5 Key Answers to Cell Cycle Worksheet Questions

📝 Note: This long-form blog post is designed for educational purposes, to assist students and educators in understanding cellular biology. Please provide accurate links, citations or resources for further study in place of placeholders like [External Link].
Unlocking the Mysteries of the Cell Cycle

Have you ever stopped to consider the intricate dance of cells that occurs trillions of times a day inside our bodies? Every moment, cells are meticulously going through the phases of the cell cycle, ensuring growth, repair, and the continuation of life. The study of the cell cycle is not just an academic exercise; it’s the key to understanding processes like cancer, embryonic development, and the effects of various treatments on living organisms. Today, we’re diving deep into five critical questions from a typical cell cycle worksheet, elucidating the mechanisms that make life possible.
Why is the Cell Cycle Important?

At the heart of cellular biology lies the cell cycle, a sequence of events that governs cell growth and division. Here’s why it matters:
- Growth and Repair: From healing wounds to the growth of a fetus, the cell cycle ensures cells are duplicated and replaced as needed.
- Replication: Accurate replication during the cell cycle ensures genetic continuity from parent to daughter cells.
- Disease and Treatment: Understanding the cell cycle helps in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases like cancer, where abnormal cell division occurs.
- Regeneration: Certain organisms can regenerate entire parts due to efficient cell cycle control.
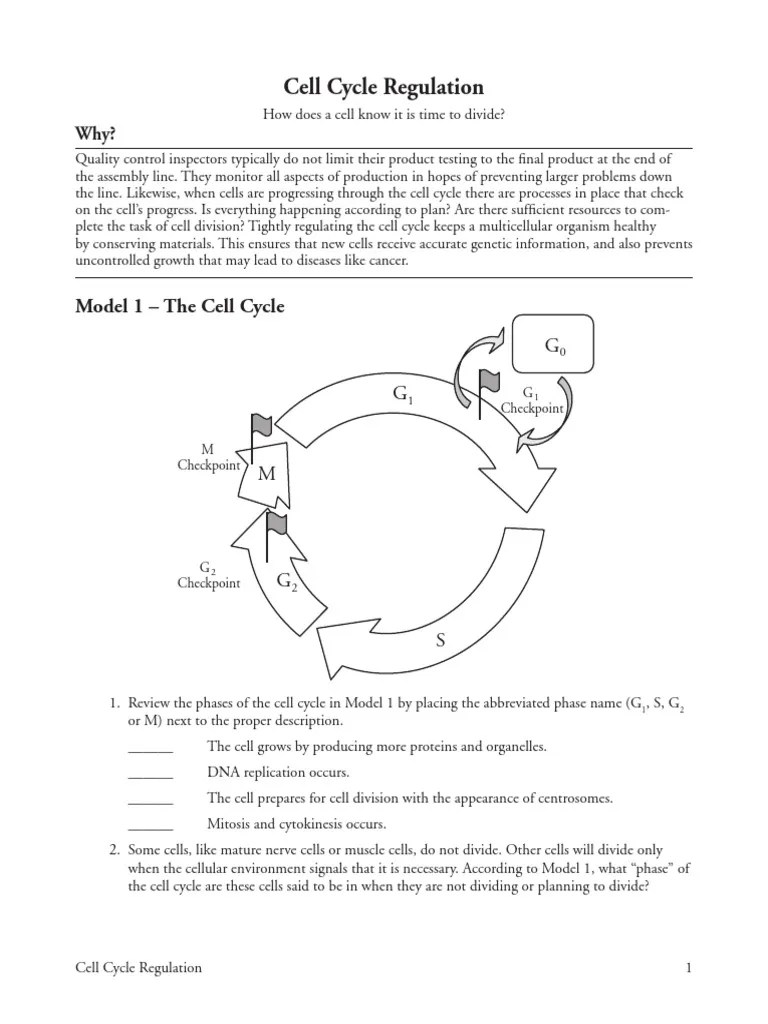
What are the Phases of the Cell Cycle?

The cell cycle can be broken down into several key phases:
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Interphase | The period of cell growth and DNA replication, split into: |
| G1 Phase | Cell grows, prepares for DNA replication. |
| S Phase | DNA synthesis; chromosomes are duplicated. |
| G2 Phase | Cell prepares for division; organelles duplicate. |
| Mitosis (M Phase) | The cell divides into two identical daughter cells: |
| Prophase | Chromatin condenses into chromosomes; spindle formation begins. |
| Prometaphase | Nuclear membrane breaks down; microtubules attach to chromosomes. |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes align at the spindle equator. |
| Anaphase | Sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles. |
| Telophase | Chromosomes de-condense; nuclear membranes reform. |
| Cytokinesis | Cytoplasm divides; two cells are fully formed. |

💡 Note: The phases mentioned above are in order, but the length of each phase varies among different cell types and conditions.
What Controls the Progression of the Cell Cycle?
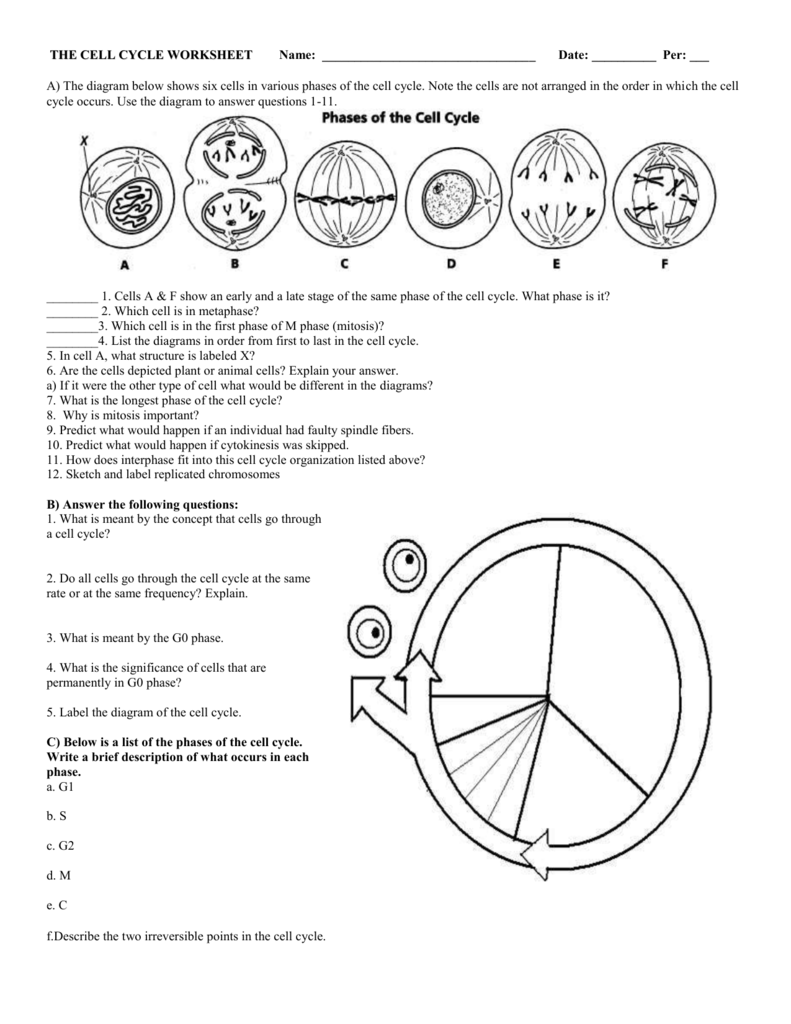
Progression through the cell cycle is tightly regulated by several mechanisms:
- Cell Cycle Checkpoints: These are critical junctures where the cell evaluates itself for problems:
- G1 Checkpoint: Checks if conditions are suitable for DNA synthesis.
- G2 Checkpoint: Assesses if DNA replication has been completed correctly.
- Mitotic Checkpoint: Ensures chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle.
- Cyclin Dependent Kinases (CDKs): These proteins, when bound to cyclins, drive cells through the cycle.
- Growth Factors: External signals like hormones can accelerate or inhibit cell cycle progression.
- DNA Damage Response: If damage is detected, cells may halt the cycle to repair or undergo apoptosis (programmed cell death).
🔬 Note: Errors in cell cycle regulation can lead to diseases like cancer, emphasizing the importance of understanding these control mechanisms.
How Can Cell Cycle Dysregulation Lead to Cancer?

Cancer cells often exhibit dysregulation of the cell cycle. Here are key mechanisms:
- Oncogenes: Mutations leading to the overproduction of growth factors or receptors, or alterations in CDKs or cyclins that push cells into uncontrolled division.
- Tumor Suppressor Genes: Inactivation of genes like p53 that normally halt cell cycle progression when damage is detected, allowing damaged cells to proliferate.
- Apoptosis Evasion: Cells become resistant to programmed cell death, enabling the survival of cells with oncogenic potential.
- Telomerase: The enzyme that prevents telomere shortening can be reactivated, allowing cancer cells to bypass senescence and divide indefinitely.
How Do Different Organisms Manage the Cell Cycle?
Various organisms have evolved different strategies to manage the cell cycle:
- Yeast: Relatively simple checkpoints, useful for basic research.
- Plants: Hormones like auxin play a role in cell cycle progression, especially in plant meristems.
- Humans: Complex interplay between CDKs, cyclins, and numerous control points, with significant variability between cell types.
- Animals (non-human): While sharing basic mechanics, certain animals show unique adaptations, such as specialized regeneration in salamanders.
The intricate process of the cell cycle is foundational to life. By understanding the stages, the control points, and the potential for dysregulation, we gain insights into life's growth, repair, and the genesis of diseases. It's a dance of molecules, proteins, and signals that sustains us, allowing for the replacement of cells that die naturally, the healing of injuries, and even the development of therapies that target abnormal cell growth.
In your journey to grasp the complexities of the cell cycle, remember that each phase is a step toward sustaining life, a marvel of biology that continues to amaze and challenge our understanding. Whether you're a student, educator, or curious mind, these five key answers to cell cycle worksheet questions provide a solid foundation for exploring this fundamental aspect of biology further.
What are the main differences between mitosis and meiosis?

+
Mitosis and meiosis both involve the division of cells, but mitosis produces two identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis produces four genetically distinct daughter cells with half the original number of chromosomes. Mitosis is for growth and repair in most body cells, while meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction, creating gametes.
Why does the cell cycle have checkpoints?

+
Checkpoints are vital to ensure quality control in the cell cycle. They act like gatekeepers, preventing cells from advancing to the next stage if there are issues like DNA damage, ensuring replication is completed, or if conditions aren’t optimal for cell division.
How does the cell cycle relate to cancer?
+
Cancer often results from errors in cell cycle regulation. Mutations in genes that control the cell cycle can lead to the unchecked division of cells, resulting in the formation of tumors. Understanding the cell cycle helps in designing targeted cancer treatments.