Can Russia Defeat NATO

Introduction to the Conflict

The question of whether Russia can defeat NATO is a complex one, involving a deep analysis of military capabilities, strategic alliances, and geopolitical dynamics. The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is a military alliance established in 1949, comprising 30 North American and European countries. Russia, with its vast military resources and strategic nuclear arsenal, poses a significant challenge to NATO’s collective defense commitments. This analysis will delve into the military strengths and weaknesses of both parties, their historical contexts, and the strategic considerations that could influence the outcome of such a conflict.
Military Capabilities of Russia and NATO

Russia boasts an impressive military arsenal, including a significant nuclear deterrent, advanced missile systems, and a large conventional force. Its military modernization efforts have focused on enhancing its capabilities in areas such as cyber warfare, electronic warfare, and precision-guided munitions. NATO, on the other hand, benefits from the collective military might of its member states, including the United States, which has the world’s most advanced and technologically sophisticated military. The alliance’s military capabilities are complemented by its integrated command structure and the principle of collective defense enshrined in Article 5 of the NATO treaty.
Strategic Considerations

Several strategic considerations are crucial in assessing the potential outcome of a conflict between Russia and NATO: - Nuclear Deterrence: Russia’s nuclear arsenal is a significant factor. The use of nuclear weapons would have catastrophic consequences, making this option highly unlikely unless in the face of an existential threat. - Conventional Military Balance: The conventional military balance between Russia and NATO is complex. While Russia has made significant strides in modernizing its military, NATO’s collective conventional military capabilities, particularly with the involvement of the United States, are considerable. - Geopolitical Alliances: The geopolitical landscape plays a crucial role. Russia’s relations with other global powers, such as China, and its ability to potentially divide NATO members, could influence the conflict’s dynamics. - Cyber and Electronic Warfare: The role of cyber and electronic warfare cannot be underestimated. Russia has demonstrated sophisticated capabilities in these areas, which could significantly impact NATO’s command and control structures and military operations.
Historical Context

The historical context of the Cold War and the post-Cold War era provides valuable insights into the current dynamics between Russia and NATO. The end of the Cold War saw a period of relative peace, with NATO expanding eastward and Russia initially engaging in cooperation with the West. However, the annexation of Crimea by Russia in 2014 and ongoing conflicts in Eastern Ukraine have significantly deteriorated relations. This historical backdrop sets the stage for current tensions and the potential for conflict.
Tactical and Strategic Advantages

Both Russia and NATO have tactical and strategic advantages: - Russia’s Advantages: - Proximity to Conflict Zones: Russia’s geographical proximity to potential conflict zones, such as the Baltic States or Ukraine, allows for quicker response times and logistical advantages. - Asymmetric Warfare Capabilities: Russia has shown proficiency in asymmetric warfare, including cyber attacks and support for separatist movements, which can weaken adversaries without engaging in conventional warfare. - NATO’s Advantages: - Collective Defense Commitment: The principle of collective defense means that an attack on one member state is considered an attack on all, providing a strong deterrent against aggression. - Economic and Technological Superiority: The combined economic and technological prowess of NATO member states, particularly the United States, provides significant advantages in terms of military technology, logistics, and sustainability of operations.
Conclusion of Analysis
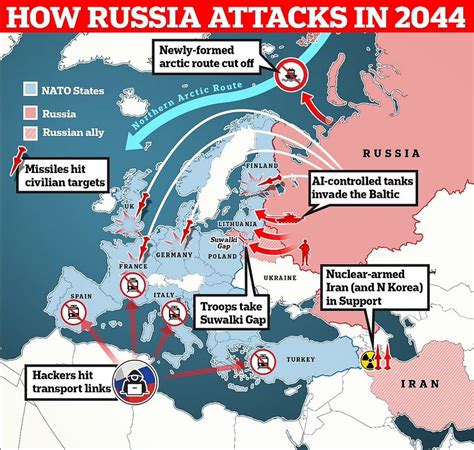
In conclusion, the question of whether Russia can defeat NATO is multifaceted and depends on various factors, including the nature of the conflict, the strategic objectives of both parties, and the geopolitical context. While Russia possesses significant military capabilities and strategic advantages, NATO’s collective might, technological superiority, and commitment to collective defense pose substantial challenges. The most likely scenario is not a conventional war but a continuation of the current state of tensions, with both sides engaging in a mix of diplomatic, economic, and military strategies to achieve their objectives without triggering a large-scale conflict.
What is the significance of NATO’s collective defense commitment?

+
NATO’s collective defense commitment, as outlined in Article 5 of the NATO treaty, signifies that an attack on one member state is considered an attack on all, thereby providing a strong deterrent against potential aggressors and ensuring the security and stability of the North Atlantic area.
How does Russia’s nuclear arsenal influence the dynamics of a potential conflict with NATO?

+
Russia’s nuclear arsenal acts as a significant deterrent, making the prospect of a large-scale conflict between Russia and NATO highly unlikely due to the catastrophic consequences of nuclear war. This deterrent effect shapes the strategic calculus of both parties, favoring the pursuit of objectives through non-military means or limited, conventional military actions.
What role does cyber and electronic warfare play in the conflict dynamics between Russia and NATO?

+
Cyber and electronic warfare are critical components of modern conflict, allowing for the disruption of command and control systems, intelligence gathering, and the degradation of an adversary’s military capabilities without the need for conventional military engagement. Russia has demonstrated significant capabilities in these areas, which could be leveraged to weaken NATO’s response capabilities in the event of a conflict.