5 Essential Tips for Bohr Diagram Worksheets
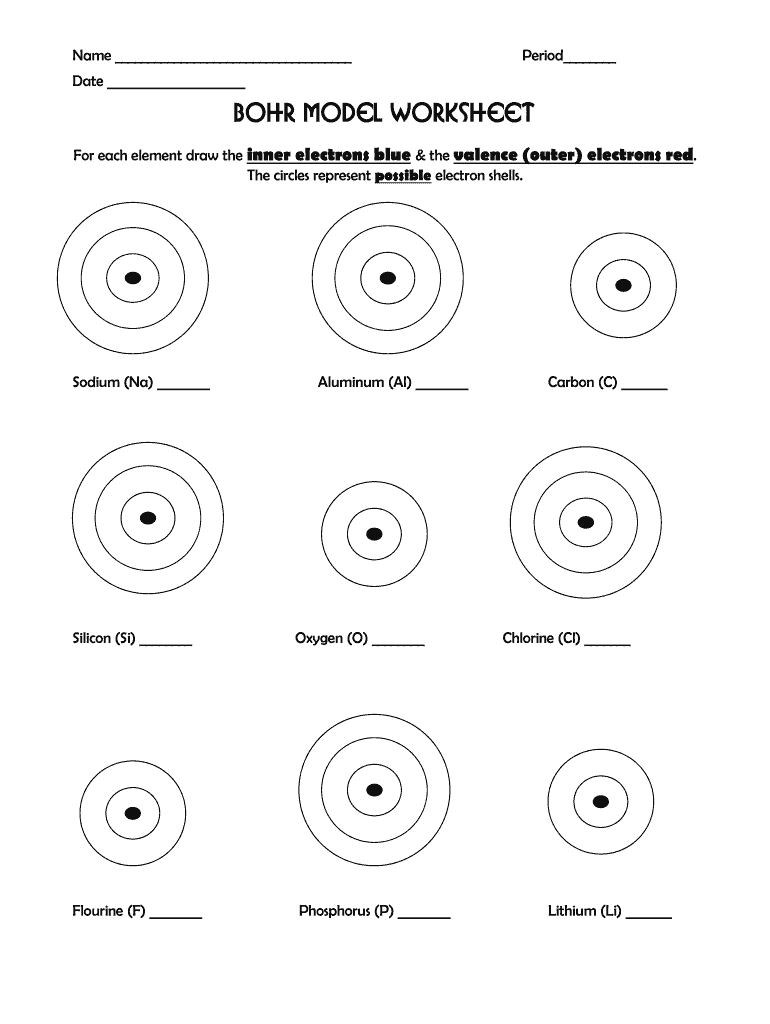
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the essential tips for creating and using Bohr diagram worksheets effectively. These tips are crucial for students, educators, and anyone interested in understanding the atomic structure through the visual representation provided by Bohr diagrams. Whether you're new to the concept or looking to enhance your teaching methods, these tips will help you master the art of Bohr diagrams.
Understand the Basics of Bohr Diagrams

Before diving into worksheet creation or usage, it’s important to grasp the fundamental principles behind Bohr diagrams:
- Nucleus and Electrons: The nucleus, at the center of the diagram, contains protons and neutrons. Electrons move around the nucleus in orbits or shells.
- Shell Capacity: Each shell has a maximum number of electrons it can hold, generally following the formula 2n², where n is the shell number (n=1, 2, 3, etc.).
- Electron Distribution: Electrons fill shells from the lowest energy level (closest to the nucleus) to the highest, following the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle.
Plan Your Worksheet Layout

When designing a Bohr diagram worksheet:
- Element Information: Include a section for the element’s name, atomic number, and atomic mass to provide context for the students.
- Diagram Area: Allocate space for students to draw the Bohr diagrams, ensuring there’s room for multiple electron shells.
- Guided Instructions: Provide step-by-step instructions on how to draw the Bohr diagram for different elements, especially for more complex atoms.
- Atomic Orbitals Table: Here’s a basic table to guide students on electron shell capacities:
- Element of the Day: Select elements from different groups or periods and have students create Bohr diagrams for these elements. This helps in understanding periodic trends.
- Chemical Bonding: Explain how Bohr diagrams can visually represent bond formation by sharing or transferring electrons, especially useful in understanding ionic and covalent bonds.
- Online Simulators: Use online Bohr model simulators where students can manipulate electron distribution interactively.
- Augmented Reality (AR): If possible, integrate AR applications that allow students to view a three-dimensional model of an atom, enhancing their understanding through visualization.
- Videos and Animations: Embed short educational videos or animations explaining key concepts, making the worksheet more engaging.
- Worksheet Reviews: Regularly review students’ work, providing corrections, explanations, and positive reinforcement.
- Self-Assessment: Include a section where students can self-assess their Bohr diagrams, checking for the correct number of electrons in each shell according to the element’s atomic number.
- Peer Review: Encourage students to review each other’s diagrams to promote collaborative learning and peer teaching.
| Shell (n) | Maximum Electrons |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 18 |
| 4 | 32 |

💡 Note: This table represents the maximum capacity, but remember, electron configurations follow the Aufbau principle and Pauli exclusion principle, which might alter this arrangement.
Integrate Practical Examples

Incorporate real-world examples to make learning interactive and relatable:
Use Interactive Learning Tools

Enhance your worksheets with digital and interactive components:
Assess Understanding and Provide Feedback

Feedback is crucial for learning:
By incorporating these tips into your Bohr diagram worksheets, you'll not only make the learning process more engaging and effective but also help students develop a deep understanding of atomic structure. These diagrams serve as a visual aid, simplifying the complex arrangement of electrons in atoms, making chemistry accessible and exciting. Understanding the basic principles, planning the layout, using practical examples, integrating interactive tools, and providing constructive feedback will ensure your students excel in grasping the intricacies of atomic structure through Bohr diagrams.
Why are Bohr diagrams useful in chemistry education?

+
Bohr diagrams visually simplify the complex nature of atoms by representing electrons in orbits around the nucleus, which helps students understand atomic structure, periodicity, and bonding at a glance.
How can I ensure students correctly fill electron shells in Bohr diagrams?

+
Teach the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule, and the Pauli exclusion principle. Also, provide a table of maximum electron shell capacities and always check for the correct atomic number.
What is the difference between a Bohr diagram and a Lewis dot structure?

+
Bohr diagrams show the distribution of all electrons in the atom’s shells. In contrast, Lewis dot structures only illustrate the valence electrons around an atom, which are involved in bonding.