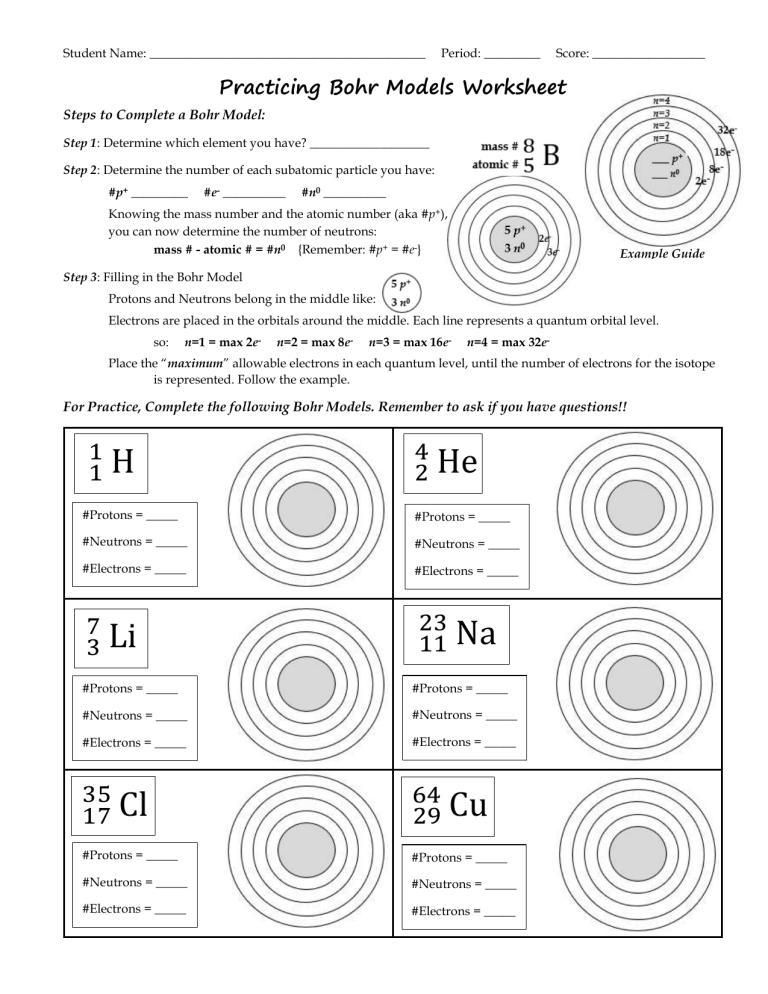
Master the Bohr Model with Our Easy Worksheet

Exploring the structure of atoms can be a complex but rewarding endeavor, and mastering the Bohr Model is a key step in understanding how atoms work. Developed by Niels Bohr in 1913, this model helps us visualize atomic structure by arranging electrons in distinct orbits or shells around the nucleus, providing a simpler yet insightful view into atomic physics. Whether you're a student looking to excel in chemistry, a curious learner, or someone revisiting fundamental concepts, our easy-to-use worksheet on the Bohr Model will guide you through this fascinating topic with clarity and ease.
Understanding the Bohr Model

The Bohr Model revolutionized our understanding of atomic structure with several key principles:
- Orbital Structure: Electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed paths, known as energy levels or shells.
- Quantum Energy: Electrons can only exist in these orbits, which correspond to specific energy levels; they cannot exist between orbits.
- Emission and Absorption: When electrons jump between orbits, they absorb or emit energy in the form of light or other electromagnetic radiation.
🧐 Note: The Bohr Model, while simplistic, isn't entirely accurate for atoms with more than one electron. For these, a more complex understanding using quantum mechanics is necessary.
How to Use the Bohr Model Worksheet
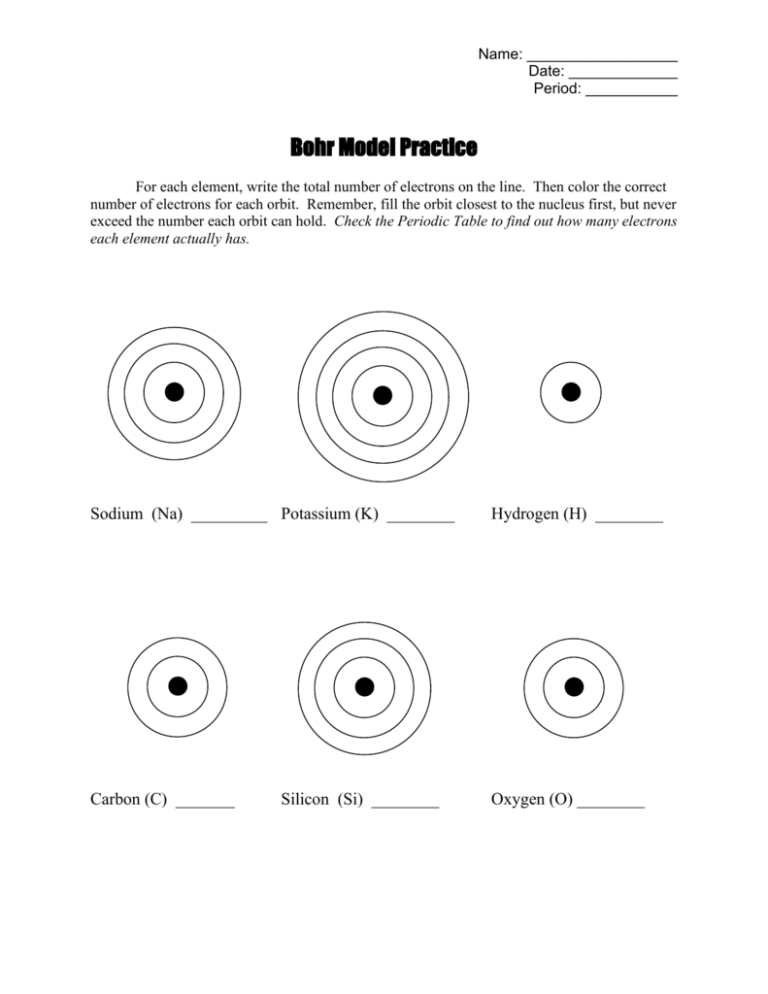
Our worksheet simplifies the learning process by breaking it down into manageable parts:
1. Identify the Number of Electrons

To start with any atom:
- Find its atomic number from the periodic table, which tells you the number of protons and, in a neutral atom, the number of electrons.
2. Filling Electron Shells
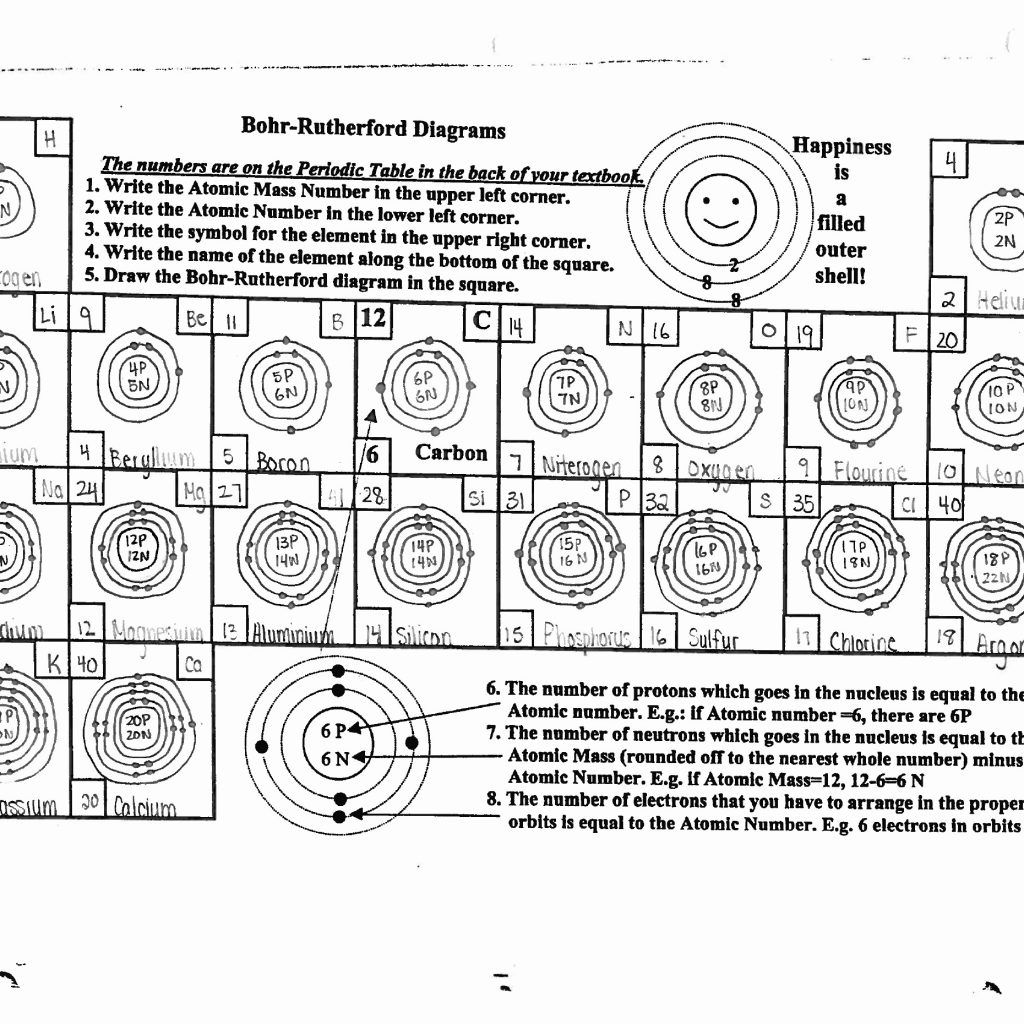
Here's how you distribute electrons in shells:
| Energy Level | Maximum Electrons |
|---|---|
| K | 2 |
| L | 8 |
| M | 18 |
| N | 32 |

- Begin filling electrons from the innermost shell (K shell) to the outermost (N shell, though usually not necessary for many elements in their natural state).
- The first shell holds a maximum of 2 electrons, the second up to 8, the third up to 18, and so on.
⚠️ Note: For simplicity, we'll stick to elements up to the M shell in this tutorial; atoms with more electrons have a more complex electron distribution.
3. Draw the Model

Here are the steps:
- Sketch the nucleus with protons and neutrons.
- Draw concentric circles around the nucleus to represent the shells.
- Place electrons as dots or small circles on the shells, following the distribution rule.
Example: Oxygen (O)
Let's use Oxygen as an example to apply what we've learned:
- Step 1: Atomic number of Oxygen is 8, meaning it has 8 protons and 8 electrons.
- Step 2: Distribute electrons:
- K Shell: 2 electrons
- L Shell: Remaining 6 electrons
- Step 3: Draw the model with the nucleus at the center, 2 electrons on the K shell, and 6 electrons on the L shell.
Benefits of Learning the Bohr Model

Mastering the Bohr Model offers several advantages:
- Understanding Atomic Structure: It provides a visual way to comprehend how electrons are arranged and interact with the nucleus.
- Predicting Chemical Behavior: Knowing the electron shell configuration helps predict how atoms might bond or react with others.
- Conceptual Foundation: It's a crucial stepping stone to more complex quantum mechanics and atomic theory.
Your Turn: Work through the Bohr Model Worksheet

Using the principles outlined, now it's your turn to practice. Here are some tips:
- Select elements from different periods on the periodic table to get a varied experience.
- Pay attention to elements with full, half-full, or close-to-full shells, as these often exhibit unique chemical behaviors.
- Try creating Bohr Models for ions, noting how electron loss or gain affects the structure.
As you work through the worksheet, remember that repetition solidifies understanding. The more you draw and analyze Bohr Models, the more intuitive the concept becomes.
In sum, the Bohr Model isn't just a visual representation; it's a gateway to understanding atomic interactions, the periodic table, and the principles behind atomic chemistry. By working through our Bohr Model worksheet, you'll not only grasp these fundamental concepts but also apply them in predicting and understanding chemical reactions, bonding, and the behavior of elements under different conditions.
Why is the Bohr Model important in chemistry?

+
The Bohr Model helps visualize atomic structure, making it easier to understand electron behavior, chemical bonding, and the periodic trends that govern the elements’ properties and reactivity.
Can the Bohr Model accurately predict the behavior of all elements?

+
No, while it’s useful for simple elements, particularly hydrogen, the Bohr Model becomes less accurate with elements having more electrons due to electron-electron interactions which are not accounted for in the model.
How does the Bohr Model differ from other atomic models?

+
The Bohr Model differs primarily in its simplicity, presenting electrons in fixed orbits or shells around the nucleus. More advanced models like the quantum mechanical model consider probability distributions of electrons, electron spin, and energy levels in a more complex manner.