5 Essential Answers for Cell Cycle Labeling Worksheet

Understanding the cell cycle is fundamental to biology, as it describes the process by which cells grow, replicate their DNA, and divide. A common educational tool to grasp these concepts is through cell cycle labeling worksheets. In this detailed guide, we will explore the five essential answers often sought in such worksheets, aiding both students and educators in comprehending this vital biological process.
What is the Cell Cycle?

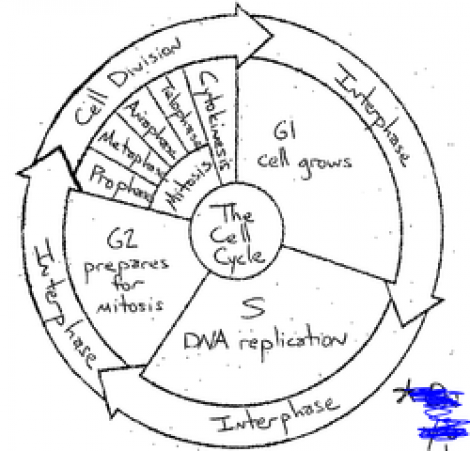
The cell cycle is a series of events that take cells through growth, DNA replication, and division. It's divided into two primary phases:
- Interphase: Where the cell grows and replicates its DNA in preparation for cell division.
- Mitotic Phase (M Phase): Where the cell divides into two daughter cells.
📌 Note: The cell cycle ensures cells replicate DNA accurately and maintain genetic stability.
Here's a brief overview of each stage:
- G1 Phase (First Gap): The cell grows in size and prepares for DNA replication.
- S Phase (Synthesis): DNA replication occurs, doubling the genetic material.
- G2 Phase (Second Gap): The cell prepares for mitosis by checking for errors in DNA replication and growing further if necessary.
- Mitosis (M Phase): This includes stages like prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase where the nucleus and genetic material divide.
- Cytokinesis: The final stage where the cytoplasm divides, marking the end of cell division.

How is the Cell Cycle Labeled in Worksheets?

In cell cycle labeling worksheets, students are typically given:
- A diagram of the cell cycle with phases labeled.
- Questions requiring them to identify and label these stages.
Here are the key elements usually labeled:
| Stage | Label |
|---|---|
| Interphase | G1, S, G2 |
| Mitotic Phase | M |
| Cytokinesis | C |

Which Phases Are Most Critical for DNA Replication?

The S phase is most critical for DNA replication during the cell cycle:
- During S phase, the cell's DNA is duplicated, ensuring that each new daughter cell has an identical set of chromosomes.
- Errors in DNA replication can lead to mutations, which might affect the cell's function or lead to diseases like cancer if left unchecked.
🔬 Note: Accurate DNA replication in the S phase is crucial for maintaining genetic fidelity.
How Does the Cell Cycle Differ Between Plant and Animal Cells?

While the fundamental principles of the cell cycle remain the same, there are notable differences:
- Plant cells:
- Have a cell plate formed during cytokinesis, which eventually develops into a new cell wall.
- May lack centrosomes but have a cell plate guiding the division plane.
- Animal cells:
- Undergo cleavage furrow formation during cytokinesis, pinching the cell into two.
- Typically have centrosomes, which organize spindle fibers during mitosis.
These differences reflect the unique structural requirements of plant and animal cells during division.
What Happens If the Cell Cycle Goes Wrong?

When the cell cycle fails, several issues can arise:
- Cell cycle checkpoint failure: If checkpoints fail, cells might divide without proper preparation, leading to mutations or chromosomal abnormalities.
- Cancer: Dysregulation in the cell cycle can result in uncontrolled cell division, a hallmark of cancer.
- Apoptosis: Cells with severe DNA damage might undergo programmed cell death to prevent propagation of errors.
Understanding these errors helps in recognizing the importance of regulation and checks during the cell cycle.
Wrapping Up

From exploring the basic stages of the cell cycle to understanding its labeling in educational settings, we've covered crucial aspects that deepen our knowledge of cellular processes. The cell cycle is not just a sequence of events but a controlled mechanism ensuring proper growth, DNA replication, and division, vital for all living organisms. By mastering these concepts through worksheets, students gain insights into fundamental biological processes, preparing them for advanced studies in genetics, molecular biology, and medicine.
Why is the S phase considered crucial in the cell cycle?
+
The S phase or Synthesis phase is where DNA replication occurs, ensuring that each daughter cell has a complete set of genetic material. Any mistakes here can lead to genetic abnormalities.
How do plant and animal cells differ in cytokinesis?

+
Plant cells form a cell plate that grows into a new cell wall, while animal cells undergo cleavage furrow formation, effectively pinching the cell in two.
What are the consequences of a disrupted cell cycle?

+
A disrupted cell cycle can lead to mutations, uncontrolled cell division (cancer), or cellular self-destruction through apoptosis to protect the organism.