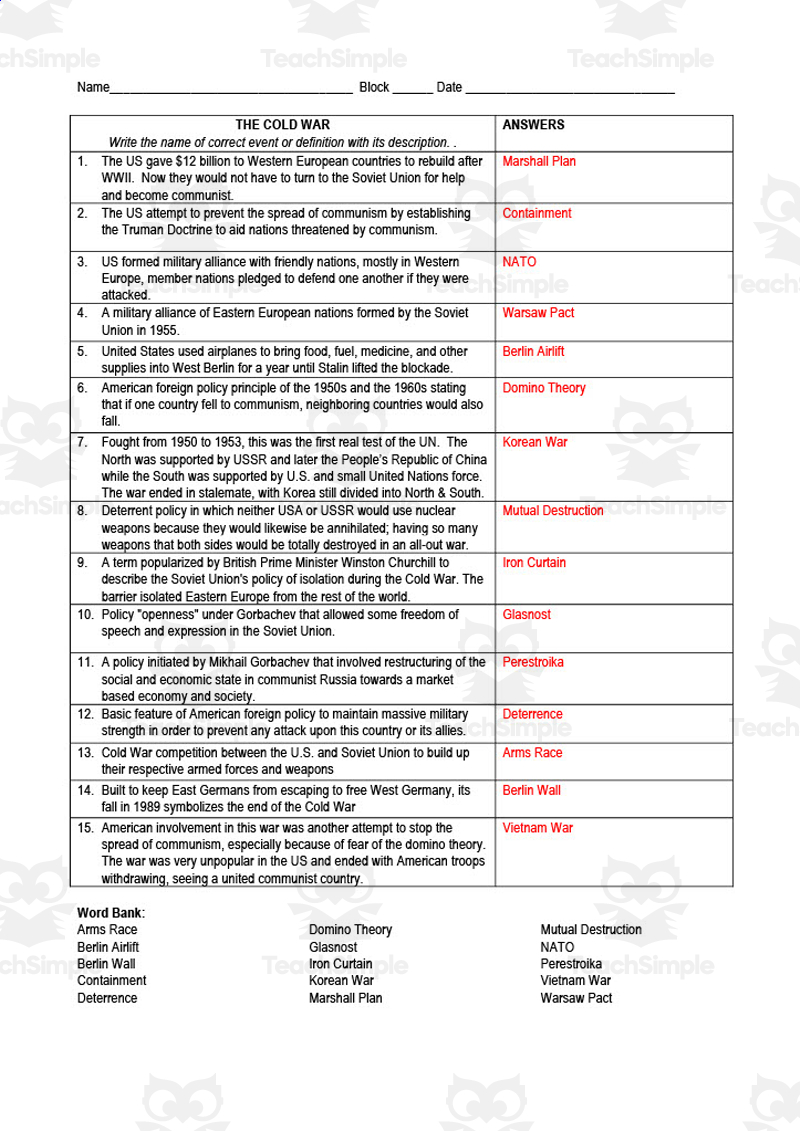
Cold War Worksheet: Key Events and Policy Answers

In this comprehensive guide, we explore some of the most pivotal moments and policy decisions of the Cold War, spanning from the late 1940s to the early 1990s. Understanding these events is crucial for any student or enthusiast of history, as they shaped the geopolitical landscape of the 20th century and continue to influence global relations today.
Formation of NATO


The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was established on April 4, 1949, as a strategic alliance formed by the United States, Canada, and several Western European nations. Its primary goal was to provide collective defense, meaning an attack on one ally was considered an attack on all. Here are the key points about NATO:
- Creation: Formed to counter the Soviet Union's expansion and the rising threat of Communism.
- Members: Initially comprising 12 countries, it has since expanded to 30 member countries.
- Strategic Significance: NATO's formation marked a formal division of Europe into two ideological blocs.
💡 Note: NATO remains one of the most significant military alliances to this day, with its role in global security and stability being a testament to its longevity.
Berlin Blockade and Airlift (1948-1949)


The Berlin Blockade was a Soviet attempt to consolidate control over the entire city of Berlin by blocking Western access to its sectors. Here's how this event unfolded:
- Blockade: The Soviets halted all road, rail, and water traffic into West Berlin.
- Airlift: In response, the Western Allies initiated an airlift, supplying the city with food, fuel, and other necessities.
- Outcome: The blockade was lifted after 11 months, with the Soviets realizing the effort was in vain, and their action had only solidified the Western resolve.
💡 Note: The Berlin Airlift was not just a logistical triumph but also a psychological victory for the West, demonstrating their commitment to fighting Soviet expansionism without escalating to direct military confrontation.
Formation of Warsaw Pact

In response to the formation of NATO, the Soviet Union established the Warsaw Pact on May 14, 1955. Here are the key details:
- Creation: A collective defense treaty among eight communist states in Eastern and Central Europe.
- Members: Initially, it included the Soviet Union, Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland, and Romania.
- Purpose: To counter the perceived threat of NATO, providing mutual defense against any external threats.
💡 Note: Unlike NATO, the Warsaw Pact was heavily influenced by Soviet control, reflecting the power dynamics of the Cold War era.
Korean War (1950-1953)


The Korean War was a significant conflict in the Cold War era, symbolizing the ideological confrontation between the Communist North and the pro-Western South:
- Start: On June 25, 1950, North Korea invaded South Korea with Soviet backing, leading to international intervention.
- UN Involvement: The United Nations Security Council authorized a multinational force to aid South Korea.
- Outcome: The war ended with an armistice on July 27, 1953, establishing a demilitarized zone but leaving the country divided.
Cuban Missile Crisis (1962)


This 13-day standoff was perhaps the most dangerous moment of the Cold War, bringing the world closest to nuclear war:
- Incident: The US discovered Soviet missiles in Cuba, leading to a naval blockade to prevent further installations.
- Resolution: After tense negotiations, Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev agreed to remove the missiles in exchange for a US promise not to invade Cuba.
- Significance: This crisis highlighted the importance of diplomatic communication and led to the establishment of a direct communication line (Hotline) between Moscow and Washington.
💡 Note: The Cuban Missile Crisis led to significant changes in Cold War strategy, emphasizing the need for détente to avoid similar escalations in the future.
The Vietnam War


The Vietnam War was a prolonged conflict with deep roots in the Cold War tensions:
- Background: Vietnam was divided into North (Communist) and South (anti-Communist) after the French defeat in 1954.
- US Involvement: The US supported South Vietnam to prevent the spread of Communism, escalating military involvement in the 1960s.
- End: The war concluded with the fall of Saigon in 1975, unifying Vietnam under Communist rule.
Collapse of the Soviet Union (1985-1991)


The late 1980s to early 1990s marked the end of the Cold War with the dissolution of the Soviet Union:
- Reforms: Mikhail Gorbachev introduced Glasnost (openness) and Perestroika (restructuring) to liberalize the economy and society.
- Economic Strain: These reforms revealed and exacerbated economic problems within the Soviet system.
- Political Changes: Various Soviet republics declared independence, leading to the Soviet Union's dissolution in December 1991.
Throughout this period, the interplay of ideology, military strategy, economic policies, and international relations created a complex web of events that influenced not only the superpowers involved but also the rest of the world. From the formation of NATO and the Warsaw Pact, the Korean and Vietnam Wars, to the Cuban Missile Crisis and the eventual collapse of the Soviet Union, each event was a stepping stone in the narrative of the Cold War. These pivotal moments underscore how the ideological conflict between Communism and Democracy shaped modern history, leaving legacies that continue to inform global politics today.
What was the primary objective of NATO?

+
The primary objective of NATO was collective defense against potential aggression from the Soviet Union and its allies, ensuring security in the North Atlantic region.
Why did the Soviet Union initiate the Berlin Blockade?

+
The Soviet Union aimed to gain control over the entire city of Berlin and to starve out the Western presence by blocking their access routes.
How did the Cuban Missile Crisis end?

+
The crisis ended with the Soviet Union agreeing to remove missiles from Cuba in exchange for a US pledge not to invade Cuba and to remove missiles from Turkey.