5 Main Branches of the US Army

The Foundation of the US Army: Understanding the 5 Main Branches

The United States Army is one of the most respected and formidable military forces in the world, with a rich history dating back to 1775. The Army is divided into several branches, each with its unique mission, responsibilities, and specialized skills. In this article, we will delve into the 5 main branches of the US Army, exploring their roles, functions, and importance in the overall military structure.
1. Infantry Branch

The Infantry Branch is the backbone of the US Army, responsible for land-based military operations. Infantry soldiers are trained to engage in ground combat, using a variety of tactics and techniques to defeat enemy forces. The Infantry Branch is further divided into several sub-branches, including:
- Light Infantry: Specializing in rapid deployment and mobility, light infantry units are trained to operate in a variety of environments, from urban to wilderness.
- Mechanized Infantry: Equipped with armored vehicles, mechanized infantry units provide mobile firepower and protection on the battlefield.
- Airborne Infantry: Trained to conduct parachute assaults and airfield seizures, airborne infantry units are elite forces capable of rapid deployment behind enemy lines.
💡 Note: Infantry soldiers must be physically fit and able to perform strenuous tasks in challenging environments.
2. Armor Branch

The Armor Branch is responsible for the operation and maintenance of armored vehicles, including tanks, infantry fighting vehicles, and armored personnel carriers. Armor soldiers are trained to conduct armored assaults, provide mobile firepower, and support infantry operations.
- Tank Crews: Operating the M1 Abrams tank, tank crews provide heavy firepower and armor protection on the battlefield.
- Armored Cavalry: Conducting reconnaissance and security missions, armored cavalry units provide real-time intelligence and early warning systems.
3. Artillery Branch

The Artillery Branch provides indirect fire support to infantry and armor units, using a variety of artillery systems, including howitzers, rockets, and missiles. Artillery soldiers are trained to conduct fire missions, provide suppressive fire, and destroy enemy targets.
- Field Artillery: Operating towed and self-propelled howitzers, field artillery units provide precision fire support to ground units.
- Air Defense Artillery: Trained to defend against aerial threats, air defense artillery units operate surface-to-air missile systems and anti-aircraft guns.
4. Aviation Branch

The Aviation Branch provides air support to ground units, using a variety of aircraft, including helicopters, planes, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Aviation soldiers are trained to conduct transportation, reconnaissance, and attack missions.
- Helicopter Units: Operating UH-60 Black Hawk and AH-64 Apache helicopters, aviation units provide transportation, medical evacuation, and attack capabilities.
- Fixed-Wing Units: Operating C-12 Huron and C-26 Metroliner aircraft, fixed-wing units provide transportation, reconnaissance, and communication support.
5. Signal Corps Branch

The Signal Corps Branch is responsible for providing communication and information systems support to the US Army. Signal soldiers are trained to install, operate, and maintain communication networks, ensuring seamless communication between units.
- Network Operations: Signal soldiers manage and maintain communication networks, ensuring reliable and secure communication.
- Cybersecurity: Trained to defend against cyber threats, signal soldiers protect Army communication systems from hacking and cyber attacks.
| Branch | Mission | Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|
| Infantry | Land-based military operations | Ground combat, tactics, and techniques |
| Armor | Armored vehicle operations and maintenance | Armored assaults, mobile firepower, and infantry support |
| Artillery | Indirect fire support | Fire missions, suppressive fire, and target destruction |
| Aviation | Air support to ground units | Transportation, reconnaissance, and attack missions |
| Signal Corps | Communication and information systems support | Communication network installation, operation, and maintenance |
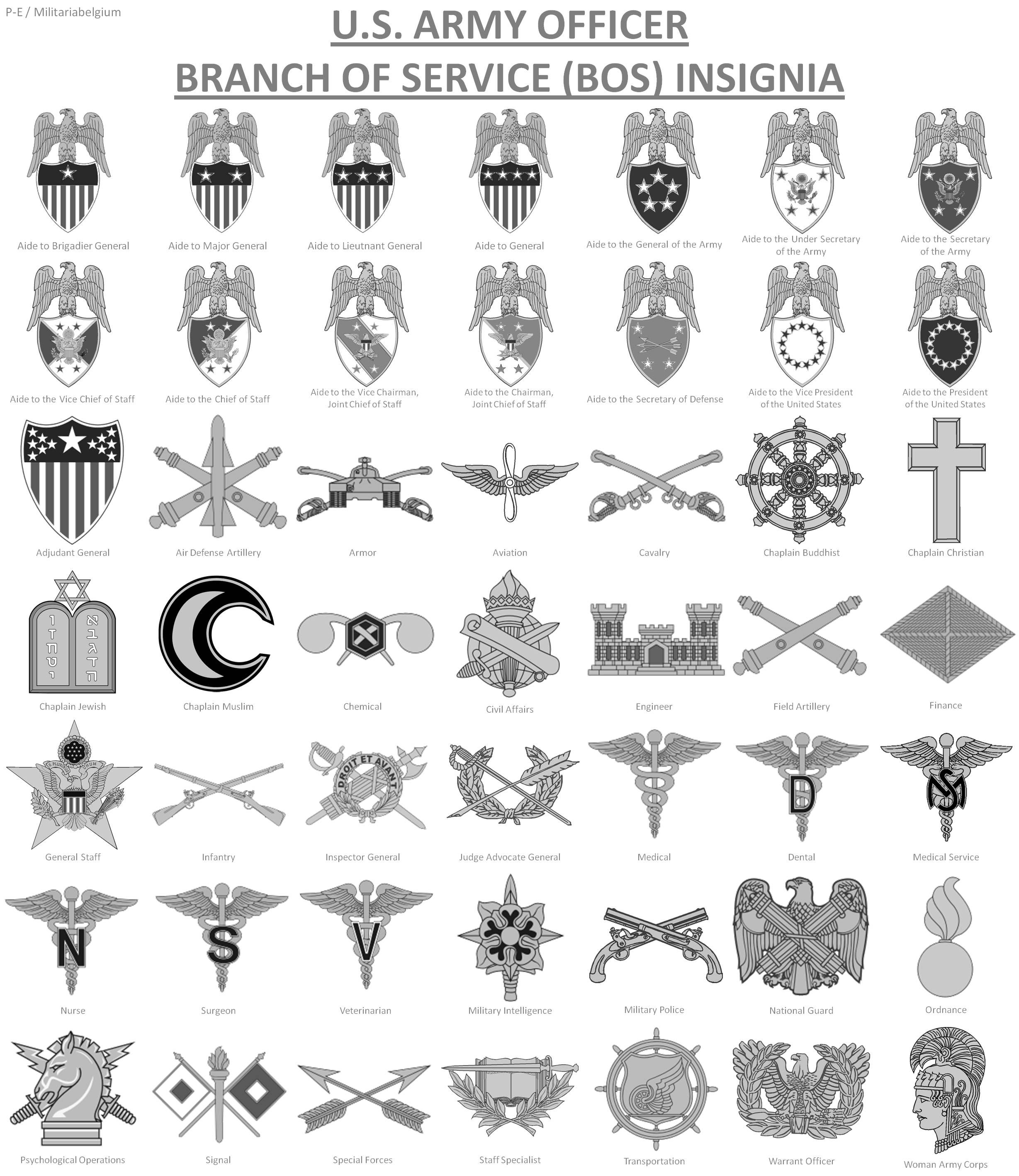

In summary, the 5 main branches of the US Army are the Infantry, Armor, Artillery, Aviation, and Signal Corps. Each branch plays a critical role in the overall military structure, providing specialized skills and capabilities that enable the Army to accomplish its missions.
What is the primary mission of the Infantry Branch?
+
The primary mission of the Infantry Branch is to engage in land-based military operations, using a variety of tactics and techniques to defeat enemy forces.
What is the role of the Signal Corps Branch?

+
The Signal Corps Branch is responsible for providing communication and information systems support to the US Army, ensuring seamless communication between units.
What type of aircraft does the Aviation Branch operate?

+
The Aviation Branch operates a variety of aircraft, including helicopters, planes, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs).



