Can You MIG Weld Stainless Steel Effectively

MIG (GMAW) welding is a popular process for joining stainless steel, but it requires careful attention to detail and technique to produce high-quality welds. Stainless steel is a versatile material with many benefits, including corrosion resistance, high strength, and low maintenance. However, its unique properties also present challenges when welding.
Challenges of MIG Welding Stainless Steel

Thermal Expansion and Contraction: Stainless steel has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, which can cause distortion and warping during welding. This can lead to uneven welds and reduced accuracy.
Oxidation and Discoloration: When heated, stainless steel can oxidize, resulting in discoloration and reduced corrosion resistance. This can be minimized by using shielding gases and controlling heat input.
Lack of Fusion: Stainless steel has a high thermal conductivity, which can lead to incomplete fusion and poor weld quality if the heat input is insufficient.
Preparation is Key

To MIG weld stainless steel effectively, proper preparation is essential. This includes:
- Cleaning the workpiece: Remove dirt, oil, and grease to prevent contamination and porosity.
- Choosing the right filler metal: Select a filler metal that matches the base metal composition and is suitable for the welding process.
- Setting up the welding equipment: Adjust the welding machine, gun, and consumables according to the manufacturer’s recommendations and the specific welding process.
MIG Welding Techniques for Stainless Steel

- Use a push technique: Hold the gun at a 10-15° angle, with the nozzle 1⁄2 inch from the workpiece. This helps to prevent oxidation and promotes a smooth, even weld.
- Maintain a consistent heat input: Use a steady, consistent motion to maintain a consistent heat input and prevent overheating or underheating.
- Use a shielding gas: Argon-rich shielding gases (e.g., 90% Ar, 10% CO2) are suitable for MIG welding stainless steel. The gas flow rate should be adjusted to maintain a stable arc and prevent porosity.
- Monitor the weld pool: Adjust the heat input and travel speed to maintain a stable, consistent weld pool.
Welding Parameters for Stainless Steel

The welding parameters for stainless steel MIG welding will vary depending on the specific application, base metal thickness, and desired weld quality. Here are some general guidelines:
| Base Metal Thickness | Welding Current | Voltage | Wire Feed Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1⁄8 inch (3 mm) | 120-180 A | 18-22 V | 200-250 ipm |
| 1⁄4 inch (6 mm) | 180-250 A | 20-25 V | 250-300 ipm |
| 1⁄2 inch (12 mm) | 250-350 A | 22-28 V | 300-350 ipm |

Note: These parameters are general guidelines and may need to be adjusted based on the specific application and welding conditions.
💡 Note: Always consult the manufacturer's recommendations for specific welding parameters and techniques for your equipment and materials.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting

- Porosity: Insufficient shielding gas, inadequate heat input, or poor wire feed speed can cause porosity. Adjust the gas flow rate, heat input, and wire feed speed to maintain a stable arc and prevent porosity.
- Lack of fusion: Insufficient heat input or poor wire feed speed can cause incomplete fusion. Adjust the heat input and wire feed speed to maintain a consistent weld pool.
- Discoloration: Excessive heat input or poor shielding gas can cause discoloration. Adjust the heat input and shielding gas to maintain a stable arc and prevent discoloration.
Conclusion
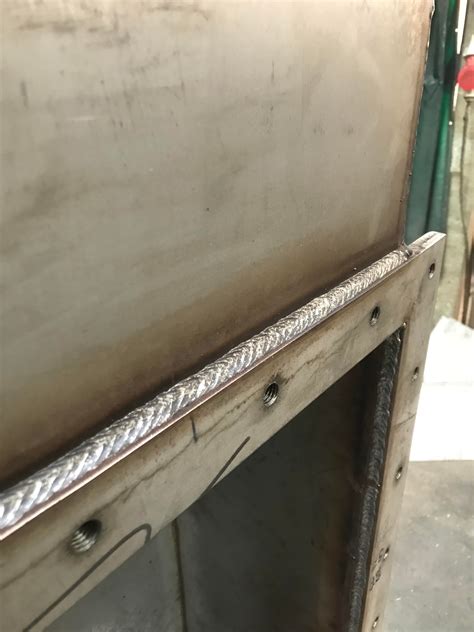

MIG welding stainless steel requires attention to detail, proper preparation, and technique to produce high-quality welds. By understanding the challenges of welding stainless steel, preparing the workpiece, and using the correct techniques and parameters, you can effectively MIG weld stainless steel.
What is the best shielding gas for MIG welding stainless steel?

+
Argon-rich shielding gases (e.g., 90% Ar, 10% CO2) are suitable for MIG welding stainless steel.
What is the recommended wire feed speed for MIG welding stainless steel?

+
The wire feed speed will vary depending on the base metal thickness and desired weld quality. A general guideline is 200-350 ipm.
How can I prevent porosity when MIG welding stainless steel?

+
Adjust the gas flow rate, heat input, and wire feed speed to maintain a stable arc and prevent porosity.
Related Terms:
- Stainless Steel MIG wire
- MIG welding stainless steel settings
- 308LSi Stainless steel MIG Wire
- Stainless MIG gas