5 Fun Facts About Isotopes in Chemistry
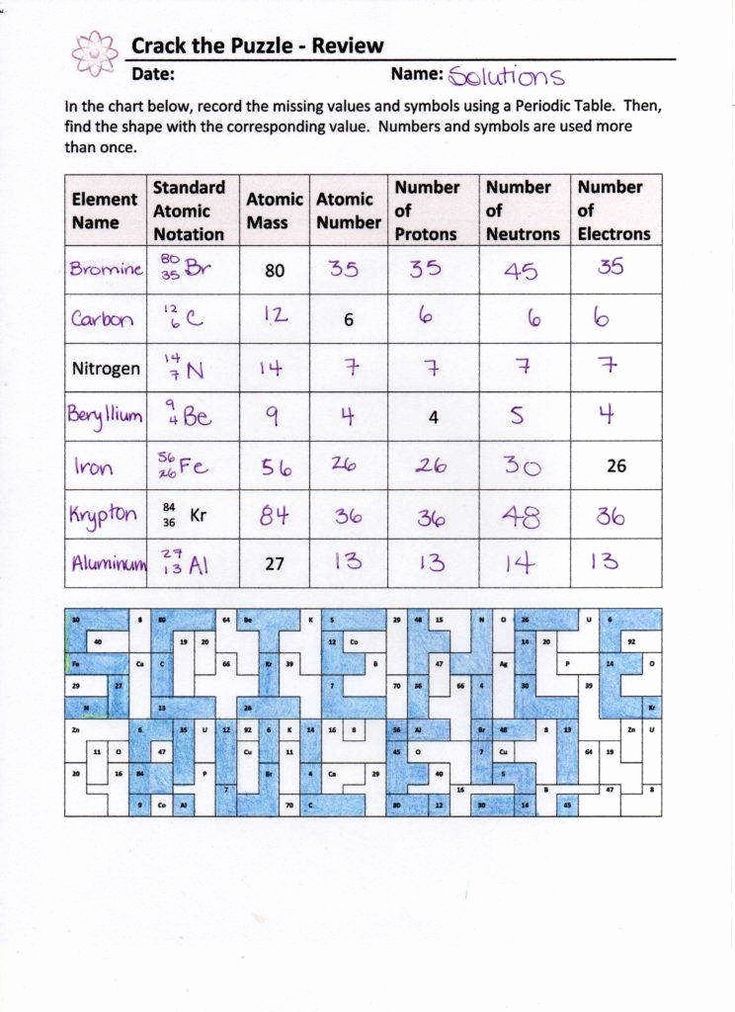
Isotopes might sound like an advanced topic in chemistry, but they are incredibly fascinating and play a significant role in various scientific applications. Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element which differ in neutron number, and despite having the same number of protons, they exhibit different physical properties due to variations in mass. Here are some fun facts about isotopes that will give you a better appreciation for these chemical chameleons:
The Variety of Isotopes


Each element on the periodic table has multiple isotopes. For instance, the element hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes:
- Hydrogen-1 (Protium): The most common isotope with no neutrons.
- Hydrogen-2 (Deuterium): Contains one neutron, making it twice as heavy as protium.
- Hydrogen-3 (Tritium): Very rare with two neutrons, it’s radioactive.
💡 Note: There are over 3,000 known isotopes of all the elements, most of which are synthetic or radioactive.
Use in Dating Techniques


Carbon-14, an isotope of carbon with six protons and eight neutrons, is used in radiocarbon dating to estimate the age of biological artifacts:
- This isotope decays at a predictable rate, allowing scientists to calculate how long ago an organism died.
- Its half-life is approximately 5,730 years.
🗓️ Note: Radiocarbon dating can be accurate up to about 50,000 years, after which other isotopes like potassium-40 or uranium-238 are used.
Medical Applications


Isotopes have a variety of applications in medicine, notably:
- Diagnostics: Technetium-99m, an isotope with a short half-life, is used in imaging techniques like SPECT scans to visualize bodily functions.
- Therapy: Iodine-131 is used to treat thyroid cancer by targeting cancerous cells specifically.
🧑⚕️ Note: These isotopes are selected for their decay properties and ability to emit radiation that can be measured or used for treatment without excessively harming surrounding tissues.
Stable and Unstable Isotopes
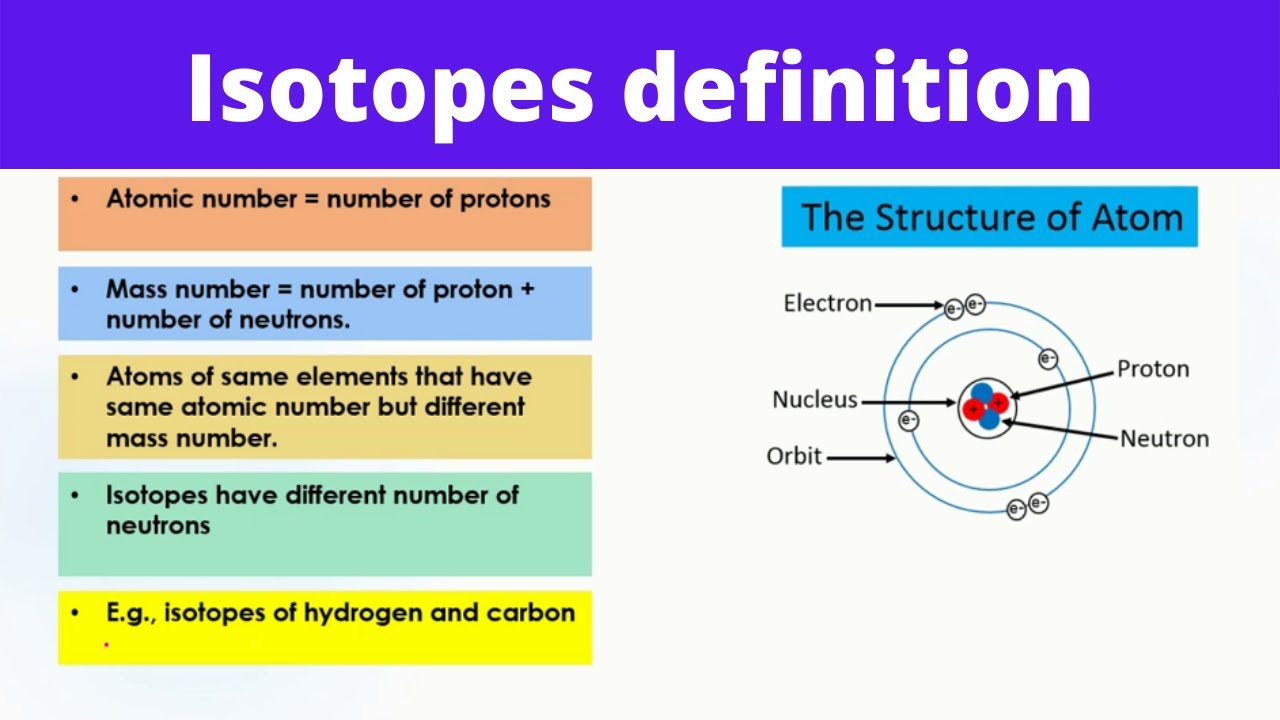

Not all isotopes are created equal; some are stable while others are radioactive:
- Stable isotopes maintain a balance of protons and neutrons in their nucleus, making them stable over long periods.
- Unstable or radioactive isotopes undergo radioactive decay to achieve stability, which can be alpha, beta, or gamma radiation.
⚗️ Note: The stability of an isotope often depends on the ratio of protons to neutrons in the nucleus.
Agriculture and Food Safety


Isotopes are employed in agriculture to enhance plant breeding, soil management, and food safety:
- Soil Analysis: Isotopes like phosphorus-32 help measure soil fertility, nutrient uptake, and erosion.
- Pesticide Tracking: Isotopes can trace the movement of pesticides in the environment to understand their distribution and persistence.
- Food Irradiation: Cobalt-60 is used to sterilize food, killing pathogens without the need for heat, which can preserve the food’s quality.
To conclude this exploration of isotopes, we've seen that these variants of elements are not just scientific curiosities but integral to numerous practical applications. From dating ancient relics to treating diseases and ensuring food safety, isotopes play a critical role in our daily lives, often without our direct awareness. Their unique properties make them indispensable in science, industry, and medicine, enriching our understanding of the world and improving our lives in countless ways.
What are isotopes?

+
Isotopes are different forms of an element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons in their nuclei, leading to differences in mass and often in stability.
Can isotopes change an element’s chemical behavior?

+
Chemically, isotopes of the same element behave very similarly since their electron configuration is the same. However, slight variations in mass can affect reaction rates and occasionally lead to isotopic fractionation in nature.
Why are some isotopes radioactive?

+
Radioactivity arises from an unstable ratio of protons to neutrons in the nucleus, causing the isotope to emit particles or electromagnetic radiation in an attempt to become more stable.
Are all isotopes of an element found in nature?

+
While many naturally occurring elements have multiple stable isotopes, some isotopes are extremely rare or not found in nature at all, existing only as synthetic creations from nuclear reactions.
What’s the benefit of using isotopes in medical treatment?

+
Isotopes used in medicine often have properties that allow for precise diagnostics or targeted therapy, reducing side effects and increasing treatment efficacy.