Discover Life's Traits: Worksheet Key Revealed
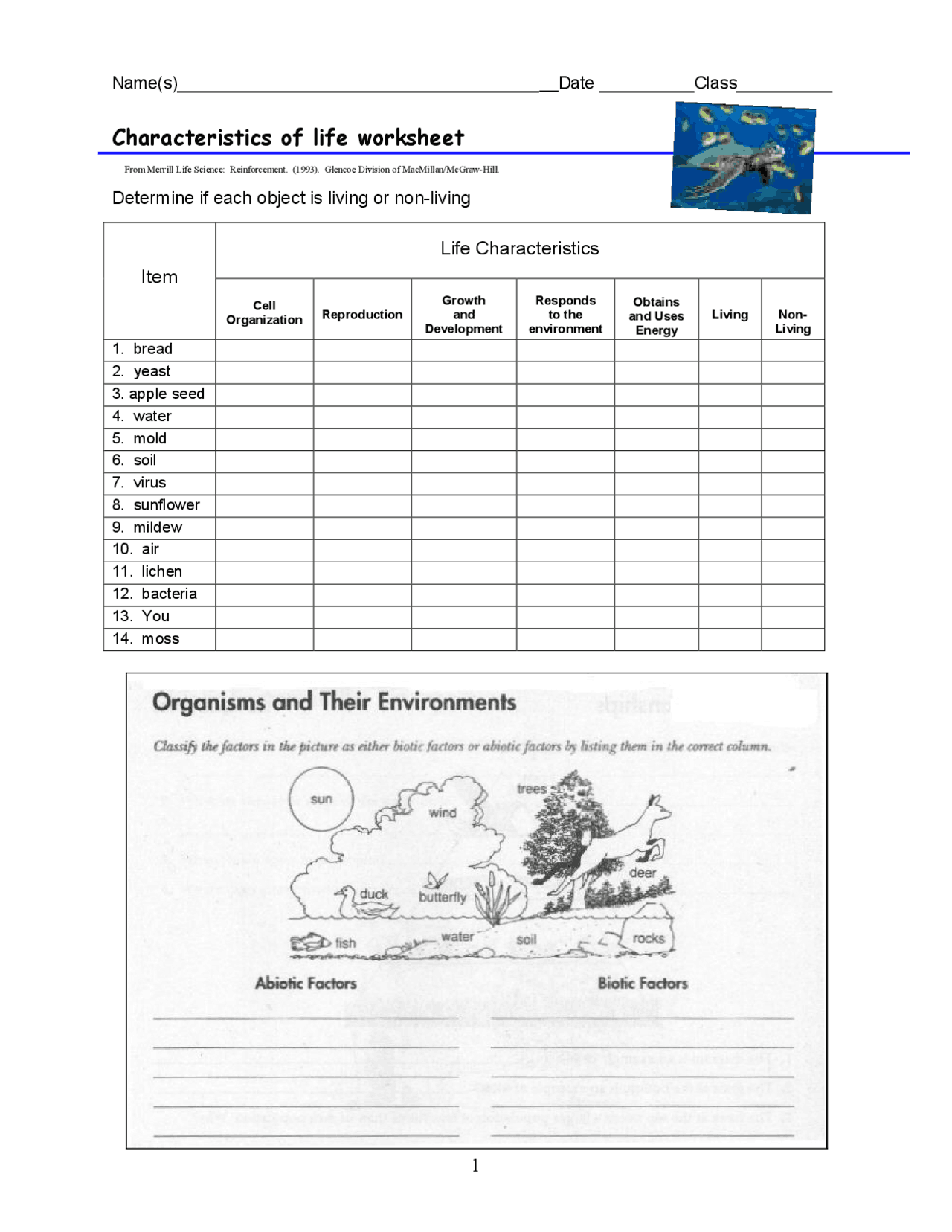
Embarking on the exploration of life's basic characteristics can be both an exciting and an educational journey, particularly within educational settings. As part of our ongoing commitment to enriching biological education, let's reveal the worksheet key to uncovering the traits of living things. This guide will walk you through the essential life processes, helping students grasp the concept of what it means to be alive.
Key Traits of Living Things

The intricate tapestry of life is woven from several fundamental traits that distinguish living organisms from non-living matter. Here, we'll unravel these key characteristics:
- Cellular Organization: Every living organism is made up of one or more cells, which are the smallest unit of life. These cells can be as simple as those in bacteria or as complex as the specialized cells in a multicellular organism like humans.
- Metabolism: The chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life. This includes energy production and use, nutrient uptake, and waste elimination.
- Growth: Living organisms increase in size or number, thanks to cell division and cell enlargement.
- Reproduction: Whether through sexual or asexual means, reproduction ensures the continuity of species.
- Response to Stimuli: Organisms react to changes in their environment, showing they are equipped with sensory systems to detect and respond to various stimuli.
- Homeostasis: The ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes. This stability is crucial for optimal body function.
- Evolution and Adaptation: Over time, species evolve and adapt through natural selection, which allows survival in varying environments.
Exploring Life's Processes Through Educational Activities

To drive home these concepts, we've designed interactive activities tailored for educators to enhance learning:
- The Cellular Investigation: Use microscopes or slides to let students view cells, illustrating the basic building block of life.
- The Metabolic Experiment: By observing yeast fermentation, students can witness the energy transformation process firsthand.
- Growth Models: Plant seeds and document growth or use simulations to show how cells grow and multiply.
- Reproduction Activity: Explore different types of reproduction through visual aids and perhaps even experiments with simple organisms like Hydra or Paramecium.
- Sensory Stimuli Exploration: Conduct experiments where students can observe reactions to stimuli like light, temperature, or sound.
- Homeostasis Challenges: Simulate situations where students must balance factors like pH or temperature to understand regulatory mechanisms.
- Evolution Simulations: Use online tools or physical models to illustrate how traits can change over generations.
🌱 Note: When using live specimens for observation, ensure ethical considerations are adhered to and all experiments follow safety guidelines.
Benefits of Understanding Life's Traits

The education system places significant importance on knowing the traits of life because:
- It lays the foundation for understanding more complex biological concepts like genetics, ecology, and biochemistry.
- It fosters critical thinking, as students must consider the implications of life's characteristics in different scenarios.
- It promotes an appreciation for the diversity and unity of life, encouraging environmental stewardship.
- It provides a backdrop for exploring the implications of life on ethical, medical, and philosophical levels.
By mastering these basic traits, students can better comprehend their own biology, the mechanisms behind diseases, and the potential for life's adaptations and survival strategies.
To enhance the learning experience, consider the following worksheet key for traits of living things:
| Trait | Activity/Example | What Students Learn |
|---|---|---|
| Cellular Organization | Observe prepared slides of animal and plant cells | Cell is the basic structural and functional unit |
| Metabolism | Yeast fermentation experiment | Energy conversion and the process of respiration |
| Growth | Seed germination experiment | Cell division, elongation, and the role of nutrients |
| Reproduction | Modeling asexual/sexual reproduction | Different strategies for perpetuating life |
| Response to Stimuli | Plant tropism experiment | How organisms interact with their environment |
| Homeostasis | Investigate temperature regulation in animals | Importance of internal stability for survival |
| Evolution and Adaptation | Case studies or natural selection simulations | How species change over time and adapt to their environment |

🌿 Note: Teachers might consider creating custom activities that cater to the particular interests or geographic context of their students, making the learning process more engaging and relatable.
As we reflect on the journey through the traits of living things, it becomes clear that the essence of life itself is a fascinating and complex subject. This understanding not only enhances students' scientific knowledge but also helps them appreciate the interconnectedness of all life forms. With this guide, educators can unlock the mysteries of life in an accessible and memorable way for all students.
What are some common misconceptions about the traits of living things?

+
One common misconception is that viruses are considered living organisms. However, since they cannot carry out life processes independently, they are typically not classified as living entities. Another mistake is believing all life forms can reproduce sexually, which is not true as many simpler organisms reproduce asexually.
How can students remember the seven traits of living things?

+
Students can use mnemonic devices like “MOGRESS” where each letter represents the initial of the trait: Movement, Organization, Growth, Reproduction, Excretion, Sensitivity, and Synthesis. Another technique is associating each trait with a daily-life example or creating a story linking all the traits together.
Why is it important for students to learn about the traits of living things?

+
Understanding these traits helps students appreciate the complexity of life at both microscopic and macroscopic levels. It also provides a framework for exploring more advanced biological concepts and understanding our own existence within the natural world.
Can non-living things exhibit traits of life?

+
Certain phenomena, like fire, can seem to display life traits like growth or response to stimuli, but they are not alive as they lack complex cellular organization and cannot reproduce independently.
What are some cross-disciplinary applications of understanding life’s traits?
+
These traits can be used in fields like:
- Environmental science to understand ecosystems.
- Medicine to study human and animal health.
- Bioethics to navigate ethical dilemmas in biological research.
- AI to model life-like behavior or algorithms based on natural selection.