Animal Cell Worksheet: Master the Answers Easily

Understanding animal cells is fundamental to grasping broader biological concepts, particularly for students stepping into the realm of life sciences. This blog post serves as a comprehensive guide to mastering the answers in an animal cell worksheet, providing insights that enhance both your understanding and exam performance.
Key Components of an Animal Cell


Animal cells, like all living entities, possess several organelles each with specialized functions:
- Nucleus: The control center where genetic material is housed, directing protein synthesis and cellular growth.
- Mitochondria: Known as the powerhouse, they produce energy through cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Both rough and smooth ER are involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, packages, and sorts proteins and lipids for transport within or out of the cell.
- Lysosomes: These membrane-bound sacs contain hydrolytic enzymes to digest various biomolecules.
- Cytoskeleton: Comprising microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, it provides structural support and enables cellular movement.
- Plasma Membrane: Selective barrier, it controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Steps to Master Your Animal Cell Worksheet

Conquering an animal cell worksheet involves more than memorization; it requires understanding, strategic learning, and application:
1. Familiarize with Cell Structure

- Begin by reviewing a detailed diagram of an animal cell, identifying each organelle.
- Use mnemonic devices to remember organelles; for example, “NECESSARY” - Nucleus, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Cytoplasm, Mitochondria, Golgi, Lysosomes, Ribosomes, Plasma Membrane.
📘 Note: While memorization is useful, comprehending the function of each organelle is vital for answering complex questions.
2. Understand Organelle Functions

To excel in worksheets, delve deeper into:
- How organelles work: The nucleus directs cellular activities, but how does it do so?
- Inter-organelle communication: For instance, the ER sends proteins to the Golgi apparatus for modification.
3. Practice Labelling Diagrams
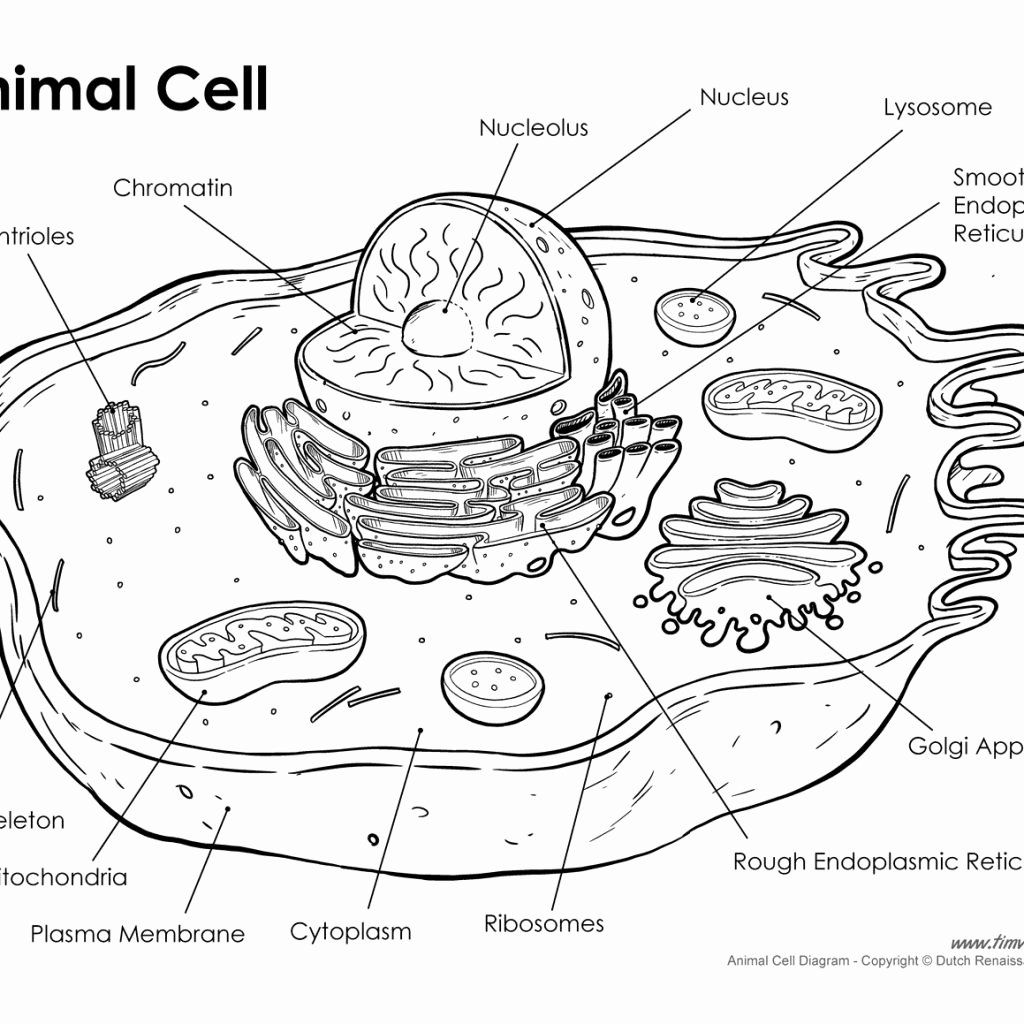
Practical exercises reinforce visual memory:
- Label diagrams, moving from labelled to unlabelled images to check your knowledge.
- Try sketching an animal cell from memory, then review it for accuracy.
4. Link Theory with Practical Scenarios

Connect concepts to real-life:
- Relate diseases to organelle dysfunction. For example, mitochondrial defects can lead to energy-related disorders.
- Discuss cellular processes like mitosis or apoptosis and how organelles play a role.
5. Use Flashcards for Review

Active recall is key:
- Create or find flashcards focusing on organelle names, functions, and structure.
- Test yourself regularly.
6. Engage in Group Study Sessions

Interactive learning helps:
- Discuss animal cell components, explaining concepts to each other.
- Simulate a quiz or teach each other to solidify understanding.
💡 Note: Teaching someone else often reinforces your own understanding, and group sessions can uncover blind spots in your knowledge.
Final Thoughts on Your Journey
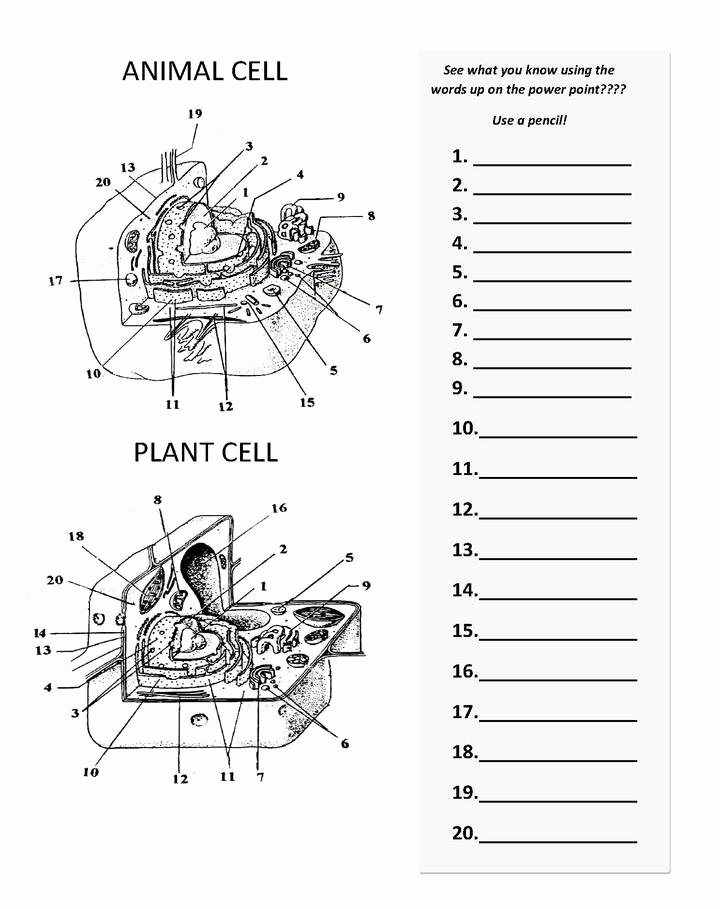
As you delve into the fascinating world of animal cells, remember that success comes from understanding rather than rote memorization. By engaging with the content through multiple lenses—visual, mnemonic, practical, and interactive—you’ll not only excel in answering worksheet questions but also foster a deeper appreciation for cellular biology. Keep this journey dynamic, interactive, and continuously evolving, and you’ll find that mastering cell biology becomes an enjoyable and rewarding adventure.
What is the primary difference between an animal cell and a plant cell?

+
Plant cells have a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole, which are not present in animal cells.
How does the Golgi apparatus contribute to cell function?

+
The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or for use within the cell.
Why do cells have both smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum?

+
Rough ER is involved in protein synthesis due to the ribosomes on its surface, whereas the smooth ER is mainly responsible for lipid synthesis and detoxification.
What role does the cytoskeleton play in animal cells?

+
The cytoskeleton provides structural support, helps in cell division, enables cell movement, and allows for intracellular transport.
How can studying animal cells benefit one’s career?
+Understanding cellular biology is fundamental for careers in medicine, biotechnology, genetics, research, and various scientific fields where cell manipulation and study are key.