5 Proven Methods to Calculate pH and pOH Easily
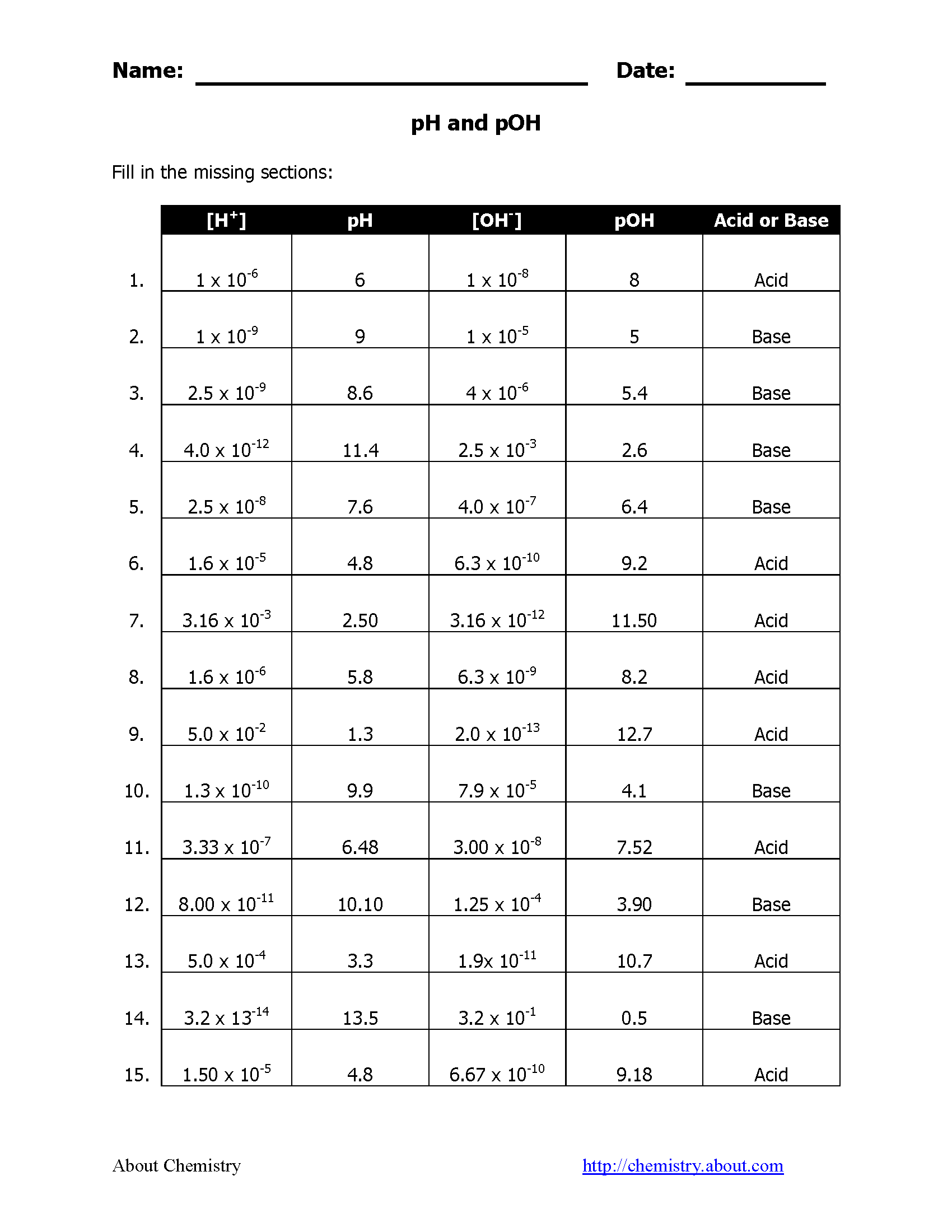
Understanding pH and pOH is essential for anyone working in chemistry, particularly in fields like water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and biology. These values indicate how acidic or basic a solution is, which impacts countless chemical reactions and biological processes. Here, we explore five proven methods to calculate pH and pOH easily, enhancing accuracy and simplifying what might otherwise seem complex calculations.
Method 1: Using a pH Meter

A pH meter is the most direct and accurate tool for measuring pH:
- Calibrate the meter using buffer solutions with known pH values.
- Insert the electrode into your sample.
- Read the pH value from the meter display.
To find pOH, use the equation:
🔍 Note: pOH = 14 - pH
Method 2: pH Indicator Paper

Indicator papers provide a quick and cost-effective method:
- Dip the strip into the solution.
- Compare the resulting color to the pH chart provided.
Important: Indicator papers are less precise than pH meters but are useful for quick estimations.
Method 3: Acid-Base Titration
This method is excellent for determining the pH of an unknown solution:
- Set up a known concentration of a strong acid or base (the titrant).
- Using a burette, add this titrant dropwise to your sample while stirring.
- At the equivalence point, note the pH using a pH meter or a visual indicator like phenolphthalein.
To calculate pOH:
🔍 Note: pOH = -log[OH-]
Method 4: The Ion Product of Water

At 25°C, the ion product of water ((K_w)) is (1.0 \times 10^{-14}). Using this, you can:
- Determine pH or pOH by measuring either the concentration of (H^+) or (OH^-) ions.
- Use the equation (K_w = [H^+][OH^-]) to find the missing concentration.
🔍 Note: pH = -log[H+] or pOH = -log[OH-]
Method 5: pH Calculation from Buffer Solution

Buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH:
- Apply the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: [ pH = pK_a + \log \left( \frac{[\text{A}^-]}{[\text{HA}]} \right) ]
- Here, (pK_a) is the negative log of the acid dissociation constant, ([\text{A}^-]) is the concentration of the conjugate base, and ([\text{HA}]) is the concentration of the undissociated weak acid.
For pOH:
🔍 Note: pOH = 14 - pH
Each method discussed offers its own set of advantages and contexts in which it is most effective. By understanding these techniques, one can choose the most suitable approach for any given situation in laboratory analysis, environmental science, or even daily applications like managing pool pH levels.
In summary, whether you're dealing with industrial processes, academic research, or personal curiosity, these methods provide a robust toolkit for measuring and understanding the acidic or basic nature of solutions. The choice of method depends on the required accuracy, resources at hand, and the nature of the solution you are working with. It's worth noting that while technology has provided more accurate tools like pH meters, traditional methods like indicator papers or titrations remain valuable for their simplicity, educational value, and application in various settings.
How accurate are pH meter readings?

+
pH meters, when correctly calibrated, offer readings accurate to ±0.01 pH units. However, accuracy can vary due to factors like temperature, electrode condition, and sample composition.
Can I measure pH without a pH meter?

+
Yes, you can use pH indicator papers, natural indicators like litmus, or conduct titrations with an acid-base indicator for pH measurement, albeit with less precision than a meter.
What is the significance of pH in biological systems?

+
pH affects enzyme activity, nutrient uptake, and many cellular processes. Most biological systems function optimally within a narrow pH range, making pH regulation vital for life.