Chemistry of Life Worksheet Answers Unveiled

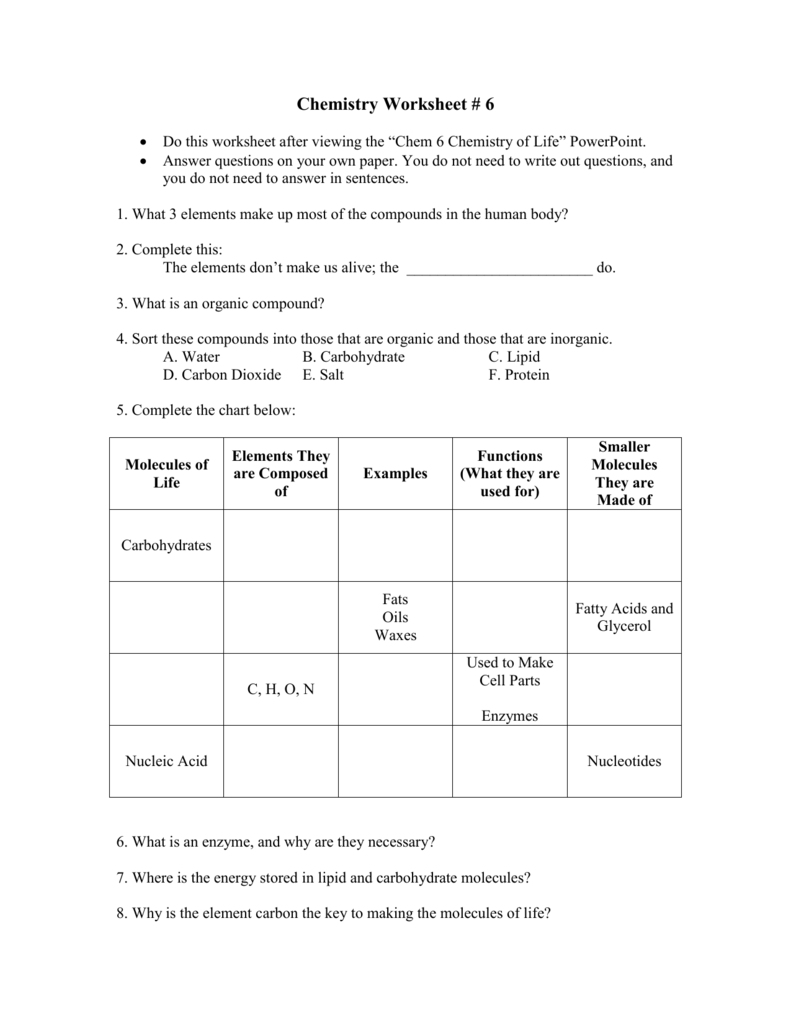
Life, as we know it, is a symphony of complex chemical processes. From the tiniest cellular activities to the grand scale of ecosystems, chemistry plays a pivotal role. This blog post delves deep into the "Chemistry of Life," providing comprehensive answers to common queries and detailing the fascinating world of biochemical interactions that make life possible.
Understanding the Building Blocks

Before diving into complex systems, it’s fundamental to understand the building blocks of life:
- Atoms: The smallest unit of matter, different arrangements of atoms give us different elements.
- Molecules: Atoms bonded together, forming compounds.
- Macromolecules: Large, complex molecules that play crucial roles in life processes. These include:
- Carbohydrates: Sugars and starches for energy and structure.
- Lipids: Fats, oils, and waxes for energy storage, insulation, and cell membrane structure.
- Proteins: Made up of amino acids, involved in virtually every function within cells.
- Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA, the genetic material of life.

Biochemical Reactions: The Dance of Life

The living world is maintained by a series of chemical reactions, often referred to as metabolism. Here are some key biochemical reactions:
- Enzyme-catalyzed reactions: Enzymes speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy.
- Photosynthesis: Plants convert sunlight into chemical energy (glucose), producing oxygen.
- Cellular Respiration: The process where glucose and other fuels are broken down for energy in the form of ATP.
- Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis: Essential for forming and breaking down macromolecules.

The Role of Water in Life

Water is the medium of life:
- Hydrophilic substances: Attracted to water, allowing for many biochemical processes.
- Hydrophobic substances: Repelled by water, important for cell membrane structure.
- Water’s unique properties like cohesion, adhesion, and its role as a solvent facilitate life’s processes.
| Property | Importance |
|---|---|
| Solvent | Enables chemical reactions in cells |
| Cohesion | Important for capillary action in plants |
| Heat Capacity | Stabilizes body temperature |
⚗️ Note: The formation of hydrogen bonds between water molecules is crucial for its properties; these bonds give water its high specific heat capacity, allowing it to absorb or release a lot of heat with only a small change in temperature.
Enzymes: Catalysts of Life

Enzymes are biological catalysts:
- They lower the activation energy needed for reactions.
- Enzymes are often protein-based, with a specific structure that ensures substrate specificity.
- Factors like temperature, pH, and inhibitors influence enzyme activity.

DNA and Genetic Information

DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the blueprint of life:
- Structure: Double helix formed by base pairing (A-T, C-G).
- Function: Replication for cell division, transcription for protein synthesis.
📌 Note: Mutations in DNA can lead to genetic variations, some of which could be beneficial for evolution, while others might cause diseases.
Life’s Complex Chemistry
The intricate chemistry of life isn’t just about macromolecules and reactions; it’s about how these components interact in complex systems:
- Homeostasis: Maintaining a stable internal environment despite external changes.
- Hormone Signaling: Chemical messengers coordinating body functions.
- Cell Signaling: Cells communicate to trigger responses, maintaining tissue integrity.
As we've explored, the chemistry of life is a vast and interconnected web, where even minor changes can have significant effects. Each building block, reaction, and process contributes to the creation, maintenance, and evolution of life, highlighting the profound interdependence of biological systems.
What are macromolecules?

+
Macromolecules are large molecules crucial for life processes. These include carbohydrates for energy storage and structure, lipids for energy storage and cell membranes, proteins for virtually every cellular function, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) for genetic information.
How does water support life?

+
Water supports life due to its unique properties. It acts as a solvent for biochemical reactions, aids in thermoregulation due to its high specific heat capacity, and its cohesive and adhesive properties facilitate the transport of nutrients and waste in organisms.
Why are enzymes important?

+
Enzymes are essential because they lower the activation energy required for biochemical reactions to occur, making life’s processes feasible at the temperatures found in living organisms. This catalytic activity is fundamental to metabolism, growth, repair, and all other life-sustaining processes.
Can you explain the significance of DNA?

+
DNA carries the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms. Its structure allows for accurate replication and transcription, which are pivotal in the continuity of life.
How does chemistry explain evolution?

+
Evolution is driven by changes in DNA through processes like mutation and gene flow. These changes lead to new traits, some beneficial for survival and reproduction, thus driving the evolution of species over generations. Chemistry underpins these molecular changes.



