Calculating Nucleus Particles Worksheet Answer Key Revealed
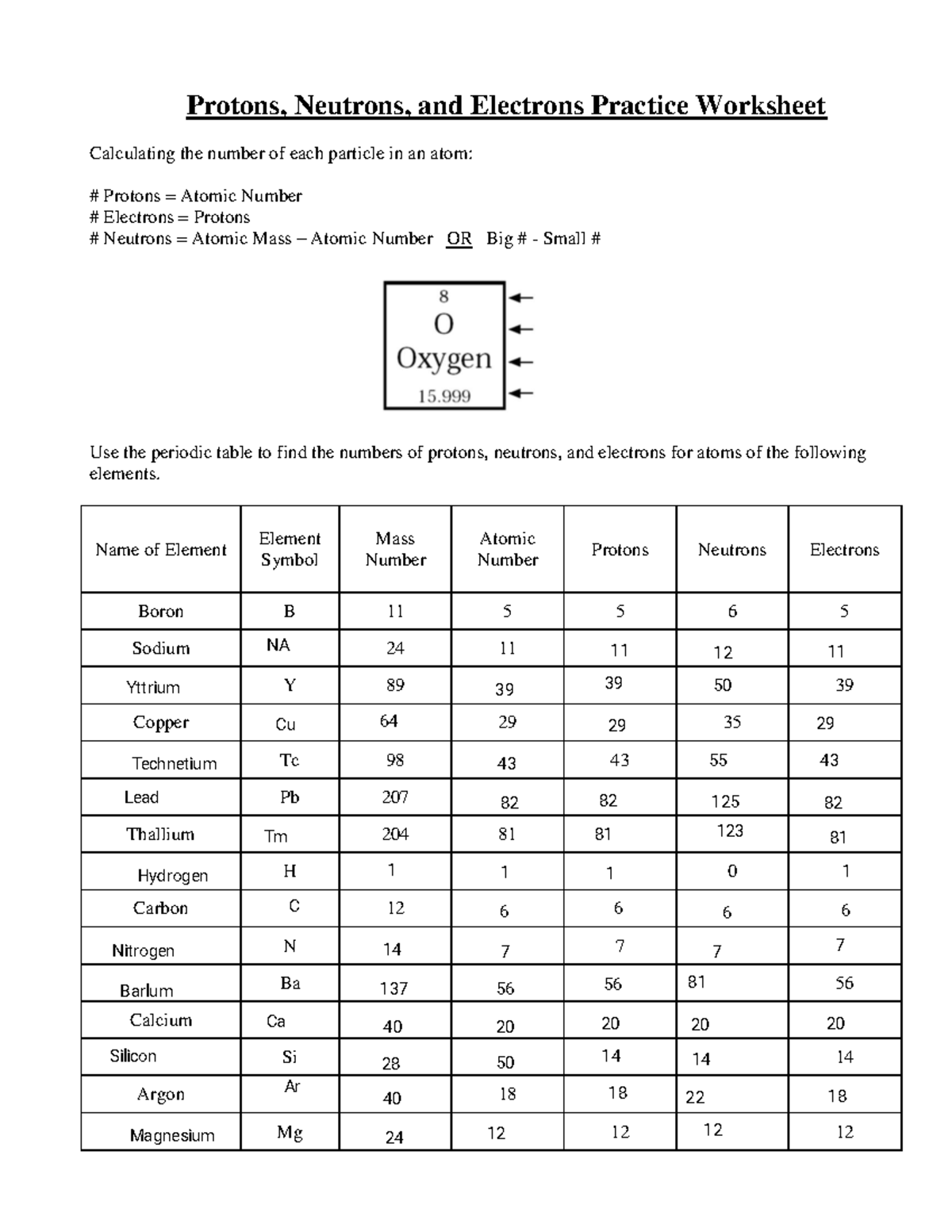
In the fascinating world of nuclear physics, understanding the components that make up an atom's nucleus is essential. A common task in educational settings involves the calculation and identification of protons, neutrons, and electrons, often referred to as the nucleus particles. Today, we're diving deep into a "Calculating Nucleus Particles Worksheet Answer Key" to provide clarity on this intricate subject. This blog post aims to guide students, educators, and enthusiasts through the process of mastering this aspect of nuclear physics, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of atomic structure and particle calculations.
Understanding Atomic Structure

Before we jump into calculations, let’s revisit the basics. An atom consists of:
- Protons - Positively charged particles found in the nucleus.
- Neutrons - Neutrally charged particles also located in the nucleus.
- Electrons - Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus.
The atomic number (Z) of an element represents the number of protons in its nucleus, which defines the element’s identity. The mass number (A) is the sum of protons and neutrons. This information is crucial for calculating the number of nucleus particles.
The Worksheet Answer Key

Let’s now delve into the key answers for a typical “Calculating Nucleus Particles Worksheet”.
Question 1:

If an atom has an atomic number of 6 and a mass number of 12, calculate the number of:
| Particle | Number |
|---|---|
| Protons | 6 |
| Neutrons | 6 (12 - 6) |
| Electrons | 6 (For a neutral atom) |

💡 Note: In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons.
Question 2:

An atom has 9 protons and a mass number of 19. Calculate the following:
- Protons: 9
- Neutrons: 19 - 9 = 10
- Electrons: 9 (For a neutral atom)
Question 3:

If an isotope has 17 protons, 18 neutrons, and 18 electrons, determine its atomic number, mass number, and charge:
- Atomic Number: 17
- Mass Number: 17 + 18 = 35
- Charge: -1 (Since there is one more electron than proton)
⚠️ Note: The charge of an ion is determined by comparing the number of electrons to protons. More electrons than protons results in a negative ion.
Advanced Calculations: Isotopes and Ions

Beyond basic calculations, understanding isotopes and ions is crucial:
Isotopes

- Isotopes are variants of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, thus having different mass numbers. For example, chlorine has two stable isotopes: chlorine-35 (17 protons, 18 neutrons) and chlorine-37 (17 protons, 20 neutrons).
Ions

- Ions occur when an atom gains or loses electrons, resulting in a net charge. An ion with more electrons than protons is negatively charged, while one with fewer electrons is positively charged.
To calculate nucleus particles for isotopes or ions:
- Identify the atomic number (protons) and mass number (protons + neutrons).
- If an ion, note the difference in the number of electrons compared to protons for charge calculation.
Wrapping Up the Insights

Navigating through this "Calculating Nucleus Particles Worksheet Answer Key" has shed light on the complex interplay of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom's nucleus. Understanding how to calculate these particles not only enriches one's grasp of nuclear physics but also equips students and educators with the tools to explore further into atomic theory. Remember, the atomic world is intricate and fascinating, where every particle has a role, and every atom is a universe of its own. Whether you're dealing with neutral atoms, isotopes, or ions, the principles we've discussed provide a solid foundation for deeper exploration into chemistry and physics.
What does the atomic number signify?

+
The atomic number signifies the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. It determines the element’s identity.
How can you calculate the number of neutrons?

+
You calculate the number of neutrons by subtracting the atomic number (number of protons) from the mass number (protons + neutrons).
What happens if an atom has more electrons than protons?

+
If an atom has more electrons than protons, it becomes a negatively charged ion, also known as an anion.
