5 Must-Know Tips for Understanding Chemical Reactions and Enzymes

Chemical reactions and enzymes are fundamental to many biological processes, underpinning everything from how our body metabolizes food to how ecosystems function. Understanding the intricacies of these reactions is not only pivotal for students of chemistry or biology but also for anyone interested in the processes that make life possible. Here are five essential tips to help you grasp the complexities of chemical reactions and enzymes better.
1. Know Your Chemical Reaction Basics

To understand chemical reactions, you must start with the basics:
- Type of Reactions: Familiarize yourself with different types like synthesis, decomposition, single-replacement, and double-replacement reactions.
- Energetics: Learn about endothermic and exothermic reactions where energy is either absorbed or released.
- Reaction Kinetics: Understand how the speed of reactions is influenced by factors like temperature, concentration, pressure, and catalysts.

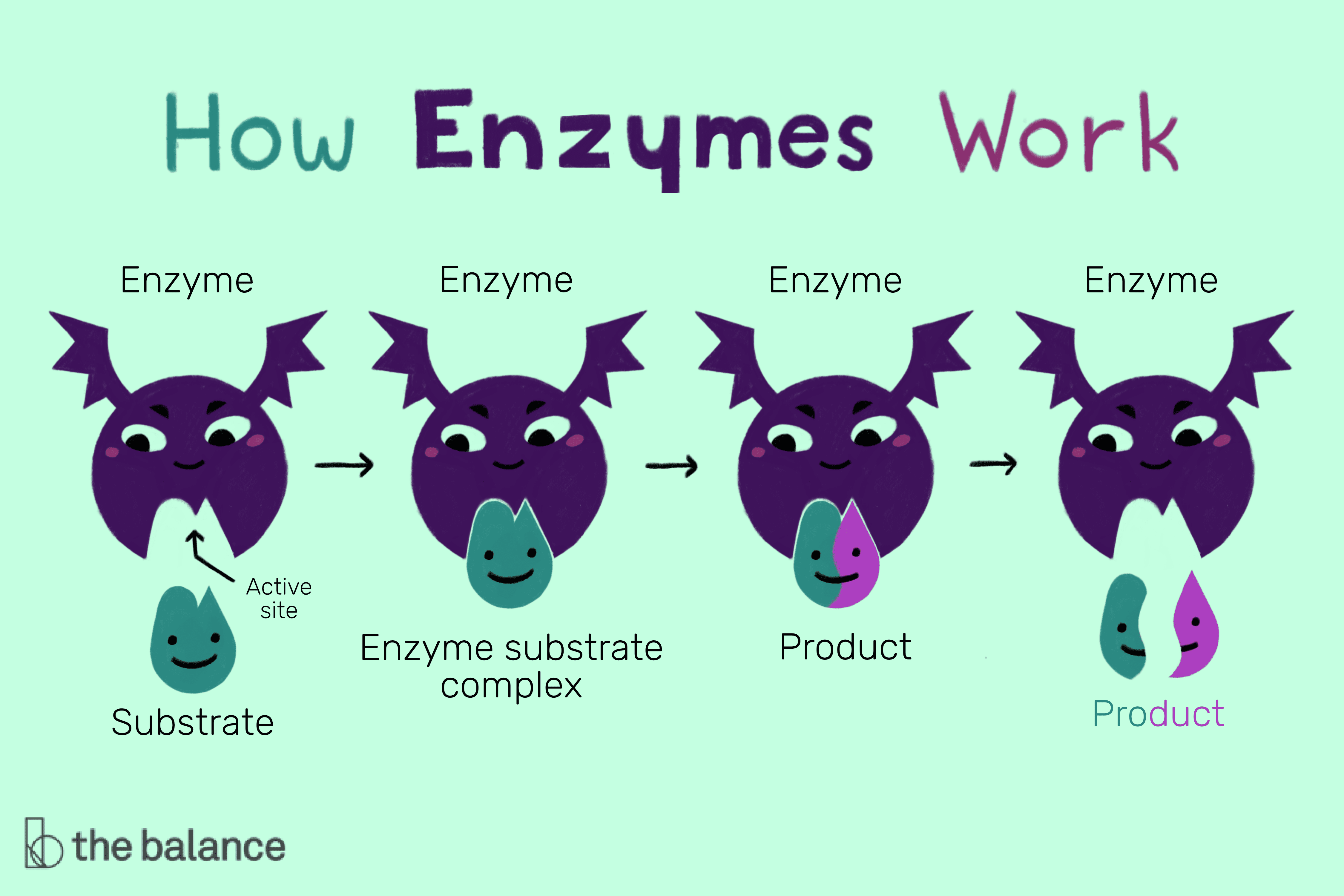
2. Enzyme-Substrate Specificity

Enzymes are biological catalysts that accelerate reactions, but not just any reaction:
- Each enzyme is uniquely shaped to interact with specific substrates, following the lock-and-key or induced fit models.
- This specificity ensures that enzymes work effectively in a cell without unwanted reactions taking place.
3. Catalytic Efficiency

Enzymes reduce the activation energy of reactions:
- They provide an alternative reaction pathway with a lower energy requirement.
- This increases the reaction rate, sometimes by millions of times.
- Understanding the concept of turnover number, which is the maximum number of substrate molecules converted to product by an enzyme per unit time, is crucial for appreciating enzyme efficiency.
4. Environmental Factors Affect Enzymatic Activity

Enzyme performance is influenced by several environmental factors:
| Factor | Effect on Enzyme Activity |
|---|---|
| Temp. & pH | Optimum levels where enzymes work best; deviations can denature the enzyme. |
| Ion Concentration | Enzymes often require specific ions for catalysis, with some ions acting as co-factors. |
| Substrate Concentration | Higher concentration increases the reaction rate until the enzyme is saturated. |

🌡️ Note: Enzyme activity can be optimized by adjusting environmental conditions to match their ideal functioning range.
5. Regulation of Enzyme Activity

Enzyme activity isn't constant; it's regulated for physiological balance:
- Feedback Inhibition: End products of metabolic pathways can inhibit earlier steps to prevent overproduction.
- Competitive and Non-competitive Inhibition: Inhibitors can compete with substrates for the active site or bind elsewhere, altering enzyme function.
- Allosteric Regulation: Some enzymes change shape when a regulatory molecule binds, altering their activity.
- Post-translational Modifications: Enzymes can be modified chemically after translation, affecting their activity through phosphorylation or other processes.
In understanding chemical reactions and enzymes, one comes to appreciate the delicate balance of biological systems. These reactions, catalyzed by enzymes, allow organisms to maintain homeostasis, react to environmental changes, and sustain life. By delving into these mechanisms, you not only gain a deeper understanding of life at a molecular level but also see the interconnectedness of biology with other sciences like chemistry and physics.
To summarize, here are the key points:
- Grasp the basics of chemical reactions to understand how reactions work.
- Recognize enzyme-substrate specificity for the efficient function of enzymes.
- Understand how enzymes lower activation energy to increase reaction rates.
- Appreciate how environmental factors affect enzyme activity.
- Learn about the various mechanisms for regulating enzyme activity.
What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions?
+
Exothermic reactions release energy to the surroundings, often in the form of heat, while endothermic reactions absorb energy from their surroundings to facilitate the reaction.
How do enzymes affect reaction rates?

+
Enzymes speed up reaction rates by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They do this by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to proceed.
What causes enzyme denaturation?

+
Enzyme denaturation occurs when the enzyme’s structure is disrupted, often due to extreme changes in temperature or pH, which can cause the enzyme to lose its function.



