Biology Chapter 10 Dynamics of Life Worksheet Answers

Understanding the Dynamics of Life
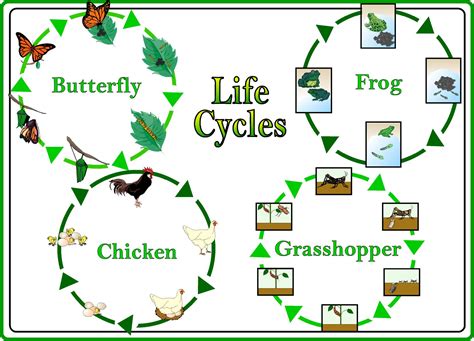
The dynamics of life refer to the complex interactions and processes that occur within living organisms and their environments. These dynamics are crucial for understanding how life functions, adapts, and evolves. In this chapter, we will explore the key concepts and principles that govern the dynamics of life.
Section 1: Organization of Life
The organization of life is a fundamental concept in biology, referring to the hierarchical structure of living organisms from atoms to ecosystems. This organization is essential for understanding how life functions and responds to its environment.
- Atomic Level: The basic building blocks of life are atoms, which combine to form molecules. These molecules are the foundation of all living structures and processes.
- Molecular Level: Molecules are organized into cells, which are the basic units of life. Cells are the smallest functional units of life and are capable of reproducing themselves.
- Cellular Level: Cells are organized into tissues, which are groups of similar cells that perform specific functions. Tissues are organized into organs, which are structures that perform specific functions.
- Organismal Level: Organs are organized into organisms, which are individual living entities. Organisms are capable of responding to their environment and reproducing themselves.
- Ecosystem Level: Organisms are organized into ecosystems, which are communities of living and non-living components that interact with each other.
Organization of Life Table

| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Atomic | Basic building blocks of life |
| Molecular | Atoms combine to form molecules |
| Cellular | Molecules organized into cells |
| Tissue | Cells organized into tissues |
| Organ | Tissues organized into organs |
| Organism | Organs organized into organisms |
| Ecosystem | Organisms and non-living components interact |

🔍 Note: The organization of life is a hierarchical structure, with each level building upon the previous one.
Section 2: Homeostasis and Regulation
Homeostasis refers to the ability of living organisms to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in the external environment. This is achieved through various regulatory mechanisms that work to maintain a balance of essential factors such as temperature, pH, and nutrient levels.
- Negative Feedback: A mechanism that reduces the intensity of a stimulus to maintain homeostasis.
- Positive Feedback: A mechanism that increases the intensity of a stimulus to maintain homeostasis.
- Regulatory Mechanisms: Various mechanisms that work to maintain homeostasis, including negative and positive feedback loops.
Homeostasis and Regulation Table
| Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Negative Feedback | Reduces the intensity of a stimulus |
| Positive Feedback | Increases the intensity of a stimulus |
| Regulatory Mechanisms | Work to maintain homeostasis |
🔍 Note: Homeostasis is essential for maintaining life, and regulatory mechanisms work to maintain a balance of essential factors.
Section 3: Energy and Metabolism

Energy is the driving force behind all living processes, and metabolism is the process by which energy is converted and utilized by living organisms.
- Energy: The driving force behind all living processes.
- Metabolism: The process by which energy is converted and utilized by living organisms.
- Photosynthesis: The process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
Energy and Metabolism Table

| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy | Driving force behind all living processes |
| Metabolism | Process by which energy is converted and utilized |
| Photosynthesis | Process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy |
🔍 Note: Energy is essential for life, and metabolism is the process by which energy is converted and utilized.
Without the dynamics of life, living organisms would not be able to function, adapt, and evolve. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for appreciating the complexity and beauty of life.
What is the organization of life?

+
The organization of life refers to the hierarchical structure of living organisms from atoms to ecosystems.
What is homeostasis?

+
Homeostasis refers to the ability of living organisms to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in the external environment.
What is metabolism?
+
Metabolism is the process by which energy is converted and utilized by living organisms.
Related Terms:
- biology solutions pdf
- biology dynamics of life quizlet
- biology solutions for life cycle
- biology the dynamics of life
- biology 1st edition
- biology 1st edition answer key