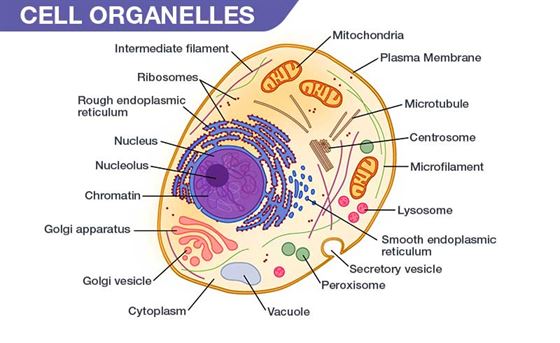
7 Key Cell Organelles and Their Functions Unveiled

Understanding the intricate world inside our cells is like peeking into a microscopic metropolis, teeming with activity where each structure, or organelle, plays a vital role. Let's explore the seven key cell organelles and delve into how these cellular components function to maintain life at its most basic level.
The Nucleus: Command Center of the Cell

The Nucleus is often termed the cell's command center. Here's why:
- DNA Storage: It holds the cell's genetic material, the DNA, meticulously arranged in chromosomes.
- Transcription and Translation: It regulates the synthesis of proteins through processes like transcription, where DNA's instructions are copied into RNA.
- Control Mechanism: The nucleus controls all cellular activities by sending out chemical messengers (mRNA) which direct protein synthesis at ribosomes.
🧬 Note: The nuclear envelope, a double membrane, separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm, allowing selective passage of molecules.
Mitochondria: The Powerhouse

The Mitochondria are crucial for:
- ATP Production: Known as the cell's powerhouse, they produce Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the cell, through cellular respiration.
- Metabolic Pathways: They're involved in the Krebs cycle, fatty acid oxidation, and the electron transport chain.
- Cellular Calcium Regulation: They manage calcium levels, which are important for signaling within the cell.
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Outer Membrane | Permeable to various molecules |
| Intermembrane Space | Space between outer and inner membranes |
| Inner Membrane | Houses the electron transport chain |
| Cristae | Increases surface area for ATP synthesis |
| Matrix | Site of Krebs cycle and fatty acid oxidation |

⚡ Note: Mitochondria have their own DNA and can divide independently of the cell, a phenomenon known as mitochondrial fusion and fission.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Protein and Lipid Synthesis


The Endoplasmic Reticulum comes in two forms:
- Rough ER: Ribosomes on its surface facilitate protein synthesis for secretory proteins, membrane proteins, or lysosomal enzymes.
- Smooth ER: Lacks ribosomes and is responsible for lipid synthesis, steroid production, and drug detoxification.
🌊 Note: The ER has a pivotal role in folding proteins correctly, a process crucial for their function.
Golgi Apparatus: The Cellular Post Office

The Golgi Apparatus plays a crucial role in:
- Sorting and Modifying: It modifies proteins and lipids transported from the ER, adding sugars or lipids to proteins (glycosylation).
- Packaging: Once processed, it packages these molecules into vesicles for transport to their destination.
- Secretion: It's involved in the secretion of cellular products like hormones.
Lysosomes: The Digestive System


Lysosomes are essential for:
- Digesting Material: They break down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign substances through hydrolysis.
- Autophagic Clearance: They remove damaged organelles or unnecessary cell parts through autophagy.
🗑️ Note: Lysosomal enzymes function best in acidic conditions, maintained by the lysosomal membrane.
Peroxisomes: Detoxification Squad

Peroxisomes are small organelles that:
- Detoxify: They break down toxic substances like alcohol and hydrogen peroxide through oxidative reactions.
- Beta-Oxidation: They perform this function to break down long fatty acids.
Chloroplasts: Photosynthesis Factories


Exclusively in plant cells, Chloroplasts:
- Photosynthesis: They convert sunlight energy into chemical energy via photosynthesis.
- Starch Storage: They store excess sugars in the form of starch granules.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Chlorophyll | Absorbs light energy for photosynthesis |
| Stroma | Houses the enzymes for the Calvin cycle |
| Thylakoids | Location of the light-dependent reactions |
| Granum | Stack of thylakoids |
In wrapping up our journey through the cellular landscape, it's clear that these organelles are not just structures but active participants in the life of a cell. Each plays a unique role, from managing genetic information to generating energy, detoxifying, and even capturing sunlight for energy. This intricate network of organelles ensures that every cell is a self-sufficient unit, optimized for the organism's needs. Remember, understanding these organelles not only sheds light on cellular function but also provides insights into health, disease, and biological engineering.
What is the primary function of the nucleus in a cell?

+
The primary function of the nucleus is to control the cell’s activities by managing its genetic material. It directs the synthesis of proteins through transcription and translation processes, ensuring cellular functions are properly executed.
Why are mitochondria called the powerhouse of the cell?

+
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse because they produce ATP, the cell’s primary energy currency, through cellular respiration. This process involves breaking down nutrients and converting them into energy.
How do lysosomes contribute to cellular health?

+
Lysosomes maintain cellular health by breaking down waste materials, damaged organelles, and external substances. They act as the cell’s digestive system, recycling components and eliminating unnecessary materials.
What is the role of peroxisomes in cellular detoxification?

+
Peroxisomes play a crucial role in detoxifying the cell by breaking down toxic substances like alcohol and hydrogen peroxide. They contain enzymes for oxidation reactions, which help eliminate these harmful compounds.
How does the Golgi apparatus differ from the Endoplasmic Reticulum?

+
The Golgi apparatus further processes, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids that have been synthesized in the Endoplasmic Reticulum. While the ER is primarily involved in synthesis, the Golgi modifies, packages, and directs these molecules for secretion or for use within the cell.