Ace Chemistry Unit 4 Worksheet 4 Easily

Delving into the world of chemistry can often seem like an uphill battle, especially when dealing with the intricacies of Unit 4. If you're here because you're struggling with Worksheet 4, fear not! We'll walk through the essentials of this unit step-by-step, ensuring that by the end of this post, you'll have a solid grasp on the necessary concepts.
Understanding Chemical Reactions
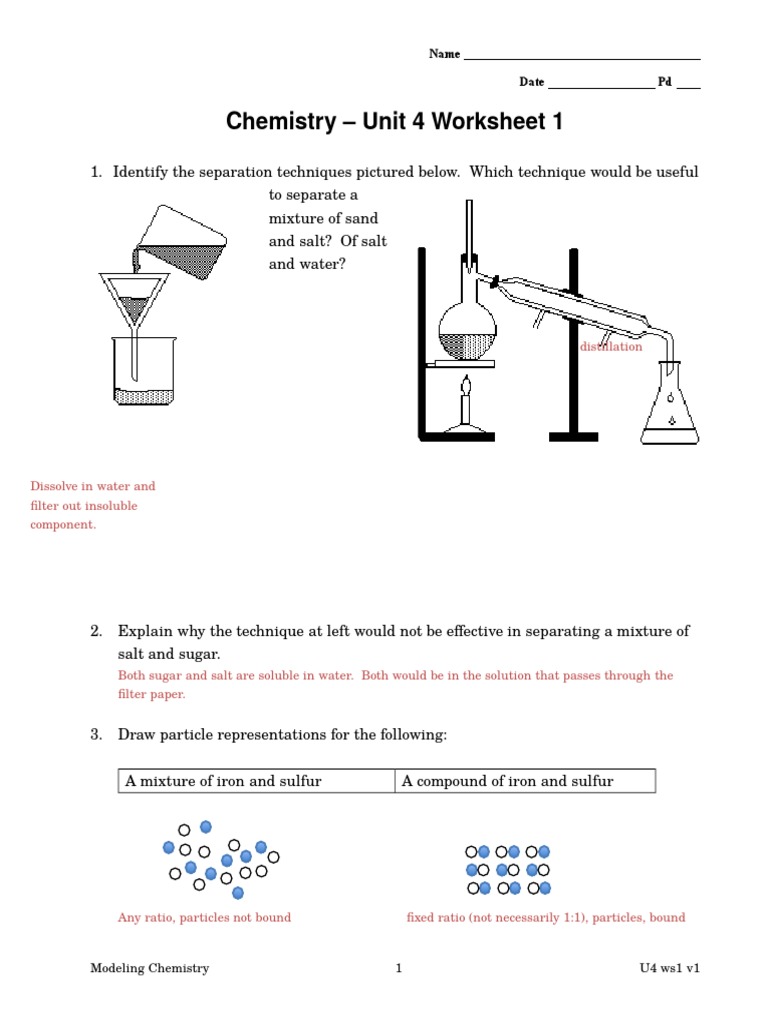
Before diving into the worksheet, let's revisit what chemical reactions are. Chemical reactions involve the transformation of substances into different substances through the breaking or forming of chemical bonds.
- Reactants - The substances that enter into a chemical reaction.
- Products - The substances that are formed as a result of the chemical reaction.
- Chemical Equations - Symbolic representations of a chemical reaction.
Here's how you can balance chemical equations:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify Reactants & Products | Write down all the substances involved in the reaction. |
| 2. Count Atoms | Make sure the number of atoms for each element is the same on both sides of the equation. |
| 3. Use Coefficients | Adjust the coefficients in front of formulas to balance the equation. Do not alter the subscripts. |
| 4. Verify | Ensure that the equation is balanced by recounting the atoms. |

🔬 Note: Remember, when balancing chemical equations, you are not altering the substance's identity but rather the amount of reactants and products involved.
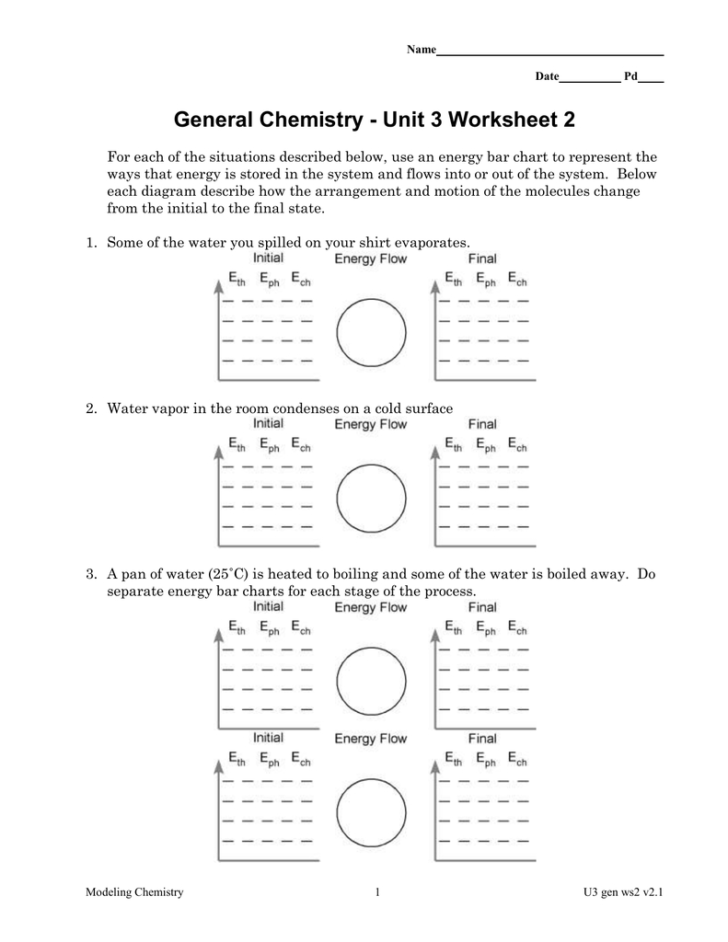
Applying Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry is crucial in understanding how much of each reactant is needed and how much product can be produced. Here's how to approach stoichiometry problems:
- Start with a balanced chemical equation.
- Identify what you're given and what you need to find (mass, moles, volume, etc.).
- Use the mole-to-mole ratios from the balanced equation.
- Convert quantities as needed using molar mass or gas law conversions.
⚗️ Note: Always check your units when solving stoichiometry problems to ensure your calculations make sense.
Analyzing Graphs and Data

In Worksheet 4, you might encounter problems that require you to analyze graphs or data sets to infer chemical properties or behaviors. Here's what to look for:
- Line Graphs: Look for trends like reaction rates or temperature changes.
- Bar Graphs: Compare quantities or properties among different substances.
- Data Tables: Use to calculate, compare, or predict quantities or properties.
When dealing with graphical data:
- Identify variables (dependent and independent).
- Observe trends or patterns.
- Make calculations or estimations based on the graph or table data.
Problem-Solving Tips

Here are some strategies to ace your worksheet:
- Break Problems Down: Divide the problem into smaller, manageable parts.
- Identify Knowns and Unknowns: Clearly write out what you know and what you need to find.
- Use Dimensional Analysis: Track units to keep your calculations correct.
- Practice Estimating: Estimation can give you a check on your final answers.
🧪 Note: If you find yourself stuck, take a step back and review the basics of the unit or seek additional resources for help.
To wrap up, mastering Unit 4 is all about understanding the principles of chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and data analysis. By focusing on these key areas, balancing equations, solving stoichiometric problems, and interpreting data effectively, you'll not only excel at Worksheet 4 but also build a strong foundation for future chemistry challenges.
What is the importance of balancing a chemical equation?

+
Balancing a chemical equation is crucial because it adheres to the Law of Conservation of Mass, which states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. A balanced equation shows that the number of atoms for each element remains the same before and after the reaction, ensuring the reaction is chemically accurate.
How does stoichiometry help in chemical calculations?
+
Stoichiometry uses the balanced chemical equation to determine the amount of reactants needed and the yield of products. It allows chemists to calculate mass-mass, volume-volume, and mass-volume relationships, which are essential for experimental design and industrial applications.
Why are graphical representations important in chemistry?

+
Graphs are critical for visualizing trends, patterns, and data relationships in chemistry. They can show changes over time, like reaction rates, or compare different chemical substances, allowing for better interpretation and understanding of experimental results.