5 Facts About the Browning Pistol from WW2

Introduction to the Browning Pistol

The Browning pistol, specifically the Hi-Power model, played a significant role in World War II, serving as a standard-issue sidearm for many Allied forces. Developed by John Browning and later improved upon by Dieudonné Saive, this pistol’s durability, reliability, and firepower made it a favorite among soldiers. Here are five key facts about the Browning pistol from WW2.
Fact #1: Origins and Design

The Browning Hi-Power was initially designed in the 1930s by John Browning, an American firearms designer. However, Browning passed away before completing the pistol’s design. Dieudonné Saive, a Belgian engineer at Fabrique Nationale (FN), continued Browning’s work and finalized the pistol’s design. The Hi-Power was eventually adopted by Belgium in 1935.
📝 Note: The Browning Hi-Power's design was influenced by the Browning M1911 pistol, which was widely used during World War I.
Fact #2: Wartime Production and Usage

During World War II, the Browning Hi-Power became a standard-issue sidearm for many Allied forces, including the British, Canadian, and Australian armies. The pistol was also used by the Belgian Resistance and other partisan groups. Due to its reliability and effectiveness, the Browning Hi-Power saw extensive use throughout the war, particularly in the European Theater.
Production Numbers:

- Fabrique Nationale (FN) produced approximately 319,000 Browning Hi-Power pistols during the war.
- The Canadian firm, Inglis, produced around 150,000 pistols under license.
Fact #3: Features and Specifications

The Browning Hi-Power was known for its durability, reliability, and firepower. Some of its key features include:
- Caliber: 9x19mm Parabellum
- Magazine capacity: 13 rounds
- Weight: approximately 900 grams (31.7 oz)
- Length: 197 mm (7.76 in)
- Barrel length: 118 mm (4.65 in)
💡 Note: The Browning Hi-Power's 13-round magazine capacity was impressive for its time, making it a popular choice among soldiers.
Fact #4: Variants and Modifications
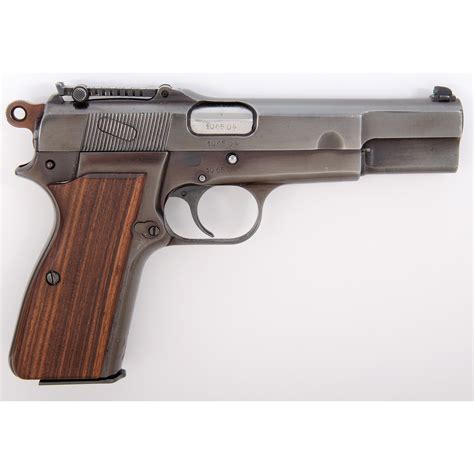

Throughout the war, several variants and modifications of the Browning Hi-Power were produced. Some notable examples include:
- Inglis Browning Hi-Power: A Canadian variant produced by Inglis, which featured a distinctive parkerized finish and a number of minor modifications.
- FN Browning Hi-Power: The standard Belgian-produced model, which was used by various Allied forces.
- T-series: A series of Hi-Power pistols produced for the British military, featuring a number of modifications, including a larger trigger guard and a redesigned safety lever.
Fact #5: Legacy and Impact

The Browning Hi-Power played a significant role in World War II, serving as a reliable and effective sidearm for many Allied forces. Its design and functionality also influenced the development of subsequent pistol designs, including the Browning BDM and the CZ 75.
🔥 Note: The Browning Hi-Power remained in service with various military forces long after World War II, with some countries still using the pistol today.
In summary, the Browning Hi-Power pistol was a significant contributor to the Allied war effort during World War II. Its durability, reliability, and firepower made it a favorite among soldiers, and its legacy continues to influence pistol design to this day.
What was the primary caliber of the Browning Hi-Power pistol?

+
The primary caliber of the Browning Hi-Power pistol was 9x19mm Parabellum.
Who designed the Browning Hi-Power pistol?

+
The Browning Hi-Power pistol was initially designed by John Browning, and later completed by Dieudonné Saive.
How many Browning Hi-Power pistols were produced during World War II?

+
Approximately 469,000 Browning Hi-Power pistols were produced during World War II, by Fabrique Nationale (FN) and Inglis.
Related Terms:
- Browning Hi Power
- browning hi power vs 1911
- Baby Browning
- WW2 machine gun
- browning hi power ww2
- Browning superposed