Cell Structure and Function Worksheet: Simplify Biology

In the intricate world of biology, understanding cell structure and function is fundamental to grasping the broader concepts of life processes. Cells are the basic unit of life, and exploring how they operate provides invaluable insights into how organisms function at the microscopic level. This article aims to simplify the understanding of cell biology through a structured worksheet, ensuring learners can easily digest the complexity of this essential topic.
Overview of Cell Types

Cells can be categorized primarily into two types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Here’s a brief overview:
- Prokaryotic Cells: These are cells without a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. They are usually found in bacteria.
- Eukaryotic Cells: Found in animals, plants, fungi, and protists, these cells contain a well-defined nucleus enclosed within a nuclear membrane, along with various organelles.
Structure of a Cell
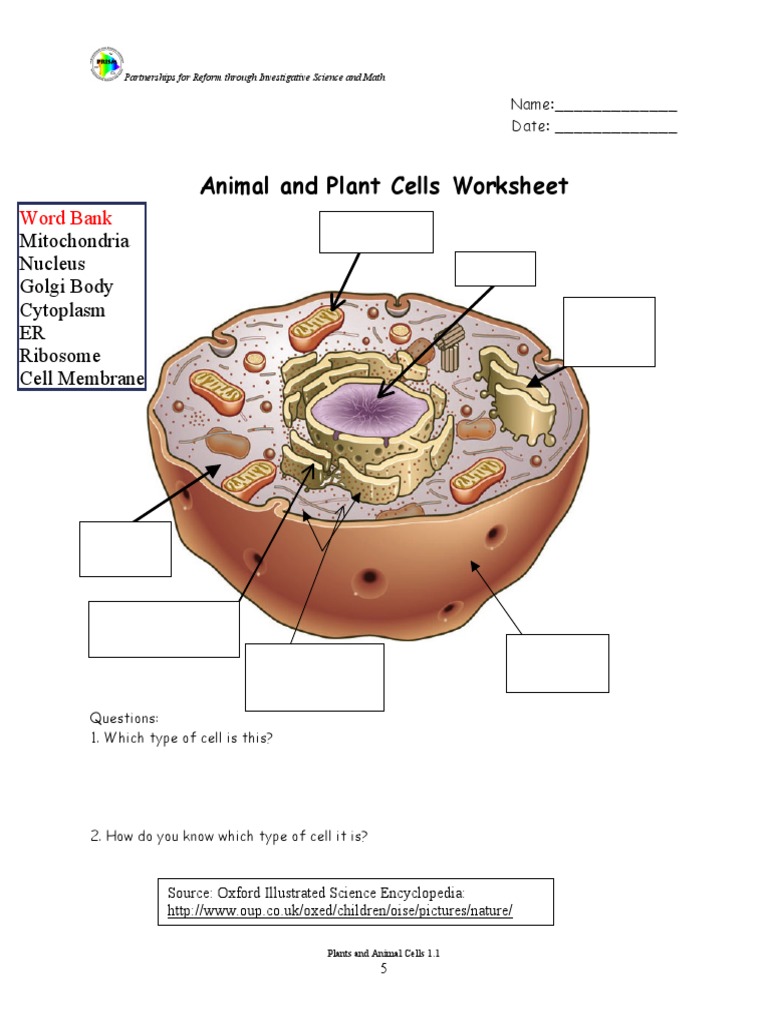

Let’s delve into the various components of a typical eukaryotic cell:
| Cell Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Cell Membrane | Acts as a barrier, controlling what enters and leaves the cell. |
| Nucleus | Contains genetic material and manages cellular activities. |
| Cytoplasm | The fluid inside the cell where organelles are suspended. |
| Mitochondria | Known as the powerhouse, generates energy via ATP. |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Protein and lipid synthesis (Rough ER), and detoxification (Smooth ER). |
| Golgi Apparatus | Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or use within the cell. |
| Ribosomes | Site of protein synthesis. |
| Lysosomes | Digestive organelles that clean up cellular debris. |
| Vesicles | Transport materials inside and outside the cell. |
| Cytoskeleton | Provides support and enables cellular movement. |
| Cell Wall (in plants) | Provides structural support and protection. |
| Chloroplasts (in plants) | Perform photosynthesis to produce energy. |

🔬 Note: This list covers the major organelles but isn't exhaustive. Cells also contain other smaller structures with specific functions.
Cell Function

Each component of the cell has specific functions that contribute to the overall operation of life processes:
- Energy Production: Mitochondria play a critical role in creating ATP through cellular respiration.
- Protein Synthesis: Ribosomes translate mRNA into proteins, a process coordinated by the nucleus.
- Transport: The Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus manage protein and lipid transport within the cell.
- Communication: The cell membrane facilitates communication between cells through signaling molecules.
How to Use This Worksheet

This worksheet can be utilized to learn cell biology through:
- Labelling: Practice identifying structures from diagrams or slides.
- Descriptions: Write short summaries on the function of each cell organelle.
- Comparisons: Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells or plant and animal cells.
- Quiz: Answer quiz questions at the end to reinforce learning.
💡 Note: Utilizing this worksheet alongside visuals like diagrams or actual microscope slides can enhance understanding.
Practical Applications

Understanding cell biology isn’t just academic; it has real-world applications:
- Medicine: Cell biology research helps in understanding diseases and developing treatments.
- Biotechnology: Genetic manipulation at the cellular level leads to advancements in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and biofuel production.
- Forensics: Cell analysis is crucial in crime scene investigation and determining genetic relationships.
To sum up, this exploration into cell structure and function provides a basic yet comprehensive overview that is essential for understanding more complex biological systems. Through engaging with this worksheet, one can gain insight into the building blocks of life, thereby fostering a deeper appreciation and understanding of biology's intricate dance at the cellular level.
What is the role of mitochondria in a cell?

+
Mitochondria are often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell. They produce ATP, which is the main energy currency used by the cell, through a process known as cellular respiration.
Can prokaryotic cells survive without a nucleus?

+
Yes, prokaryotic cells like bacteria do not have a nucleus. Their DNA floats freely in the cytoplasm, and they still perform all necessary life processes effectively.
What happens if the cell membrane is damaged?

+
A damaged cell membrane can lead to the uncontrolled exchange of substances, disrupting the cell’s homeostasis. If severe, it can lead to cell death.
Why do plant cells have cell walls?
+
Cell walls provide structural support and protection to plant cells, helping them to withstand environmental pressures, maintain shape, and resist pathogen attacks.