Biology Molecules Worksheet: A Simple Guide to Success

In the realm of biology, understanding the molecular building blocks of life is not just beneficial; it's essential for mastering the subject. This guide will delve into the essentials of biology molecules, breaking down complex concepts into digestible parts, aiding students, and enthusiasts in their journey through the fascinating world of biological chemistry.
Why Understanding Biology Molecules is Crucial
Delving into the molecules of life offers insight into how cells function, how organisms grow and interact with their environment, and how diseases can be combated or prevented. Here are a few reasons why understanding these molecules matters:
- Cells and Their Functions: Every process within a cell is mediated by molecules, from energy conversion in mitochondria to protein synthesis in ribosomes.
- Genetic Information: DNA and RNA, the nucleic acids, carry the code of life, governing heredity, and directing protein synthesis.
- Biochemical Pathways: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids participate in metabolic pathways, providing energy, signaling, and structural support.
- Disease and Health: Knowledge of molecular interactions can lead to breakthroughs in medicine and drug design.
The Four Main Types of Molecules

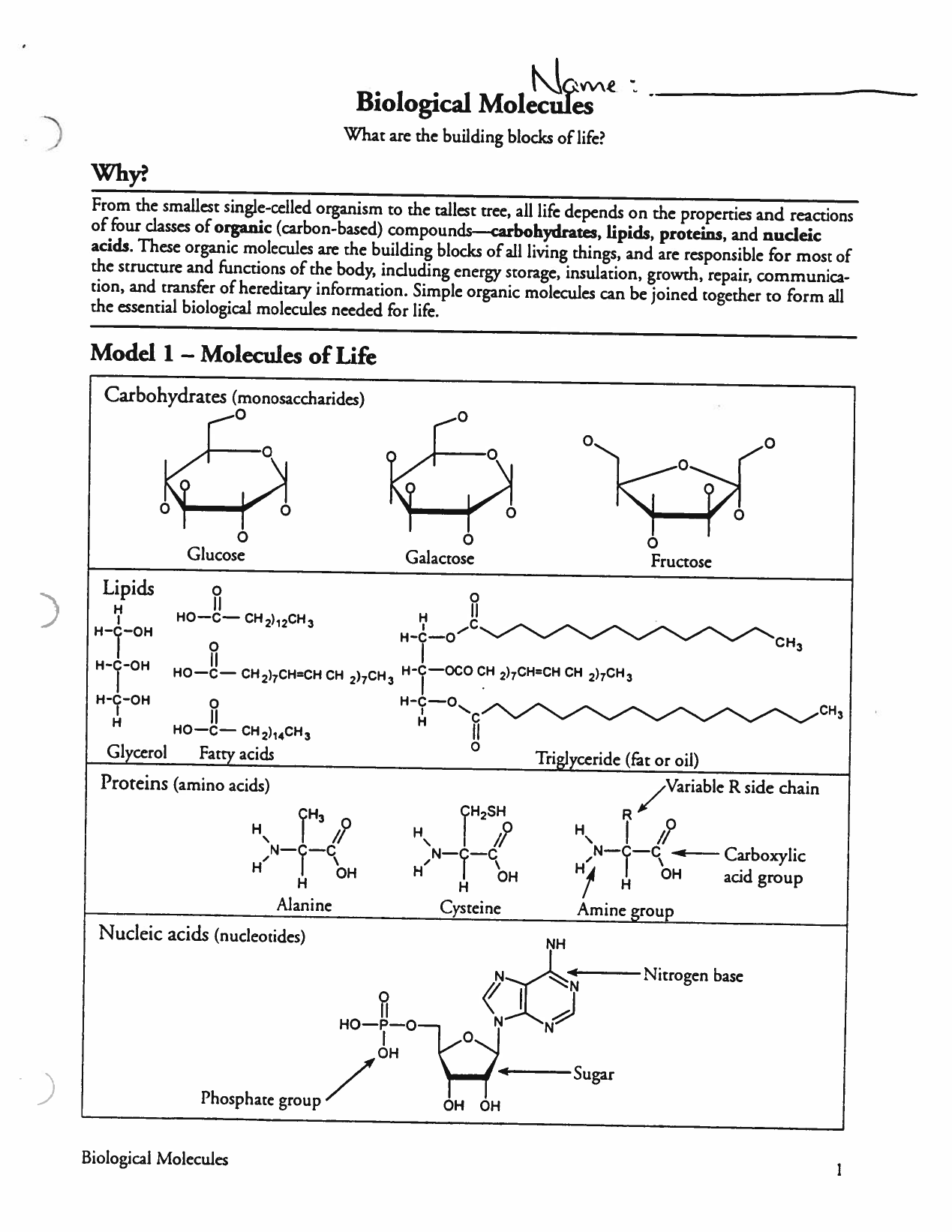
Biological molecules can be categorized into four main types:
- Carbohydrates: Energy sources and structural components.
- Lipids: Energy storage, insulation, and membrane formation.
- Proteins: Catalysts of biochemical reactions, structural elements, and information carriers.
- Nucleic Acids: Storage and transmission of genetic information.
Carbohydrates: The Body's Quick Fuel

Carbohydrates, or saccharides, are known as the main energy source for living organisms. Here’s how they work:
- Monosaccharides: Simple sugars like glucose and fructose, the basic units of carbohydrates.
- Disaccharides: Made up of two monosaccharides, like sucrose (table sugar).
- Polysaccharides: Chains of monosaccharides, such as starch (energy storage in plants), glycogen (energy storage in animals), and cellulose (structural in plants).

🔬 Note: Complex carbohydrates provide sustained energy, while simple sugars give a quick burst of energy.
Lipids: More Than Just Fats

Lipids are crucial for various biological functions:
- Fatty Acids: Building blocks of fats, providing energy.
- Phospholipids: Key components of cell membranes.
- Steroids: Such as cholesterol, involved in hormone production.

🧫 Note: Lipids also play essential roles in insulation, waterproofing, and protecting organs.
Proteins: The Workhorses of the Cell

Proteins are incredibly versatile, with functions ranging from structural to enzymatic:
- Structure: Proteins like collagen support tissues.
- Enzymes: Catalyze chemical reactions.
- Hormones: Such as insulin regulate metabolism.
- Transport: Hemoglobin carries oxygen in the blood.

🔬 Note: Proteins have four levels of structure, primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary, each contributing to its specific function.
Nucleic Acids: The Blueprint of Life

Nucleic acids store, replicate, and transmit genetic information:
- DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, the genetic material in most organisms.
- RNA: Ribonucleic acid, involved in protein synthesis.

🧬 Note: The order of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in proteins, hence controlling the organism's traits.
Utilizing Biology Molecules Worksheets for Mastery

To truly master the topic of biology molecules, students can utilize worksheets. Here are some strategies:
- Interactive Diagrams: Filling out diagrams helps in visualizing molecular structures.
- Concept Mapping: Connecting different molecules and their functions in a map enhances understanding.
- Practice Questions: Multiple choice, fill-in-the-blanks, and short answer questions reinforce learning.
- Experiments and Models: Building models or conducting simple experiments can solidify concepts.
Final Thoughts

The exploration of biological molecules is not just an academic exercise; it's a window into the complexities of life itself. From the energy currency of cells to the genetic code that defines us, understanding these molecules provides a foundation for both biological research and practical applications in various fields, from medicine to environmental science. Whether you're a student or a lifelong learner, the journey through biology molecules is filled with wonder and insight, revealing the intricate machinery of life at its most basic level.
What are the differences between carbohydrates and lipids?

+
Carbohydrates are mainly energy storage molecules in plants and animals, providing quick energy, while lipids serve more as long-term energy reserves, insulation, and structural components of cell membranes.
How do proteins function in the body?

+
Proteins perform diverse functions: they catalyze chemical reactions as enzymes, regulate body processes as hormones, transport molecules like oxygen, and form structural elements like muscles and tendons.
Why are nucleic acids called the blueprint of life?

+
Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) contain the genetic code that directs the synthesis of proteins, which in turn build and regulate all life forms, essentially providing the instructions for life’s processes.