Box Method Worksheet: Simplified Multiplication for Kids

Teaching multiplication to young children can often seem daunting, but with the right techniques and tools, it can become an engaging and enjoyable learning experience. The Box Method is one such approach that simplifies multiplication for kids by breaking it down into visual steps. This method utilizes a grid or box to make the multiplication process more intuitive and accessible, particularly for those who struggle with traditional multiplication methods.
What is the Box Method?


The Box Method, also known as the Area Model or Grid Method, is an instructional strategy where multiplication is viewed as finding the area of rectangles or squares. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Step 1: Draw a box or grid to represent the multiplication problem.
- Step 2: Split the numbers to be multiplied into their place values (tens, ones, etc.).
- Step 3: Place each part in a separate cell of the box.
- Step 4: Multiply the numbers in each cell.
- Step 5: Add all the results together to get the final product.
Benefits of the Box Method

The Box Method offers several benefits:
- Visual Learning: It provides a visual representation of multiplication, making abstract concepts more tangible.
- Error Reduction: By segmenting the process, children are less likely to make calculation errors.
- Understanding: It helps in understanding how multiplication works, particularly with larger numbers.
- Preparation: It prepares students for algebraic thinking by demonstrating how to break down complex problems.
How to Use the Box Method
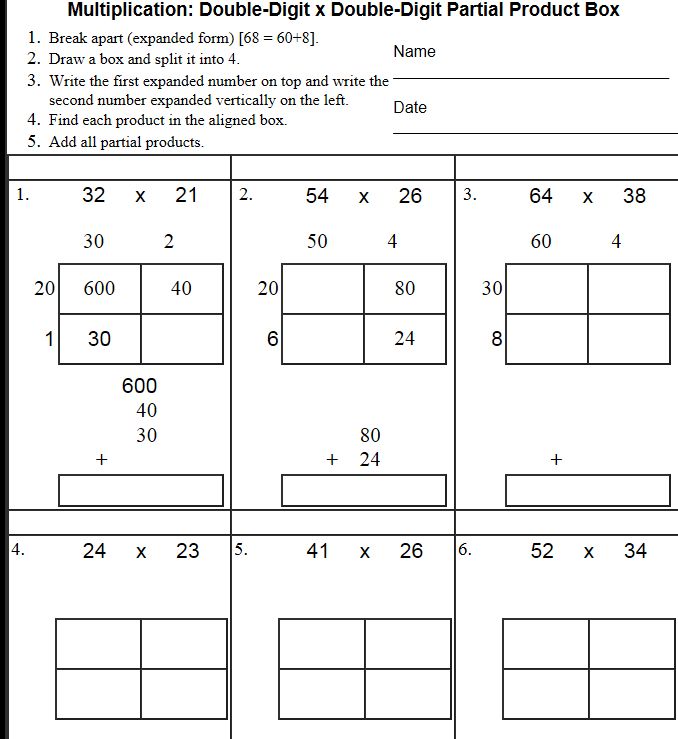
Let’s walk through the Box Method with an example:
Consider the problem 34 × 5.
- Draw a box with two columns and one row, labeling the columns as 30 and 4 to represent 34.
- Write 5 on the left side as it is the second factor in the multiplication.
- Multiply:
- 5 × 30 = 150 (Write this in the top cell)
- 5 × 4 = 20 (Write this in the bottom cell)
- Add the results: 150 + 20 = 170.
Here is how the box would look:
| 30 | 4 | |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 150 | 20 |
👉 Note: Ensure your children understand the concept of place values before introducing the Box Method. This foundational knowledge will make the technique more intuitive.
Incorporating the Box Method into Daily Learning

To maximize the effectiveness of the Box Method, incorporate it into daily learning:
- Practice: Use worksheets or flashcards focusing on the Box Method.
- Real-Life Applications: Show how multiplication is used in real life (e.g., finding areas, calculating costs).
- Games and Activities: Engage children with multiplication games that utilize the box method concept.
- Gradual Progression: Start with simpler problems and gradually increase complexity.
In summary, the Box Method provides a unique and engaging way to teach multiplication. By breaking down complex multiplication problems into smaller, more manageable parts, children can grasp the underlying mechanics of arithmetic in a way that fosters understanding and confidence. This approach not only helps in mastering multiplication but also builds a strong foundation for future mathematical concepts.
Is the Box Method suitable for all ages?

+
The Box Method is particularly effective for younger learners, typically from first to third grade. However, it can also be adapted for older students who are learning or struggling with multiplication concepts.
Can the Box Method be used for division?

+
Yes, the Box Method can be adapted for division as well. It involves a similar process but in reverse, essentially finding the factors of a number.
Are there any limitations to the Box Method?

+
While the Box Method is effective for visual learners, it might not be as intuitive for children who prefer numerical methods. It also becomes more cumbersome with larger numbers.