Cladogram Worksheet Answers: Worm, Spider, and Fly Breakdown

In the fascinating realm of evolutionary biology, the study of cladograms provides insightful views into how species are related and evolved over time. Today, we're focusing on understanding the relationships between a worm, a spider, and a fly using a cladogram. This tool is not just useful for academic purposes but also for understanding biodiversity and ecological relationships.
What is a Cladogram?

Before we dive into the specifics of our worm, spider, and fly analysis, let's start with a brief definition:
- A cladogram is a diagram used in phylogenetics to show evolutionary relationships among species, based on shared characteristics.
- It typically includes branching lines or "clades," representing ancestors, and nodes where evolutionary events happened.
- Each species or group of species is positioned at the end of a branch, indicating their unique evolutionary path from a common ancestor.
The Cladogram: Worm, Spider, and Fly
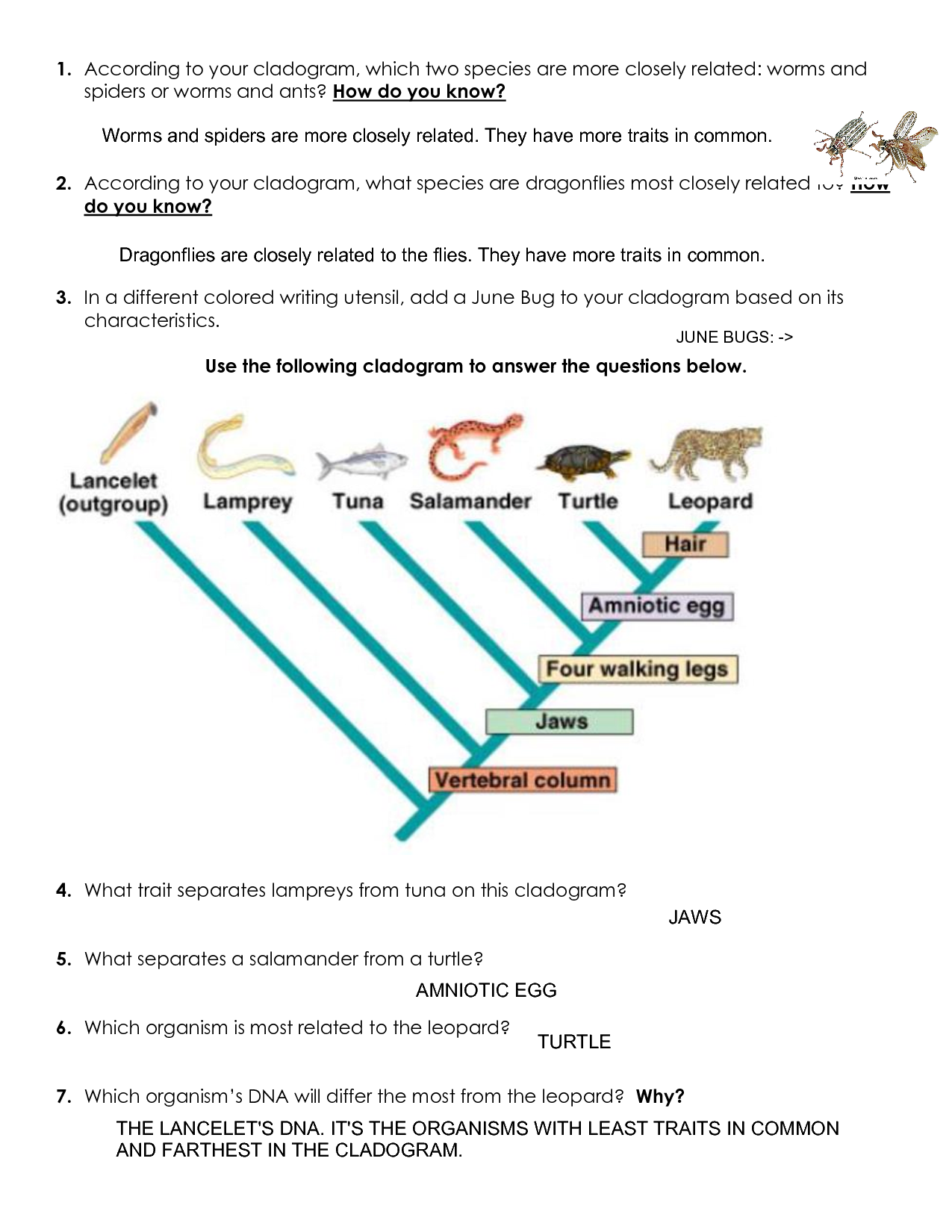
Let's construct a simplified cladogram for our subjects:
| Characteristic | Worm | Spider | Fly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Segmentation | Yes | Yes | No |
| Jointed Appendages | No | Yes | Yes |
| Exoskeleton | No | Yes | Yes |
| Wings | No | No | Yes |

Analyzing the Relationships

Now, let's analyze this cladogram:
Segmentation
- The presence of segmentation in both worms and spiders indicates they share a closer common ancestor than with flies, which lack segmentation.
Jointed Appendages
- Spiders and flies possess jointed appendages, a trait absent in worms, showing another evolutionary divergence point.
Exoskeleton
- The presence of an exoskeleton unites spiders and flies in terms of evolutionary development, something absent in worms.
Wings
- Flies are the only ones with wings, suggesting they diverged later, developing this unique trait.
Evolutionary Pathways and Ancestral Traits

This cladogram helps us visualize how each species evolved from their last common ancestor:
- The common ancestor of all three would have lived millions of years ago, possessing a simple body plan.
- Worms likely followed a path of simple, unsegmented or segmented body without appendages or an exoskeleton.
- Spiders and flies evolved jointed appendages and an exoskeleton, likely for protection and complex movement.
- Flies further evolved wings, suggesting an adaptation for flight, a trait not shared with spiders or worms.
💡 Note: Cladograms can change with new scientific discoveries. Always consider that evolutionary biology is a continually evolving field.
Practical Applications of Cladograms

Understanding these relationships has several real-world applications:
- Ecology: Helps in understanding species interactions within ecosystems.
- Medicine: Comparative biology can lead to new medical treatments based on related species' adaptations.
- Conservation: Knowing evolutionary relationships aids in protecting biodiversity and managing species populations.
Conclusion

Delving into the evolutionary relationships between a worm, a spider, and a fly through a cladogram not only elucidates how species have evolved but also underscores the interconnectedness of life. These insights teach us about shared ancestry, divergence points, and the natural processes that have shaped life on Earth. Cladograms are invaluable tools for education, research, and conservation, providing a visual representation of life's complex web.
What is the purpose of a cladogram?

+
A cladogram’s purpose is to visually represent the evolutionary relationships among species, highlighting shared characteristics and the divergence of species from common ancestors.
How does the cladogram change with new discoveries?

+
With new evidence from fossil records, genetics, or morphological studies, cladograms can be updated to reflect more accurate relationships, sometimes altering the understood position of species.
Can cladograms help in pest management?

+
Yes, understanding the evolutionary relationships can help in devising strategies for controlling pest populations, as species closely related to pests might share similar weaknesses or behaviors.
What role do common ancestors play in cladograms?

+
Common ancestors are crucial in cladograms as they represent the divergence points from which different species evolved, helping to trace back evolutionary pathways.