Market Equilibrium Shifts: Worksheet Answers Explained

Understanding market equilibrium and how it shifts is crucial for anyone interested in economics. Market equilibrium occurs where the supply and supply of a good or service are equal, setting the price at which the quantity people want to buy is exactly balanced with what sellers are willing to sell. However, numerous factors can cause this equilibrium to shift, leading to changes in market dynamics. This article will delve into these shifts through a detailed exploration of a worksheet, offering insights into how various events impact equilibrium prices and quantities.
Shifts Due to Demand Changes
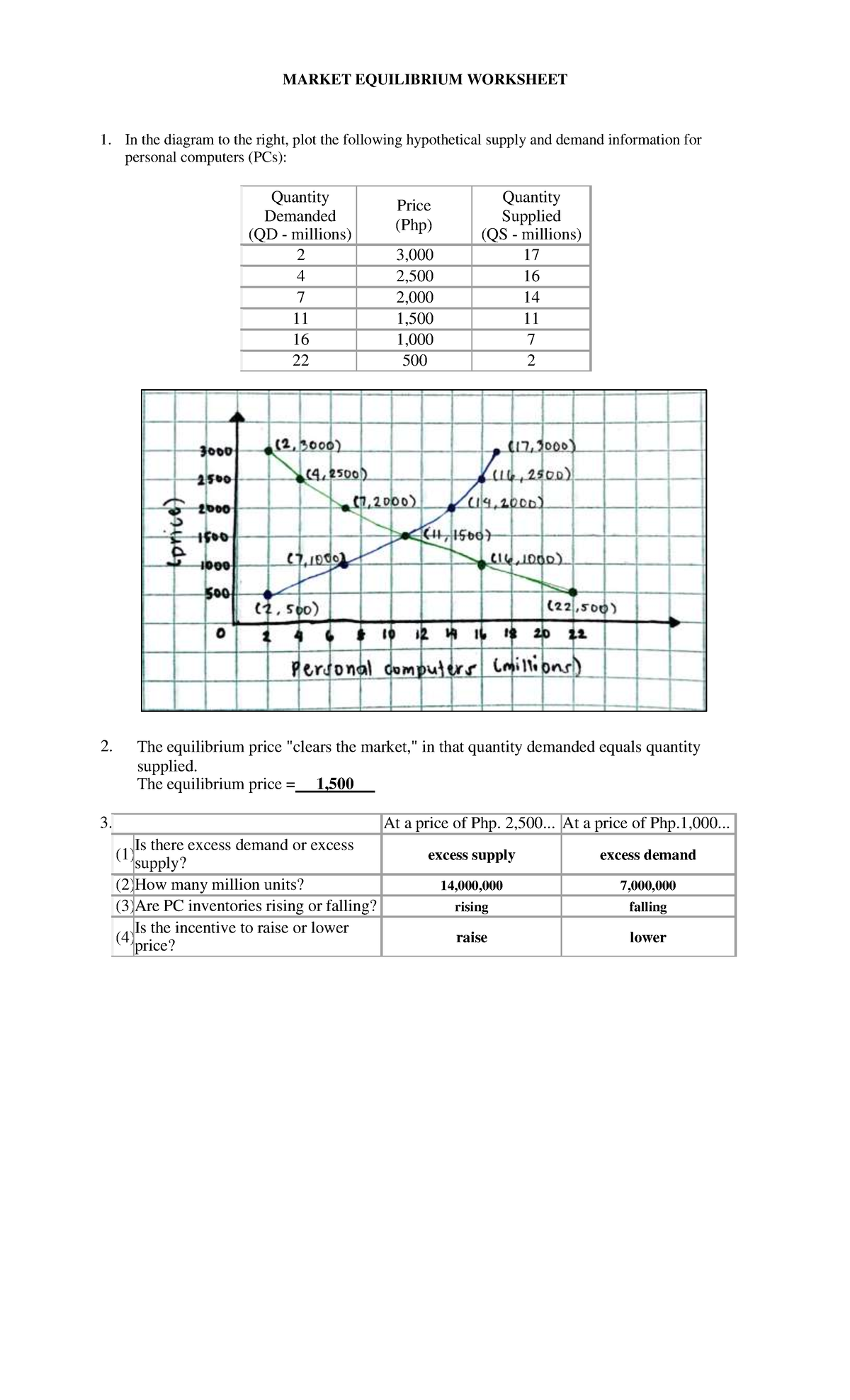

Demand for a product can change due to several reasons:
- Changes in Consumer Preferences: A surge in popularity for a product can shift the demand curve to the right.
- Income Variations: For normal goods, an increase in income increases demand. Conversely, for inferior goods, demand decreases.
- Price of Related Goods: This includes substitutes and complements. An increase in the price of substitutes often increases the demand for the product in question, while an increase in complement prices might decrease demand.
- Expectations: If consumers expect prices to rise, current demand might increase as they rush to buy at current prices.
- Number of Buyers: A larger population or a growth in market size can shift demand outwards.
Sample Worksheet Problem

Here is a common problem from a market equilibrium worksheet:
| Scenario | Change in Demand | Effect on Price | Effect on Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| An increase in consumer income for normal goods. | Increase (Demand curve shifts right) | Price Increases | Quantity Increases |

🎯 Note: This shift assumes a demand curve movement while the supply curve remains static.
Shifts Due to Supply Changes


On the supply side, here are some reasons that might lead to a change in supply:
- Input Prices: If the cost of production goes up, the supply curve shifts to the left.
- Technology: Technological advancements that make production more efficient increase supply, shifting the curve right.
- Number of Sellers: An increase in the number of sellers increases market supply.
- Expectations of Sellers: If sellers expect higher prices in the future, they might withhold products now, reducing current supply.
- Taxes and Subsidies: Taxes increase production costs leading to lower supply, whereas subsidies can increase supply.
Sample Worksheet Problem

| Scenario | Change in Supply | Effect on Price | Effect on Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| A decrease in production costs due to technological improvement. | Increase (Supply curve shifts right) | Price Decreases | Quantity Increases |
This analysis helps to predict the impact of external changes on market dynamics, allowing businesses to adapt to or even anticipate market trends.
Simultaneous Shifts

In real markets, both supply and demand can shift simultaneously due to different events:
- Introduction of a New Technology: This might increase both supply (due to cost reduction) and demand (due to new features). Here, the net effect on price depends on the relative size of these shifts.
- Natural Disasters: While a disaster might reduce supply (e.g., destroying crops), it might also increase demand for necessities or recovery-related goods.
Such simultaneous shifts can complicate predictions about market equilibrium, often requiring careful analysis to understand the final state of equilibrium:
- Price Indeterminate: If demand increases while supply decreases, or vice versa, the equilibrium price could go in either direction.
- Quantity Indeterminate: The same scenario might leave quantity supplied and demanded uncertain if both curves shift in opposite directions.
📝 Note: When both supply and demand shift, careful comparative statics analysis is necessary to determine the new equilibrium point.
The intricacies of market equilibrium shifts offer a comprehensive lens through which to view economic fluctuations. By understanding how different factors can alter demand and supply, one can better predict how markets will react to various scenarios. This knowledge is not only essential for economic students but also for anyone involved in business, policy-making, or consumer behavior analysis. In summary, the movements of market equilibrium reflect the dynamic nature of economic interactions, highlighting the need for both market participants and policymakers to adapt to the ever-changing economic landscape.
What causes market equilibrium to shift?

+
Market equilibrium shifts due to changes in demand and supply. These changes can occur from variations in consumer preferences, income levels, technological advancements, input prices, government policies like taxes or subsidies, natural events, and expectations about future market conditions.
How do we predict the direction of market equilibrium shifts?

+
Predicting shifts involves understanding which direction the demand or supply curve will move. For instance, if consumer income rises for a normal good, demand increases, shifting the curve right, leading to higher equilibrium price and quantity. Conversely, if production costs go up, supply decreases, shifting the curve left, resulting in higher prices but lower quantities.
Can shifts in market equilibrium occur simultaneously?

+
Yes, simultaneous shifts can occur. When both demand and supply shift due to different events, the impact on price and quantity can be indeterminate, necessitating a detailed analysis to understand the final equilibrium point.