Predicting Chemical Products: Chm 130 Worksheet Guide

Understanding chemical reactions is a cornerstone of chemistry education. One way to deepen this understanding is through structured practice with worksheets, which not only reinforce theoretical knowledge but also enhance the predictive skills necessary for future scientific endeavors. This guide will walk you through the process of predicting chemical products using Chm 130 worksheets, providing you with step-by-step instructions, tips, and common pitfalls to avoid.
Why Predicting Chemical Reactions is Important

Before diving into the specifics, it’s vital to understand why predicting chemical reactions is crucial:
- Safety: Knowing what reactions might produce can prevent hazardous situations in labs and industries.
- Efficiency: It allows for more effective experimental design and optimization in chemical synthesis.
- Innovation: Predicting products can lead to the discovery of new compounds with potentially valuable applications.
Basic Principles of Predicting Chemical Products

To accurately predict the products of a chemical reaction, you need to understand the following principles:
- Balancing Equations: Chemical reactions must balance according to the law of conservation of mass. Every element involved in the reactants must appear in the products in the same quantity.
- Types of Reactions: Familiarize yourself with different reaction types such as synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, combustion, and redox reactions.
- Solubility Rules: Understanding which salts dissolve and which form precipitates is essential for predicting products in precipitation reactions.
Steps to Predicting Chemical Products
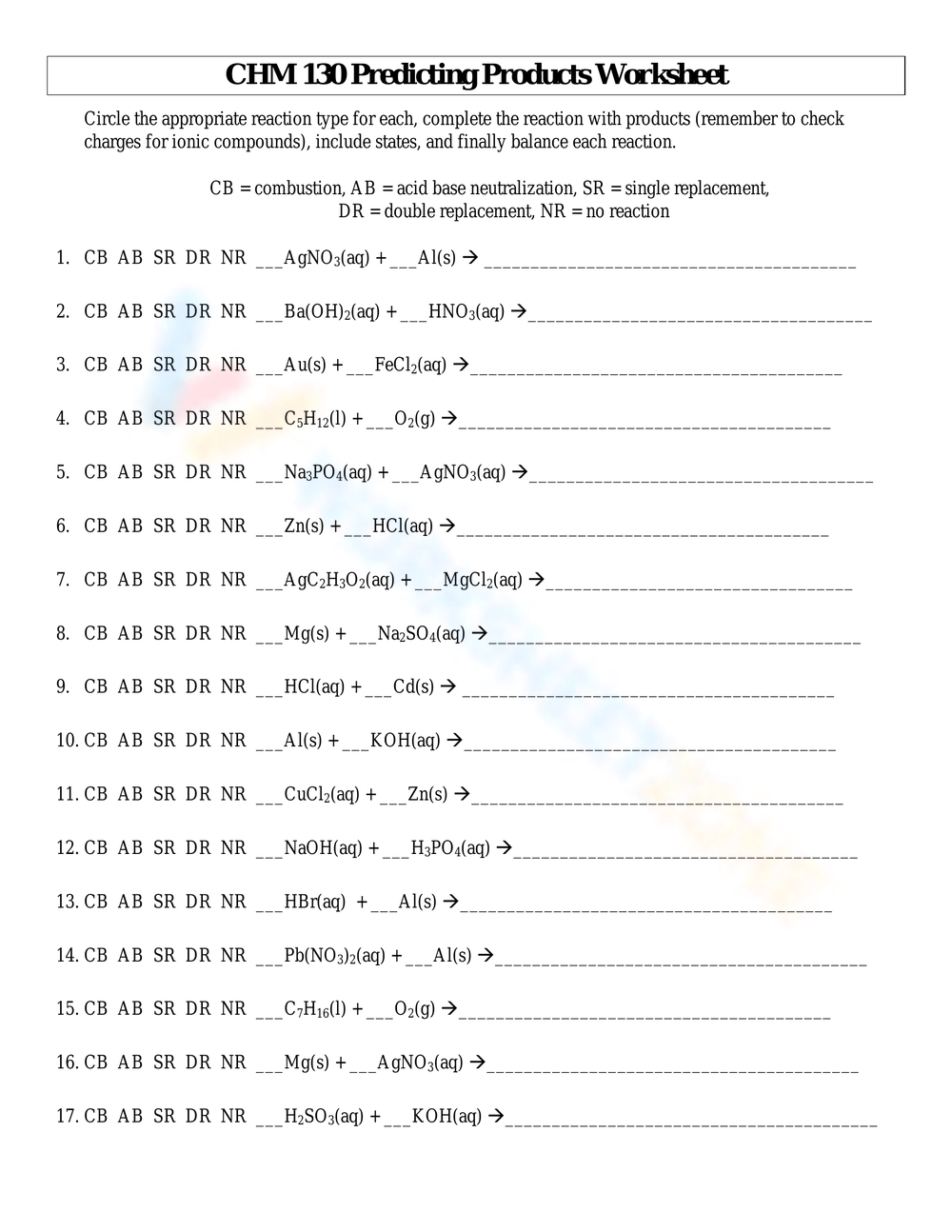
- Identify the Type of Reaction: Determine if the reaction is a synthesis, decomposition, etc., by examining the reactants and conditions.
- Write Reactants and Predict Products: Based on the reaction type, hypothesize what the products might be.
- Balance the Equation: Adjust coefficients to ensure the equation is balanced. This step often requires trial and error.
- Consider Energy Changes: Think about whether heat or light will be absorbed or emitted. This can influence the reaction’s direction or completeness.
- Check Solubility: For reactions involving salts, use solubility rules to determine if a precipitate will form.
⚗️ Note: Always double-check your work with common reaction conditions and known chemical properties.
Common Challenges in Product Prediction

Here are some common hurdles you might encounter when working through your Chm 130 worksheet:
- Complex Ions and Polyatomic Ions: These can make balancing more challenging since they react as units rather than individual atoms.
- Reactions in Solutions: Solubility can be a major factor, especially when reactions involve aqueous solutions.
- Competing Reactions: Sometimes multiple reactions might occur simultaneously, which can confuse product prediction.
Examples and How-to Guide

Let’s walk through a couple of examples to illustrate how to predict products:
Example 1: Synthesis Reaction

Consider the reaction between calcium oxide (CaO) and water (H₂O):
Reactants: CaO + H₂O
Predicted Products: You predict calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂), which is a synthesis reaction where two or more substances combine to form one product.
Balanced Equation:
CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂
🔬 Note: This reaction is exothermic, meaning heat will be released.
Example 2: Combustion Reaction

Here’s an example involving the combustion of methane (CH₄):
Reactants: CH₄ + O₂
Predicted Products: You would expect carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
Balanced Equation:
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
To facilitate understanding, here is a basic table of common reaction types:
| Type of Reaction | Example |
|---|---|
| Synthesis | CaO + H₂O → Ca(OH)₂ |
| Decomposition | 2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂ |
| Single Replacement | Zn + CuSO₄ → Cu + ZnSO₄ |
| Double Replacement | AgNO₃ + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO₃ |
| Combustion | CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O |
| Redox | 2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO |

By consistently practicing these types of reactions, you'll develop an intuitive sense for predicting chemical products.
After delving into the theory and walking through examples, here are some key takeaways:
- Predicting chemical products involves understanding the principles of reaction types, balancing equations, and considering the state and properties of reactants and products.
- It requires both logical reasoning and experience with chemical behavior to accurately predict outcomes.
- Worksheets like those in Chm 130 are invaluable tools for honing these skills, providing structured practice and a framework for learning.
- Remember, predicting products is not just about getting the right answer but also understanding the underlying chemical principles and reaction mechanisms.
What are the most common types of chemical reactions?

+
The most common types include synthesis, decomposition, single and double replacement, combustion, and redox reactions.
How important is balancing equations in predicting products?

+
Balancing equations is critical as it ensures conservation of mass, which is fundamental to understanding chemical reactions.
Can the state of matter change the outcome of a reaction?

+
Yes, the state of matter can significantly affect reaction rate, solubility, and thus the products formed.



