Charge and Electricity Worksheet Answers: Simplified Solutions

Understanding how electricity works, including concepts like charge, voltage, and current, is essential not just for students in physics and electrical engineering but also for anyone curious about the technology that powers our world. This Charge and Electricity Worksheet aims to clarify these concepts with simple explanations and step-by-step solutions. Whether you're a student grappling with complex ideas or a professional revisiting fundamentals, let's break down these principles into manageable parts.
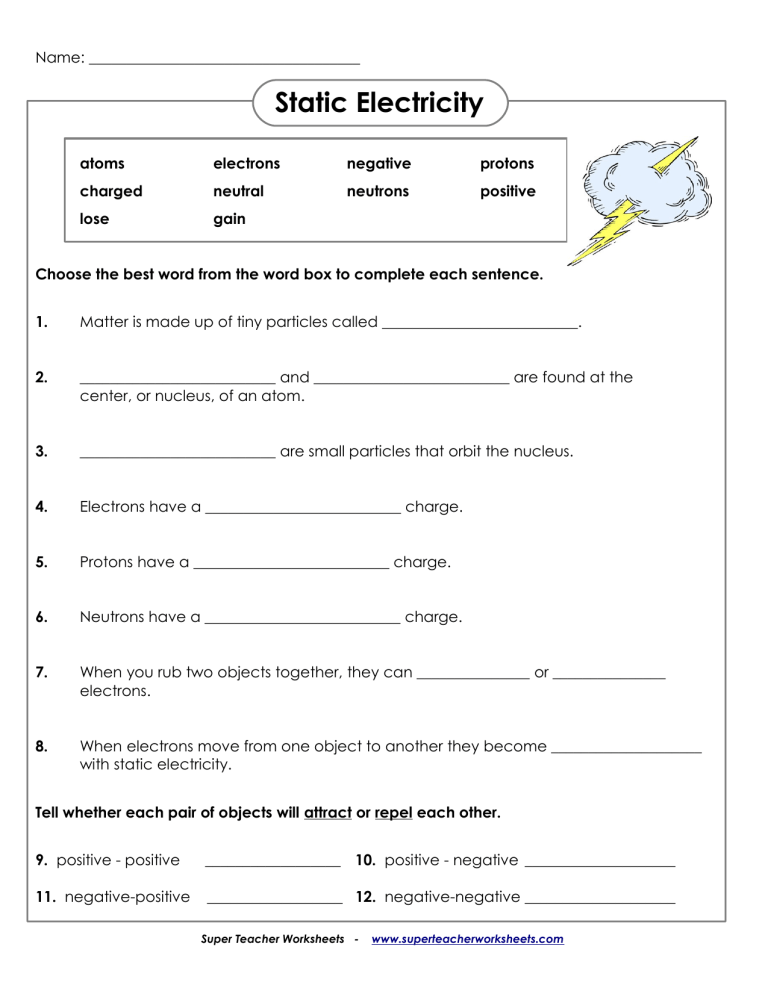
Understanding Electrical Charge

Electrical charge, denoted by Q, is a fundamental property of matter. Here are the key points about electrical charge:
- Charges come in two types: positive and negative. Like charges repel, whereas opposite charges attract.
- The basic unit of charge is the electron, which has a negative charge.
- The unit of charge is the coulomb (C), where one coulomb equals approximately 6.242 × 1018 electrons.
- Charge is conserved; in any closed system, the net charge remains constant.
Q1: Finding Charge When Charge Density and Area Are Given

To find the charge on a surface when the surface charge density (σ) and the area (A) are given, you can use the formula:
[Q = σ \cdot A]

📝 Note: In the formula, charge density (σ) has units of C/m2, and area (A) is measured in square meters (m²).
Understanding Voltage and Potential Difference

Voltage, or potential difference, is the energy per unit charge that is needed to move a charge from one point to another. Here's what you need to know:
- It is measured in volts (V) or joules per coulomb (J/C).
- The potential difference between two points in a circuit is responsible for the movement of charges.
- Electrical potential, or voltage, is analogous to gravitational potential energy; just as water flows downhill due to gravity, electrons flow in response to a voltage difference.
Q2: Calculating Voltage Across a Resistor

Ohm's Law states that:
[V = I \cdot R]
Where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance. Here's how you can calculate the voltage drop across a resistor given current and resistance:
| Current (I) | Resistance (R) | Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|
| 2A | 10Ω | 20V |
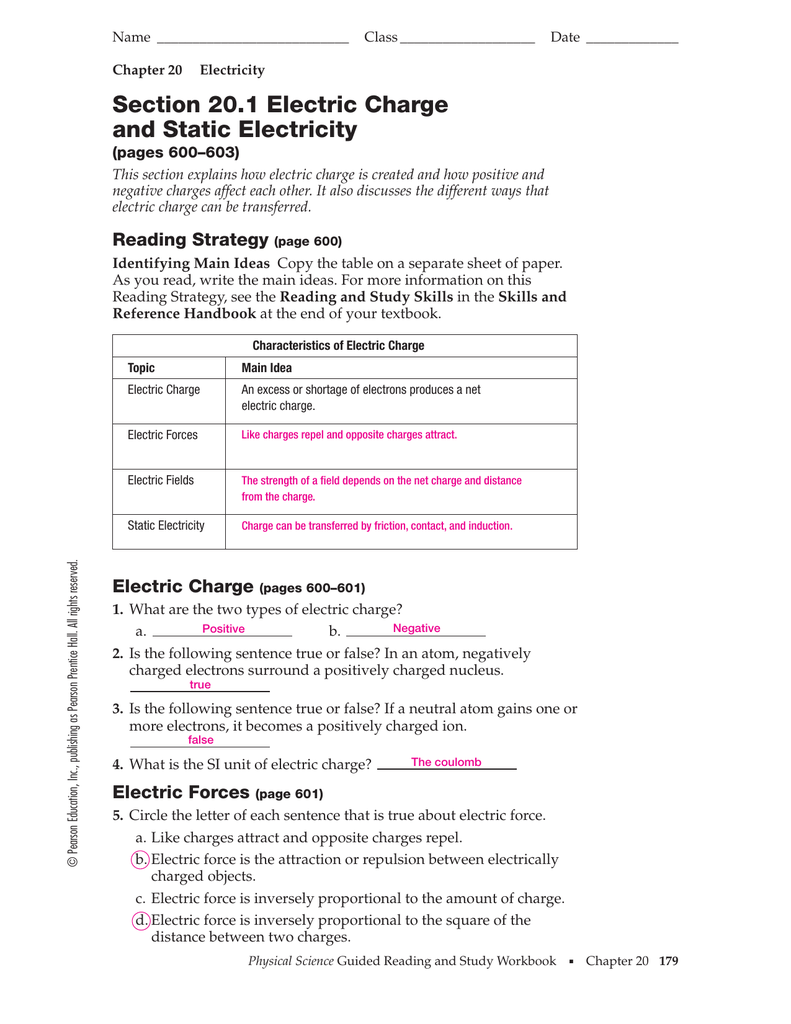
This table illustrates that for a 2A current passing through a 10Ω resistor, the voltage drop would be 20V.
Current and Its Relationship to Charge
Current, denoted as I, is the rate at which electric charge flows past a point in a circuit. Here are the essentials:
- The unit of current is the ampere (A), which is defined as coulombs per second (C/s).
- The amount of charge flowing through any cross-section of a conductor per unit time gives the current through it.
- DC (Direct Current) is when the flow of charge is in one direction, whereas AC (Alternating Current) involves the direction changing periodically.
Q3: Determining Charge Flow Over Time

Since current is the rate of charge flow, you can calculate the total charge passing through a circuit over a period by multiplying current by time:
[Q = I \cdot t]
Where I is the current, t is time, and Q is the total charge.
🔍 Note: This formula assumes a constant current flow, which might not always be the case in real-world scenarios.
Summary of Charge, Voltage, and Current

The interplay between charge, voltage, and current is what allows electricity to function. Here's a quick recap:
- Charge is the property of matter that causes it to experience a force in the presence of an electric field.
- Voltage provides the 'push' for charge to move, similar to how gravity pulls objects towards the ground.
- Current is the result of this charge movement, and its control and management is fundamental to electrical engineering.
By grasping these foundational concepts, one can start to understand more complex electrical principles and phenomena. Our exploration of the charge and electricity worksheet has provided a straightforward path through the maze of electrical science, offering clarity through simple calculations and foundational knowledge.
As you progress in your journey through electricity and its wonders, remember that these principles are the building blocks for further understanding of circuits, electromagnetic phenomena, and much more. They are not just abstract concepts but the very essence of the technology that shapes our modern lives.
Remember, knowledge of charge, voltage, and current is not just for academics or engineers but for anyone interested in understanding the invisible forces that light our homes, power our devices, and drive innovation.
What does charge density mean, and how does it relate to surface charge?

+
Charge density (σ) measures the amount of charge per unit area on a surface. It relates to surface charge as the product of charge density and area gives the total charge on that surface.
Why does voltage matter in an electrical circuit?

+
Voltage provides the potential difference that drives the flow of electric charges, ensuring they move in an orderly manner from areas of high potential to low potential, much like water flowing downhill.
How can I remember the difference between DC and AC?

+
A simple mnemonic is to think of DC as “Direct Current” where the flow of charge is straightforward or in one “direction,” whereas AC is “Alternating Current” where the flow is constantly switching back and forth like an “alternator.”
Can you clarify why a charge is conserved?

+
Charge conservation comes from one of the fundamental laws of physics. In any closed system, the sum of electric charge is constant. When charges are created or destroyed, positive and negative charges are created or destroyed in equal amounts, keeping the total charge constant.
What are the units for electrical quantities?

+
Here are the basic units in electricity:
- Charge (Q): Coulomb ©
- Voltage (V): Volt (V)
- Current (I): Ampere (A)
- Resistance ®: Ohm (Ω)