5 Essential Answers for Cell Cycle Label Worksheet

The cell cycle is a critical process in biology, involving several stages where cells grow and divide, ensuring the continuation of life. For students tackling cell cycle label worksheets, understanding this process is vital. Here are five essential answers to common questions on these worksheets, which will help clarify and reinforce your knowledge.
1. What is the Cell Cycle?

The cell cycle refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication of its DNA to produce two daughter cells. It consists of two main phases: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase:
- Interphase: The cell prepares for division, involving growth (G1), DNA replication (S), and preparation for division (G2).
- Mitotic (M) Phase: This phase includes nuclear division (mitosis) and the division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis).
2. How to Label the Phases of the Cell Cycle?
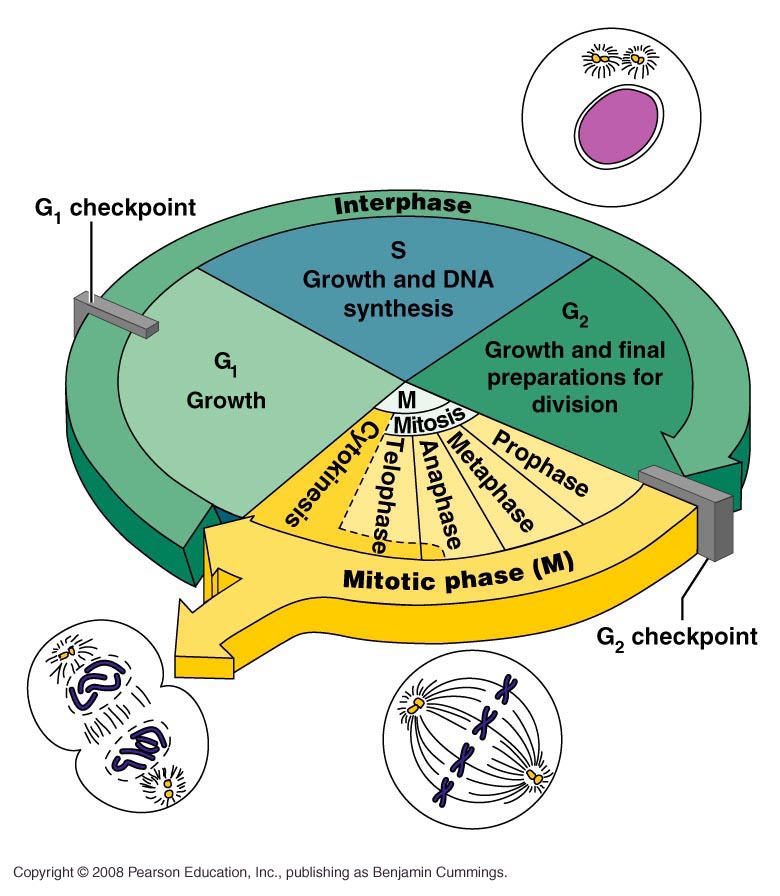
When working on cell cycle label worksheets, here’s how you can label the different stages:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Interphase (G1, S, G2) |
|
| Mitotic (M) Phase |
|

3. Understanding Checkpoints in the Cell Cycle

Worksheets often ask about checkpoints:
- G1 Checkpoint: Ensures cell size is adequate, nutrients are sufficient, and DNA is undamaged.
- G2 Checkpoint: Checks for proper DNA replication before entry into mitosis.
- Mitotic Checkpoint (Spindle Assembly Checkpoint): Ensures chromosomes are correctly attached to the spindle fibers before anaphase.
💡 Note: Checkpoints act as quality control points to prevent cell cycle progression if conditions are not met.
4. Labeling DNA Replication and Mitosis

Here are key points to keep in mind when labeling DNA replication and mitosis:
- S Phase (DNA Replication): You should label the stage where DNA is being duplicated.
- Mitosis (M Phase): This includes several steps, but for labeling purposes, focus on:
- Prophase: Chromatin condenses into chromosomes.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align at the spindle equator.
- Anaphase: Chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles.
- Telophase: Chromosomes decondense and new nuclear envelopes form.
5. Common Mistakes in Labeling the Cell Cycle

Avoid these common errors when completing cell cycle worksheets:
- Mixing up interphase phases or incorrectly labeling the order of events.
- Confusing mitosis stages, especially prophase with telophase or metaphase with anaphase.
- Overlooking the checkpoints, which are not stages but critical control points.
The cell cycle is foundational for growth, development, and repair in all living organisms. Understanding its mechanics, through exercises like cell cycle label worksheets, not only helps in visualizing these complex processes but also in appreciating the intricate control mechanisms governing life at the cellular level. Keep in mind the importance of accurate labeling to reflect the true sequence and function of each phase, ensuring a deeper comprehension of how cells perpetuate life.
What is the purpose of the cell cycle?

+
The cell cycle ensures cell growth, DNA replication, and division, which are crucial for organism growth, repair, and reproduction.
How can one differentiate between mitosis and cytokinesis?

+
Mitosis involves the division of the cell’s nucleus, while cytokinesis divides the cytoplasm, creating two separate cells.
Why are checkpoints important in the cell cycle?

+
Checkpoints ensure the cell’s DNA is intact and prepared for division, preventing the replication of damaged or improperly prepared cells which could lead to diseases like cancer.