Master Net Force Calculation with Our Worksheet

Understanding net force is fundamental for anyone studying physics, especially in mechanics. It's the sum of all forces acting on an object, determining whether it accelerates, decelerates, or stays at rest. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the concept of net force, providing practical examples, and introducing a net force calculation worksheet to help you master this essential skill.
Understanding Net Force


Net force is the total force exerted on an object after accounting for all the forces acting upon it. Here’s what you need to know:
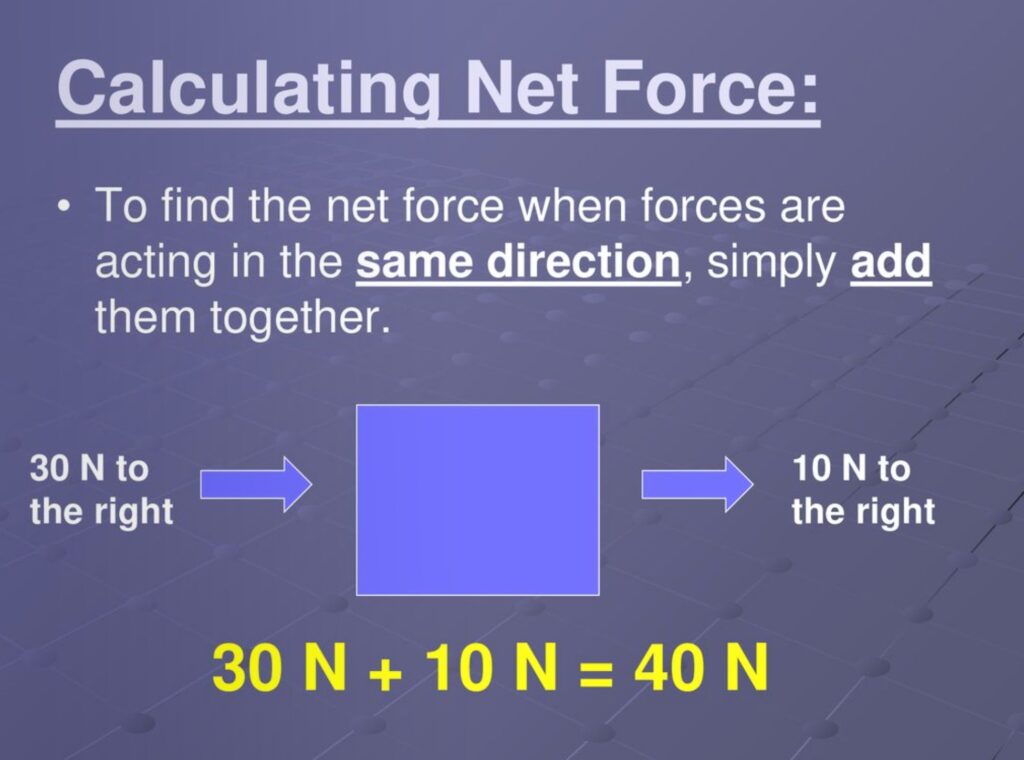
- Directionality: Forces are vector quantities, meaning they have both magnitude and direction. When calculating net force, we must consider the direction each force is applied.
- Equilibrium: When the net force on an object is zero, the forces are balanced, and the object is in static or dynamic equilibrium.
- Acceleration: A net force not equal to zero leads to acceleration or deceleration, governed by Newton’s Second Law: F = ma.
Newton’s First Law
An object at rest tends to stay at rest, and an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced net force.
Newton’s Second Law

The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. Mathematically, Fnet = ma.
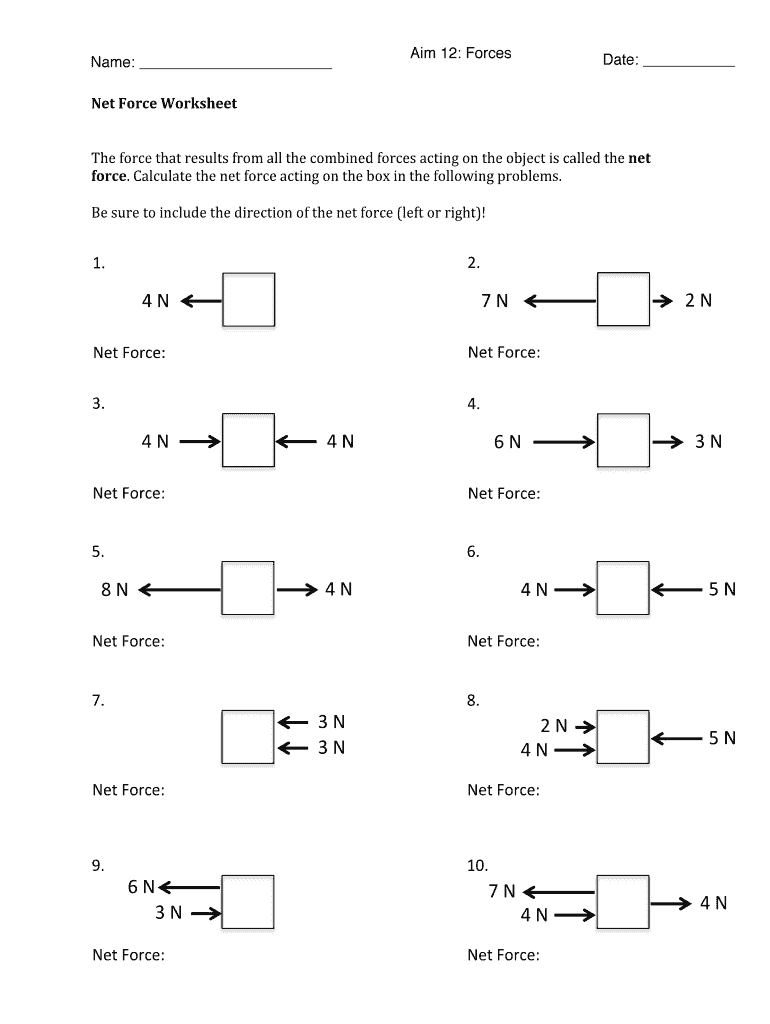
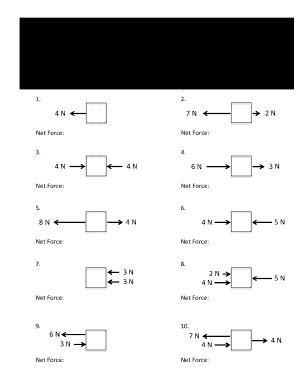
Net Force Calculation Worksheet


To hone your understanding and calculation skills, we’ve created a net force calculation worksheet. Here’s how to approach the problems:
- Identify All Forces: Draw free-body diagrams to visualize the forces acting on an object.
- Determine Direction: Assign positive and negative directions to simplify calculations. Typically, forces to the right or upward are positive, and left or downward are negative.
- Sum Forces: Add forces as vector sums. Remember to use the correct sign for direction.
- Calculate Acceleration: Use the net force to find the acceleration if required.
| Force | Direction | Magnitude (N) | Net Force Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Push | Right (+) | 25 | +25 |
| Friction | Left (-) | 10 | -10 |
| Net Force: | +15 | ||

Example Problem

Consider a book on a table with the following forces: - Gravity pulling down with a force of 10N, - Normal force from the table pushing up with 10N, - A hand pushing the book to the right with 20N, - Friction from the table pulling to the left with 15N.
To calculate the net force:
- Net force in the vertical direction: 10N (up) - 10N (down) = 0 N.
- Net force in the horizontal direction: 20N (right) - 15N (left) = 5 N to the right.
📌 Note: When calculating net force, remember to consider the resultant direction after summing vectors.
Advanced Net Force Scenarios


Real-world applications often involve complex force scenarios where multiple forces act in different planes:
- Multidirectional Forces: When forces are in different planes (e.g., horizontal and vertical), consider resolving them into their components.
- Pulley Systems: Involving forces like tension, gravity, and friction, understanding net force here requires considering each segment of the system separately.
- Circular Motion: Net force includes centripetal force, requiring understanding of how forces balance to maintain circular motion.
Strategies for Complex Calculations
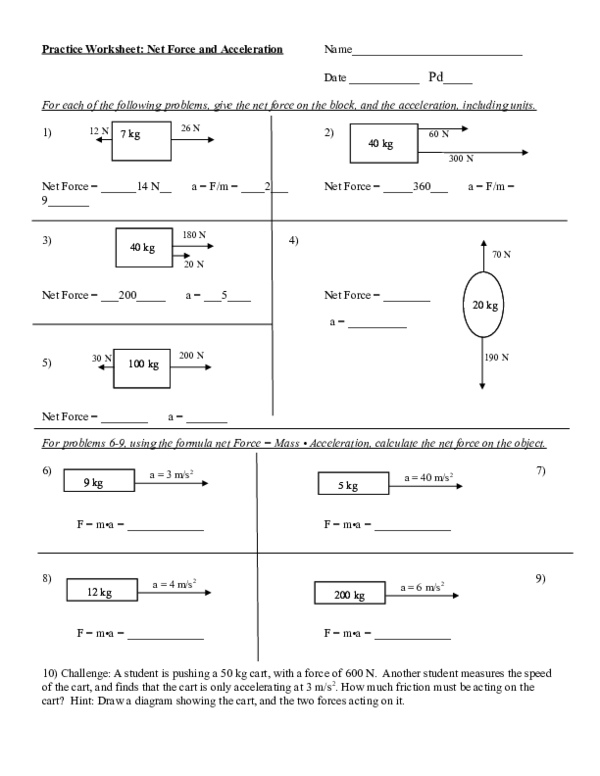
For complex net force calculations, follow these steps:
- Vector Decomposition: Break down forces into their x and y components when dealing with multidirectional forces.
- Free Body Diagrams: Always start with a detailed diagram to visualize all forces.
- Dynamic Equilibrium: Solve systems where multiple forces interact dynamically, often involving the application of several physical laws simultaneously.
- Check your Work: Verify your calculations by ensuring the net force matches your understanding of the object’s motion.
To solidify your understanding, practicing with real-world applications like elevators, car crashes, or sports mechanics can be insightful. Each scenario provides unique challenges in net force calculations, from uniform acceleration to variable motion.
📌 Note: In complex scenarios, precision in calculations is crucial as small errors can significantly affect the final net force.
In summary, mastering net force calculation involves understanding its basic principles, applying them to straightforward problems, and then expanding to more complex, real-world scenarios. The worksheet provided acts as a stepping stone, offering structured practice that reinforces theoretical knowledge with practical application. Whether you're studying physics or dealing with engineering problems, proficiency in calculating net forces will serve you well in analyzing and predicting the motion of objects.
What is net force?

+
Net force is the overall or resultant force acting on an object after summing up all the individual forces applied to it.
How do I determine the direction of net force?
+
To determine the direction, you add forces as vectors. Positive directions are typically right or upward, while left or downward are considered negative.
Can net force be zero?
+
Yes, when all forces acting on an object are balanced, the net force is zero, resulting in static or dynamic equilibrium.