5 Key Tips for Acing Your Climograph Worksheet
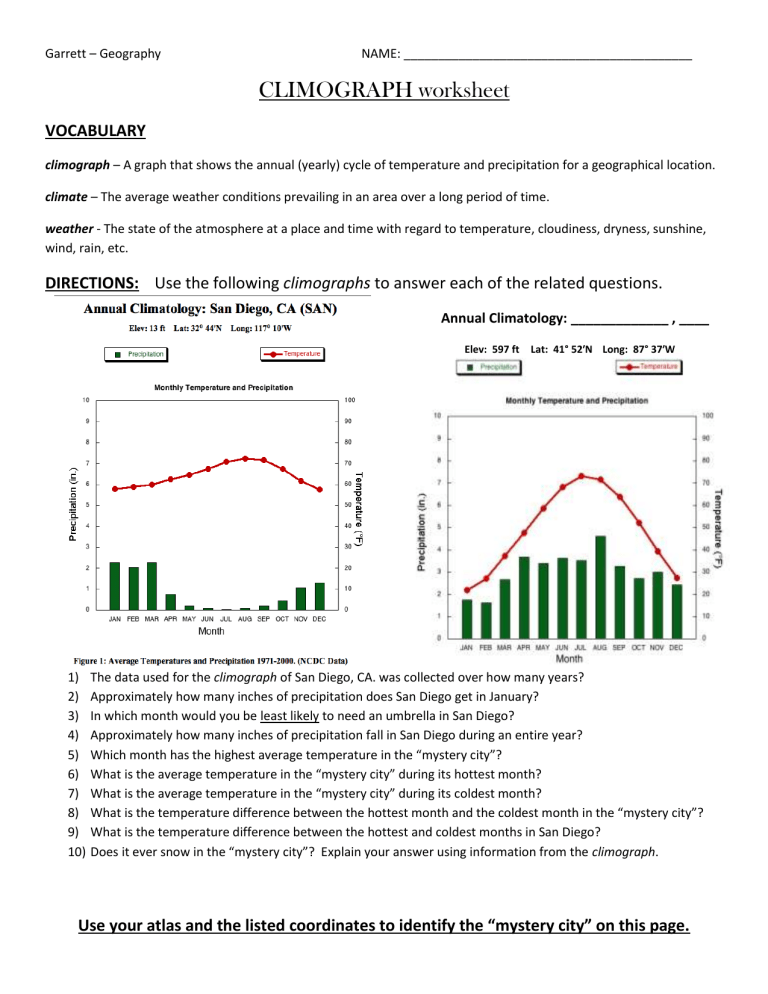
The study of geography often involves visualizing and interpreting data in various forms, with one particularly useful tool being the climograph. A climograph is a graphical representation that combines the monthly average temperature and precipitation data for a given location, enabling students and professionals to understand weather patterns over time. This blog post will walk you through five key tips to help you ace your climograph worksheet, making the task not just manageable but enjoyable.
Understanding the Climograph
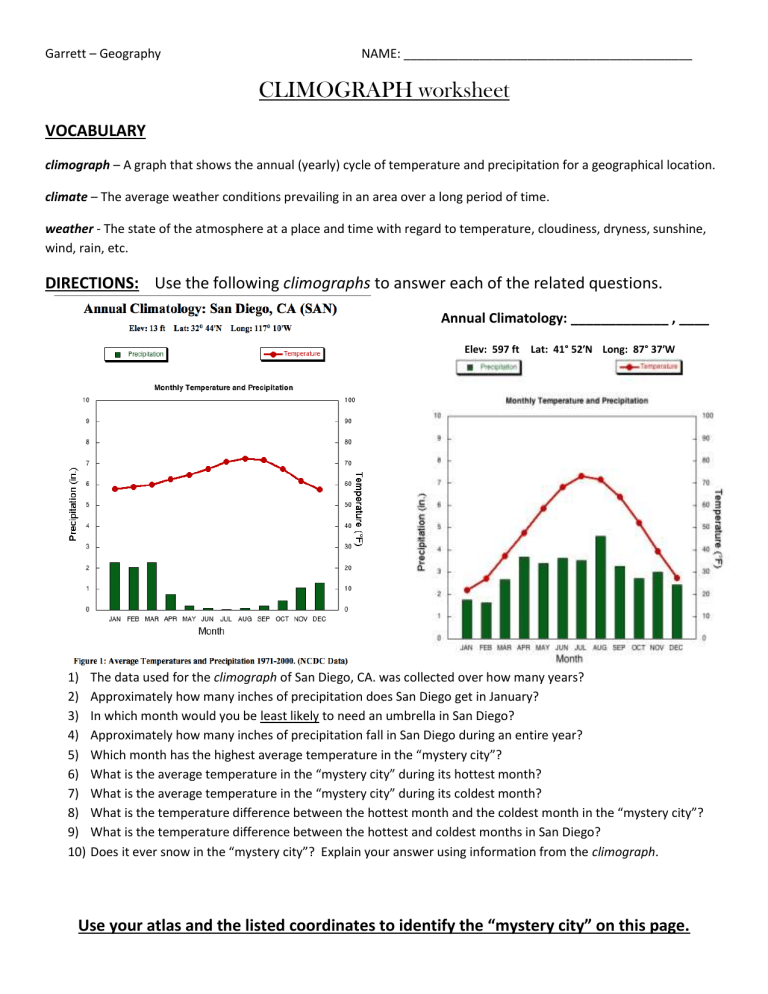
Before diving into how to handle a climograph worksheet, it’s essential to grasp what this tool does:
- Temperature Line: Usually represented by a line graph, it shows the average monthly temperature.
- Precipitation Bar: Each month’s total rainfall is depicted by vertical bars.
🌦️ Note: While the term precipitation includes all forms of moisture from the atmosphere (rain, snow, sleet), for simplicity, we'll refer to it as rainfall.
Tip 1: Read the Scales Correctly
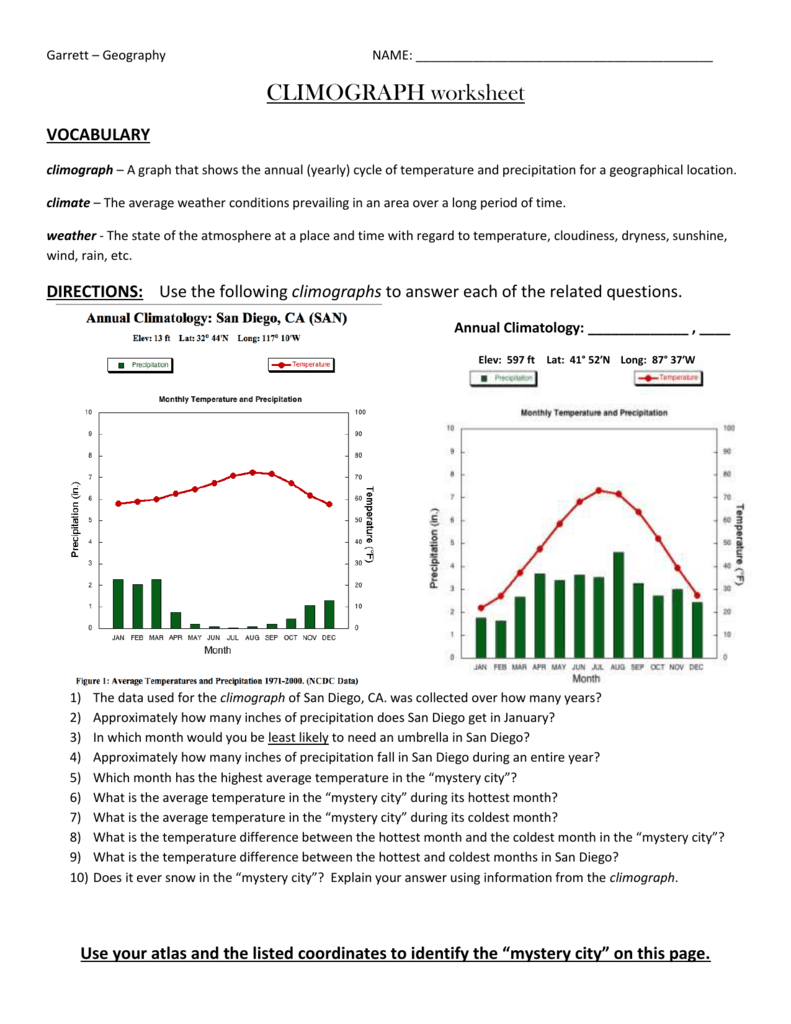
When you look at a climograph, you’ll notice two separate scales:
- One on the left for temperature, often in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F).
- Another on the right or below for precipitation, measured in millimeters (mm) or inches (in).
Getting these scales right is crucial for interpreting data accurately.
📏 Note: Don't be fooled by similar-looking numbers; double-check which axis to use!
Tip 2: Analyze Seasonal Patterns

A climograph isn’t just about plotting data; it’s about understanding seasonal shifts. Here’s what to look for:
- Identify the dry season by months with lower rainfall.
- Mark the wet season where rainfall peaks.
- Observe how temperature changes correspond to rainfall patterns.
🕒 Note: Many locations have distinct wet and dry seasons, making it easier to spot seasonal changes.
Tip 3: Compare with Other Climographs

Comparing climographs from different locations helps in:
- Understanding regional climate variations.
- Noting unique climatic features like monsoons, which might not be apparent from a single location.
To do this:
- Gather Data: Collect climographs from regions with similar latitudes but different longitudes or elevations.
- Compare Patterns: Look for similarities in temperature and precipitation trends, as well as anomalies.
🌍 Note: Regions with similar latitude often share similar seasonal patterns due to solar insolation, but altitude and terrain play significant roles.
Tip 4: Understand the Influence of Local Factors

Climographs show general trends but overlook:
- Proximity to Oceans: Coastal areas usually have milder temperatures with sea breezes moderating both summer heat and winter cold.
- Elevation: High-altitude areas have cooler temperatures year-round.
⛰️ Note: Microclimates within a region can differ significantly, so consider local geography when interpreting climograph data.
Tip 5: Make Accurate Predictions

By interpreting a climograph, you can make educated predictions on:
- What to expect in terms of weather during different months.
- The best times for agricultural activities or tourism.
Here’s how:
- Look for Trends: Identify patterns like a wet season followed by a dry season, which might influence agricultural planting.
- Extrapolate: Use the data to predict upcoming weather conditions or seasonal changes.
📊 Note: Don't forget to consider the accuracy of the data and potential long-term climate changes when making predictions.
In mastering your climograph worksheet, remember that understanding the data isn't just about the mechanics of plotting points but about interpreting the story behind the numbers. This ability to visualize and interpret weather patterns can offer insights into not only the current climate but also future trends, ecological systems, and human activities. By following these tips, you'll not only excel at your climograph worksheet but also gain a deeper appreciation for how climate shapes our world.
What is the main purpose of using a climograph?

+
The main purpose of a climograph is to provide a visual representation of the average monthly temperature and precipitation for a specific location. This helps in understanding the climate of that location over a year, making it easier to analyze seasonal patterns, plan agricultural activities, and study ecological conditions.
How can I compare two climographs accurately?

+
To compare climographs accurately:
- Ensure they are for the same time period or have similar data ranges.
- Use similar scales for temperature and precipitation.
- Consider geographical and topographical differences that might influence the data.
Can a climograph predict the weather for a specific day?
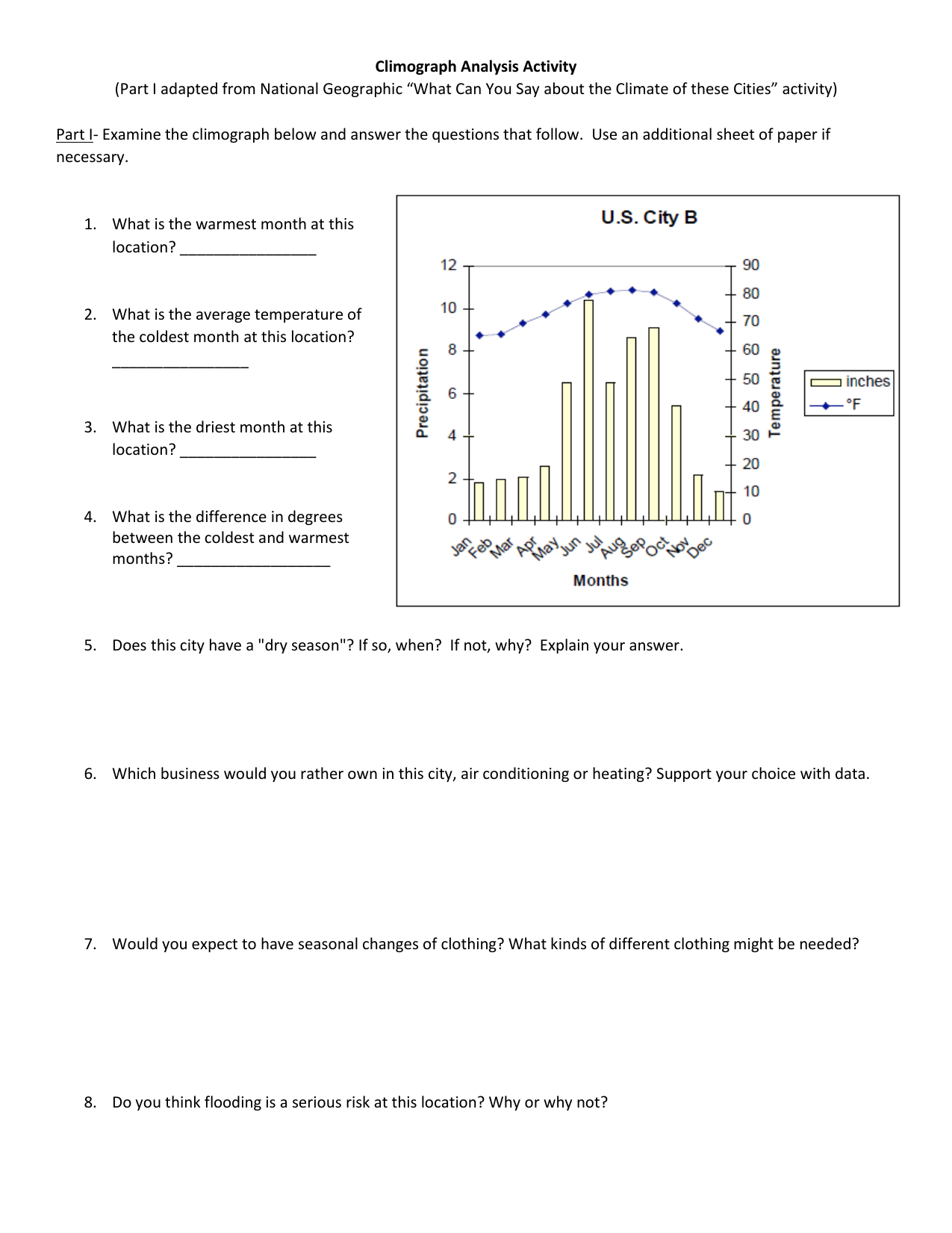
+
No, a climograph provides averages over a month, not daily weather predictions. It helps in understanding long-term weather patterns and trends rather than short-term forecasts.
Why do some months on a climograph show no rainfall?

+
Months with no rainfall on a climograph indicate a dry season or periods with very low precipitation. This can be due to seasonal atmospheric conditions, geographical influences, or simply a lack of weather systems that bring rain.
What should I do if the scales on a climograph are confusing?

+
If the scales on a climograph are confusing, look for:
- Units of measurement for temperature and precipitation.
- Whether the scales start from zero or another number.
- If there’s a key or legend explaining the graph.
Related Terms:
- Climograph worksheet answers page 2
- Climograph worksheet answer key pdf
- Climograph worksheet pdf