Master Stoichiometry: Chm 130 Worksheet Guide
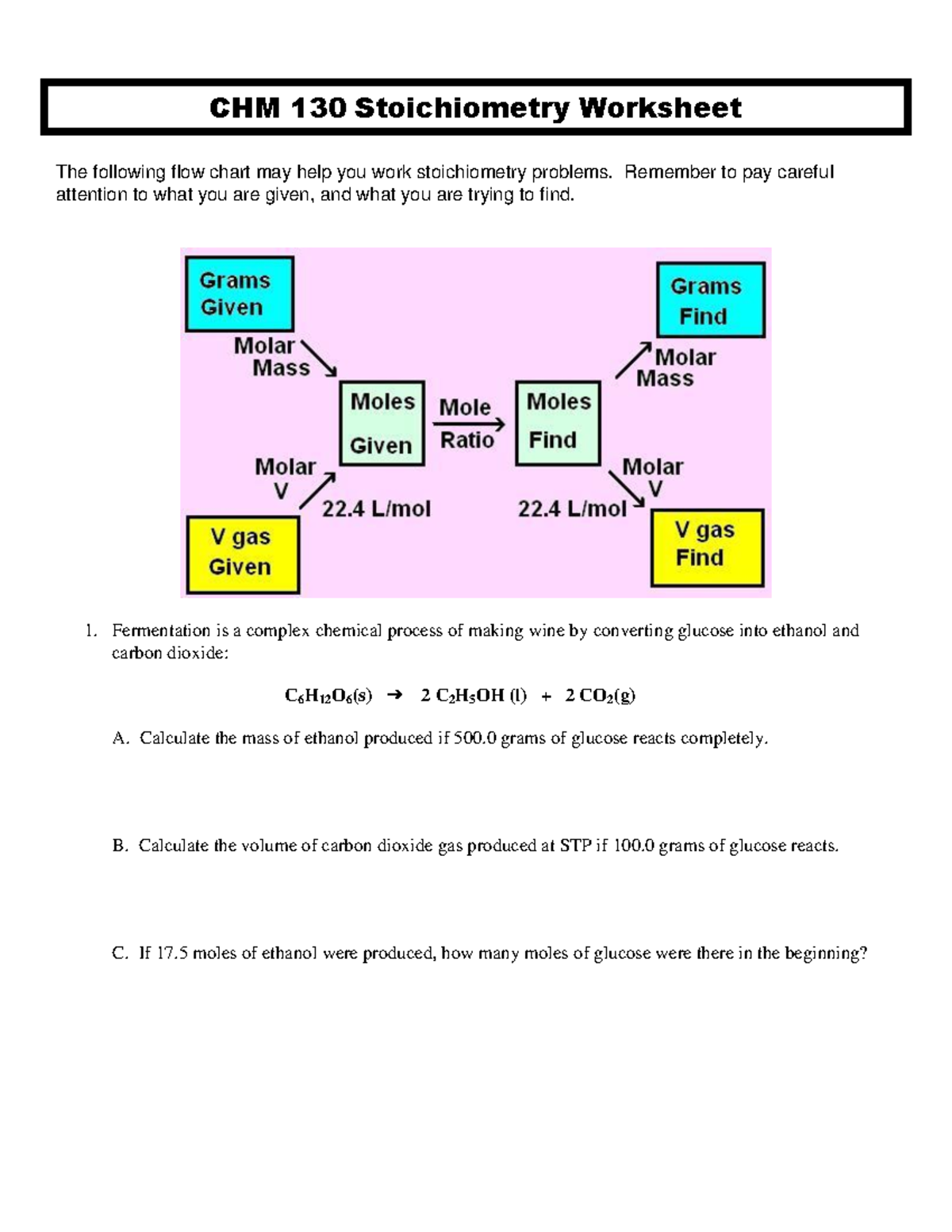
Understanding Stoichiometry Basics

Stoichiometry, at its core, is the calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions. This field relies heavily on understanding the chemical equations where reactants turn into products, based on the conservation of mass principle, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. When we dive into CHM 130 worksheets, you'll often find questions that require balancing equations, determining limiting reagents, or calculating the yield of a reaction. Here's a step-by-step guide to get you started:
- Balancing Chemical Equations: The first step in any stoichiometric problem is to ensure the chemical equation is balanced. A balanced equation has the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation, reflecting the law of conservation of mass.
- Setting Up the Molar Ratios: From the balanced equation, you can determine the molar ratios between reactants and products. This ratio is crucial for calculating how much product you can get from a given amount of reactant.
- Using Dimensional Analysis: This is where stoichiometry really shines. By converting between moles, grams, liters, or particles using the molar mass, Avogadro's number, and the molar volume at STP, you can navigate through various units to find what you're looking for.

After you've balanced the equation and set up the ratios, you'll encounter scenarios where you need to figure out which reactant will run out first, known as the limiting reagent. Here's how to identify it:
- Calculate moles of all reactants.
- Determine how much product each reactant can produce.
- The reactant that produces the least amount of product is the limiting reagent.
📝 Note: Always double-check your molar ratios to ensure accuracy in your calculations. A small mistake can lead to significantly wrong answers.
Working with Limiting Reagents and Yield

Once you've identified the limiting reagent, you can calculate theoretical yield and, by extension, the percent yield if actual yield is given:
- Theoretical Yield: The maximum amount of product you can make based on the amount of limiting reagent available.
- Actual Yield: This is the amount of product obtained experimentally.
- Percent Yield: Calculated as (actual yield / theoretical yield) * 100%, it shows the efficiency of the reaction.

If you are given a reaction like N2 + 3H2 → 2NH3, and you have 5 moles of N2 and 10 moles of H2, here's how you determine the limiting reagent:
| Reactant | Moles Available | Molar Ratio | Theoretical Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | 5 | 1 | 10 moles NH3 |
| H2 | 10 | 3 | 6.67 moles NH3 |

H2 is the limiting reagent, as it limits the production of NH3 to 6.67 moles.
⚙️ Note: When working with actual yield, ensure you're using the limiting reagent's amount to calculate theoretical yield. It's common to miscalculate yields by using the wrong reagent's quantity.
Solving Problems Involving Concentrations and Solutions

Some CHM 130 worksheet problems will involve calculations with concentrations. Here's how to approach them:
- Molarity (M): Defined as moles of solute per liter of solution, you'll often use this to determine how much solute is needed or how much volume of a certain molarity you require.
- Using Dilution Formula: For preparing solutions, use M1V1 = M2V2 where M stands for molarity and V for volume.
- Reactions in Solutions: Here, you'll combine stoichiometry with concentration calculations, often involving the use of molarity to find moles.
An example problem might ask you to find out how much NaOH you need to neutralize 50 mL of 0.1 M HCl. Here, you'd use stoichiometry to determine the moles of HCl, then calculate the volume or moles of NaOH needed based on the balanced equation.
⚗️ Note: Ensure that your units are consistent, especially when dealing with concentrations. Converting between milliliters and liters is a common stumbling block.
Practical Applications and Real-World Scenarios

Stoichiometry isn't just an academic exercise. It has numerous practical applications:
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Precision in medication preparation is paramount, where stoichiometry ensures the correct dosage and formulation.
- Environmental Science: Understanding and predicting the impact of pollutants in chemical reactions in the environment.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Efficient production, minimizing waste, and optimizing yield in industrial processes.
By working through these practical examples, students not only learn stoichiometry but also its importance in real-world scenarios, making the subject more relatable and interesting.
In wrapping up, we've explored the foundational principles of stoichiometry in the context of CHM 130 worksheets, from balancing equations, dealing with limiting reagents, calculating yields, to handling concentrations in solutions. Each step builds on the previous one, forming a logical and systematic approach to problem-solving in chemistry. Remember, stoichiometry is about understanding the chemical relationships between reactants and products, using the tools of mathematics to quantify these relationships. The key is to practice, ensuring each calculation step is understood and correctly applied, leading to an enhanced understanding of chemical reactions and their outcomes.
Why is stoichiometry important in chemistry?

+
Stoichiometry provides the framework for predicting the amounts of reactants and products in chemical reactions, which is crucial for both theoretical understanding and practical applications like chemical engineering, environmental analysis, and pharmaceuticals.
How can I improve my skills in stoichiometry?

+
Practice is key. Work through various types of problems, understand the underlying principles, and don’t skip any steps. Using resources like textbooks, online problem sets, and working with peers or tutors can also help solidify your understanding.
What are common mistakes to avoid in stoichiometry problems?

+
Common mistakes include not balancing the equation properly, using the wrong molar ratio, confusion between limiting reagent and excess reactant, and incorrect unit conversion, especially in concentration calculations.


