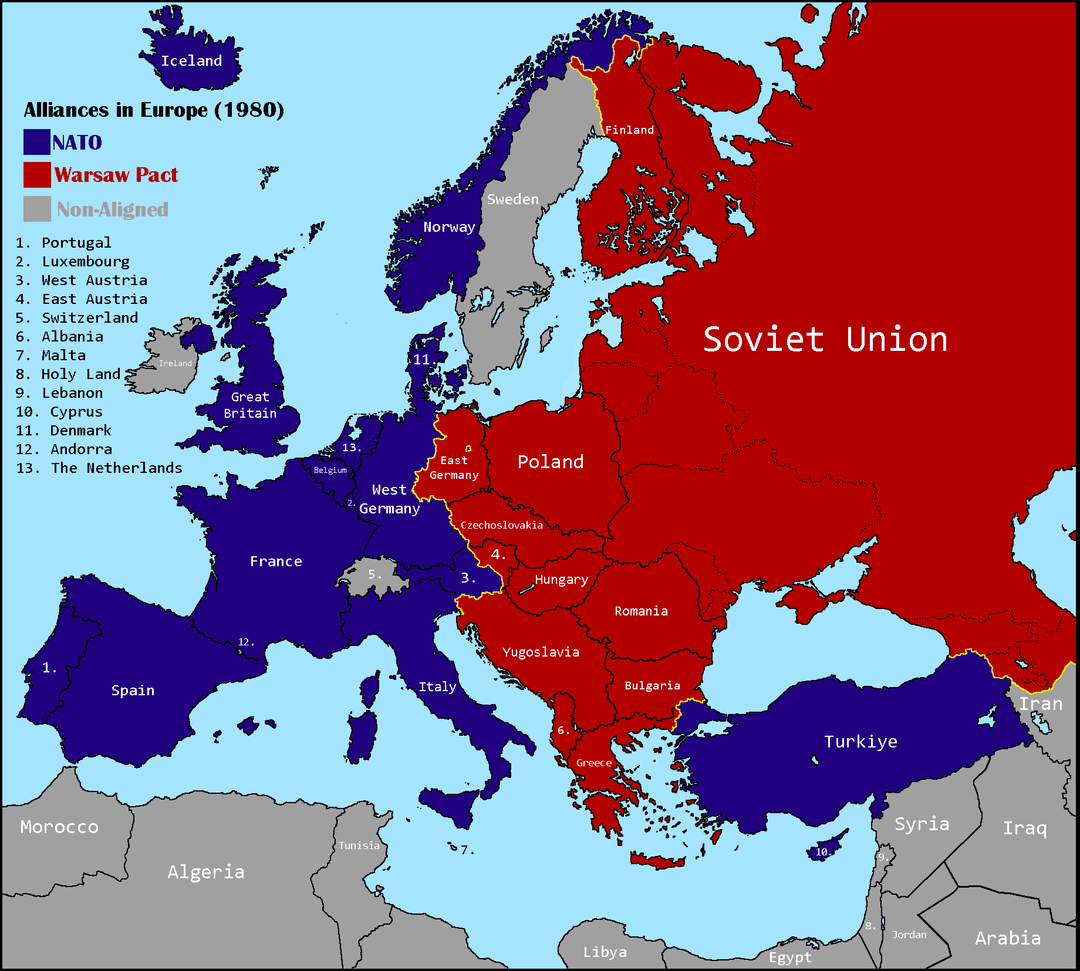
The Cold War was a period of geopolitical tension between the Soviet Union and the United States and their respective allies. The division of Europe into two blocs became visually stark by 1945, as the Yalta and Potsdam Conferences set the stage for the post-World War II landscape. Here, we'll delve into understanding the map of Europe in 1945, which is crucial for comprehending how the Cold War's ideologies and political influences shaped the continent.
Key Features of the Cold War Map of Europe in 1945

When looking at the map of Europe in 1945, several prominent features stand out:
- Iron Curtain: This term, coined by Winston Churchill in 1946, symbolizes the division of Europe into two ideological blocks: The Eastern Bloc under Soviet influence and the Western Bloc allied with the United States and Britain.
- Occupied Germany: Germany was split into four zones controlled by the USA, UK, France, and the USSR. This division was key to understanding the eventual split into West Germany and East Germany.
- Soviet Influence: Eastern European countries including Poland, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria were now under Soviet control, often referred to as the “Communist Buffer States.”
- Western Allies: Countries like Italy, Greece, and parts of Germany were solidified in the Western bloc.
- Neutral Nations: Countries like Switzerland, Sweden, and Austria chose to remain neutral during the Cold War.
Answers to the Cold War Europe Worksheet

If you’ve come across worksheets or quizzes relating to the Cold War map of Europe in 1945, here are some typical questions and their answers:
- What was the Iron Curtain?
The Iron Curtain was an ideological and physical barrier dividing Europe into two blocs, with Eastern Europe under Soviet influence and Western Europe under American and British influence.
📝 Note: While the Iron Curtain is a metaphorical term, it refers to very real borders and boundaries that separated families, cultures, and economies.
- Which country was divided into zones controlled by the Allies?
Germany was divided into four zones after World War II: the American, British, French, and Soviet zones.
- What role did the United Nations play?
The United Nations, although not visible on the map, was a crucial international organization established post-World War II to maintain peace and prevent conflicts like the ones that led to the Cold War.
- Why was Eastern Europe considered a “buffer zone” for the Soviet Union?
Eastern Europe acted as a buffer zone to protect the Soviet Union from any potential attack from the West, given the traumatic memory of Nazi invasions during WWII.
🌍 Note: This buffer strategy also meant Soviet influence and control over the politics and economies of these Eastern European nations.
- Which countries remained neutral?
Switzerland, Sweden, and Austria were among the countries that remained neutral during the Cold War, not aligning strictly with either bloc.
The Ideological Divide

Beyond geography, the map of Cold War Europe also reflected an ideological divide. Here’s how:
- Capitalism vs. Communism: The Western European countries embraced capitalism with varying degrees of social democracy, while the Eastern bloc was firmly under communist rule.
- Economic Systems: The West focused on free-market economics, while the East implemented centrally planned economies.
- Political Systems: Western nations generally were democracies with multi-party systems, whereas Eastern Europe had one-party communist states.
- Human Rights: The Western bloc emphasized individual freedoms, whereas the Eastern bloc was marked by suppression of political dissent and restrictions on freedom of speech and movement.
💡 Note: The ideological conflict wasn't just about communism vs. capitalism; it was also about how these ideologies influenced human rights, freedom, and economic development in both blocs.
The complex interplay of ideologies, military alliances, and political control defined the European landscape of the Cold War era. The division was not only marked on the map but also in the minds and lives of Europeans, each bloc fostering its own identity, defense systems, and diplomatic strategies. This divide influenced global politics, with proxy wars, espionage, and the arms race, making the Cold War map of Europe in 1945 a historical document that captures the beginning of a tension-filled era.
🌐 Note: Understanding this map is pivotal for students of history, as it illustrates the geopolitical chessboard that played out over the following decades.
Cold War Conferences

The Cold War map of Europe in 1945 was a direct result of decisions made at several international conferences:
- Yalta Conference: Held in February 1945, this conference saw Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin agree on the post-war reorganization of Europe.
- Potsdam Conference: Convened in July 1945 after Germany’s surrender, where the Allies decided on the de-Nazification and demilitarization of Germany, further shaping the political landscape.
| Conference | Location | Date | Key Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yalta Conference | Yalta, Crimea | February 1945 | Agreement on German zones of occupation, the United Nations, and Soviet influence in Eastern Europe. |
| Potsdam Conference | Potsdam, Germany | July 1945 | Decisions on German reparations, de-Nazification, and Soviet retention of territories gained from the Red Army. |

Summarizing, the Cold War map of Europe in 1945 showcases the deep ideological, political, and military rifts that emerged post-World War II. The division, symbolized by the Iron Curtain, not only defined the immediate geopolitical landscape but set the stage for decades of tension between the East and West. The enduring legacies of these divisions are still visible in the political and economic structures of contemporary Europe. As we reflect on this era, it's clear that the map was not just a representation of territory but a canvas for one of the most significant standoffs of the 20th century, with lasting implications for global relations, politics, and the very identity of Europe.
What was the primary cause of the division in Europe post-World War II?

+
The primary cause was the ideological conflict between Soviet communism and Western democracy, leading to the formation of the Eastern and Western Blocs.
How did the division of Germany impact the Cold War?
+
The division of Germany into East (communist) and West (capitalist) was a key battleground of the Cold War, symbolizing the broader ideological divide in Europe.
Was neutrality an option for all European countries during the Cold War?

+
Neutrality was an option, but maintaining it required a careful balance. Countries like Austria, Sweden, and Switzerland chose this path, often at the cost of military self-restriction.