Cell Biology Coloring Worksheet Answers: Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes

🔬 Understanding the basic differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes can be fun and educational with a coloring worksheet. Here, we'll dive into what these cells look like under a microscope, how they function, and why each type has evolved in its unique way.
Introduction to Cells

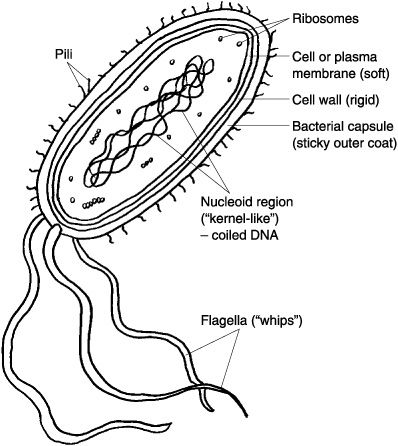
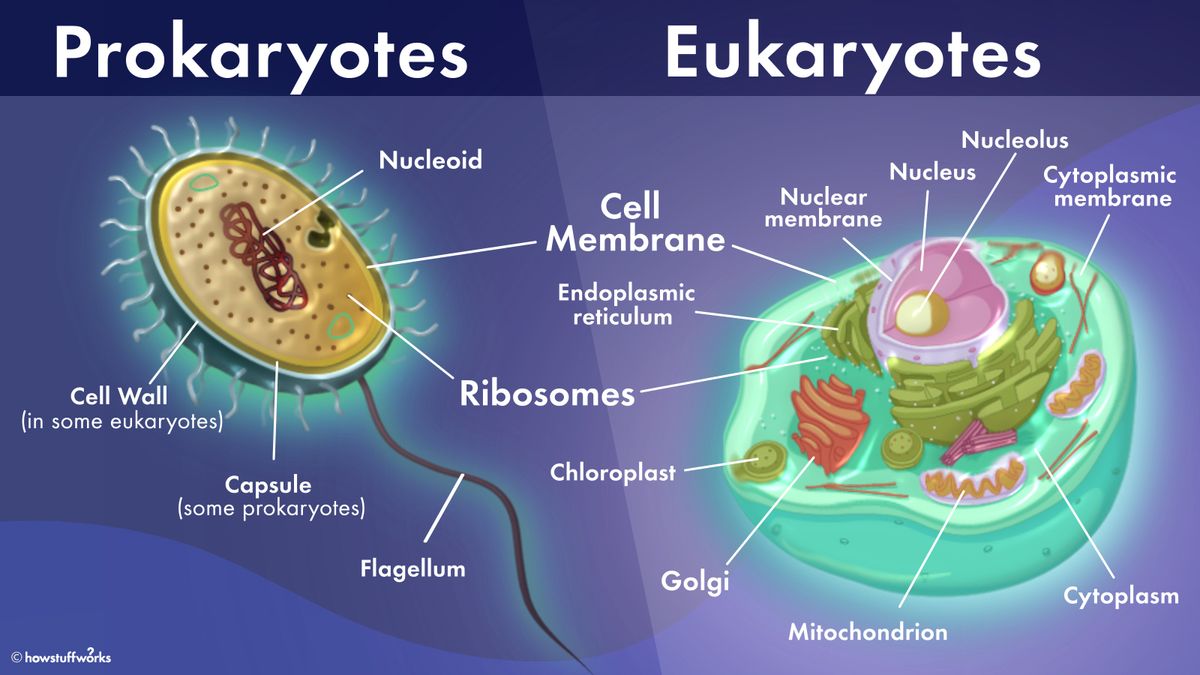
What Are Prokaryotes?

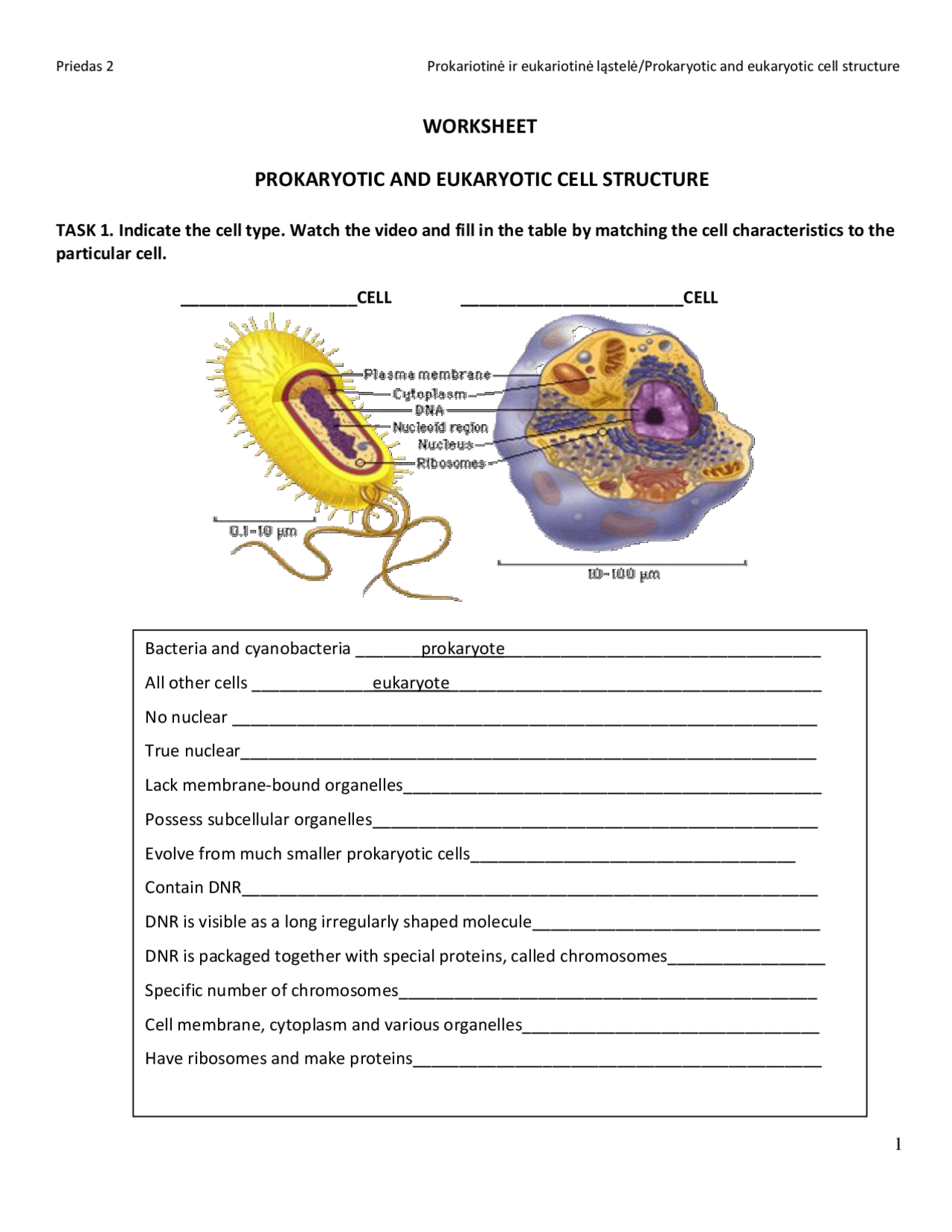
Prokaryotic cells are simpler and usually smaller than eukaryotic cells. Here are some key features:
- No Nucleus: Their DNA is not enclosed in a nuclear membrane, floating freely in the cytoplasm.
- Single-Cellular: Though some can form colonies, they primarily exist as single cells.
- Binary Fission: Their method of asexual reproduction, where a cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
🔍 Remember: Prokaryotes are not just simple; they play a crucial role in various ecosystems, including the human gut microbiome.
Exploring Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotes are characterized by their complexity:
- Nucleus: Contains the genetic material surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope.
- Membrane-bound Organelles: Such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, each with specific functions.
- Multicellular Organisms: Most eukaryotic organisms are multicellular, although some are single-celled, like yeast.
| Feature | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 0.1-5.0 μm | 10-100 μm |
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Reproduction | Binary fission | Mitosis or Meiosis |
| DNA | Circular, without histones | Linear, complexed with histones |
| Organelles | None | Mitochondria, chloroplasts, etc. |

Coloring Guide for Worksheet

When you’re working through your Cell Biology Coloring Worksheet, here’s how to color:
- Prokaryotic cell: Color the cell wall in light blue, the cytoplasm in pink, and the DNA loop in green.
- Eukaryotic cell: Use dark blue for the nucleus, orange for the mitochondria, yellow for the Golgi apparatus, and red for the cell membrane.
🎨 Ensure you use distinct colors for different organelles to make it easier to differentiate between them at a glance.
Key Differences in Function

The differences in structure reflect their different functions:
Energy Production:
- Prokaryotes: Produce energy through glycolysis in the cytoplasm, with some having electron transport chains in their cell membrane.
- Eukaryotes: Mitochondria in eukaryotic cells are the powerhouse, producing ATP via aerobic respiration.
Reproduction:
- Prokaryotes have a straightforward approach with binary fission.
- Eukaryotes have more complex methods like mitosis and meiosis, allowing for genetic diversity.
Cellular Complexity:
- Prokaryotes have less specialization, performing many functions in the same cytoplasmic environment.
- Eukaryotes can compartmentalize functions, optimizing cellular processes.
The evolutionary path has shaped these cells for different environments:
- Prokaryotes: Have adapted to extreme environments, from the hot springs to the human gut, thanks to their resilience and simple structure.
- Eukaryotes: Their complexity has allowed for the development of multicellular life forms, increasing their adaptability to various niches through specialization.
Why This Matters

Understanding these distinctions is crucial for various fields:
- Biotechnology: Manipulating prokaryotes for the production of medicines and biofuels.
- Medicine: Knowing how cells function aids in understanding diseases, like how bacterial infections differ from viral ones at a cellular level.
- Ecology: Prokaryotes and eukaryotes play distinct roles in ecosystems, from decomposition to oxygen production.
In this journey of coloring and learning, you’ve explored not just the structural but also the functional differences between these two cell types. Through this, you’ve gained insight into the marvelous world of cellular biology, where every difference has shaped the course of life on Earth.
To wrap up, recognizing the basic units of life through their differences not only enhances our understanding of biology but also inspires awe at the microscopic world’s complexity and functionality. Each cell, whether prokaryotic or eukaryotic, tells a story of life’s resilience and adaptability, reminding us of the intricate beauty in diversity.
What are the primary differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
+
Prokaryotes lack a nucleus, have simple DNA structure, and perform basic functions. Eukaryotes have a nucleus, complex DNA, and specialized organelles for varied functions.
Why don’t prokaryotes have a nucleus?

+
Their genetic material is organized differently, not requiring a nuclear membrane, which suits their simple and rapid reproductive strategies.
How do mitochondria function in eukaryotic cells?

+
Mitochondria are the primary sites of ATP production, converting nutrients into usable energy through cellular respiration.